Digital learning transforms education by leveraging technology to provide interactive and personalized experiences that enhance knowledge retention and engagement. It enables flexible access to resources and fosters collaboration across diverse locations, making education more inclusive and adaptable to individual needs. Discover how digital learning can revolutionize your educational journey and improve outcomes by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
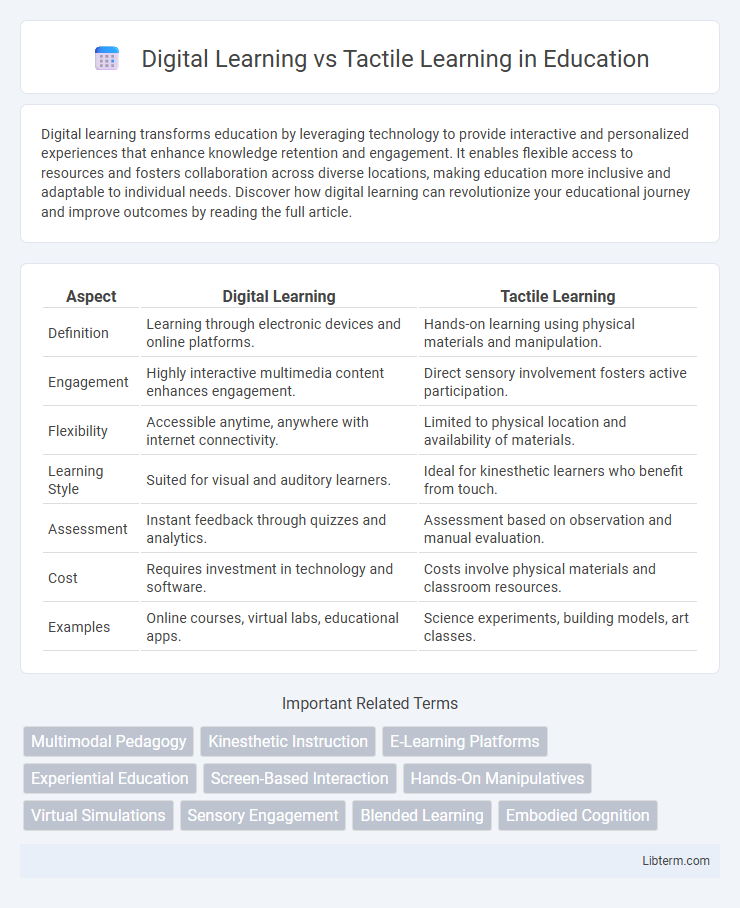
| Aspect | Digital Learning | Tactile Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Learning through electronic devices and online platforms. | Hands-on learning using physical materials and manipulation. |
| Engagement | Highly interactive multimedia content enhances engagement. | Direct sensory involvement fosters active participation. |
| Flexibility | Accessible anytime, anywhere with internet connectivity. | Limited to physical location and availability of materials. |
| Learning Style | Suited for visual and auditory learners. | Ideal for kinesthetic learners who benefit from touch. |
| Assessment | Instant feedback through quizzes and analytics. | Assessment based on observation and manual evaluation. |
| Cost | Requires investment in technology and software. | Costs involve physical materials and classroom resources. |
| Examples | Online courses, virtual labs, educational apps. | Science experiments, building models, art classes. |
Introduction to Digital and Tactile Learning
Digital learning leverages technology through online platforms, multimedia content, and interactive software to facilitate education, enhancing accessibility and personalized pacing. Tactile learning emphasizes hands-on experiences and physical interaction with materials, aiding memory retention and kinesthetic engagement. Both methods cater to diverse learning styles, combining visual, auditory, and sensory inputs to optimize knowledge acquisition.
Defining Digital Learning: Tools and Methods
Digital learning employs electronic devices such as computers, tablets, and smartphones to deliver educational content through platforms like Learning Management Systems (LMS), virtual classrooms, and interactive simulations. Tools commonly used in digital learning include multimedia presentations, educational apps, video tutorials, and online assessments that facilitate personalized and self-paced study. Methods emphasize accessibility, engagement, and real-time feedback, leveraging technologies such as artificial intelligence and augmented reality to enhance the learning experience.
Understanding Tactile Learning: Hands-on Approaches
Tactile learning emphasizes hands-on approaches that engage multiple senses to enhance memory retention and comprehension, allowing learners to directly manipulate materials and experience concepts physically. This method supports kinesthetic learners by fostering active participation, which often leads to deeper understanding compared to passive digital learning formats. Integrating tactile activities with digital tools can create a balanced educational experience that maximizes cognitive connections and practical skill development.
Key Benefits of Digital Learning
Digital learning offers unparalleled flexibility, enabling access to a vast array of educational resources anytime and anywhere through devices connected to the internet. Interactive multimedia elements such as videos, quizzes, and simulations enhance engagement and retention compared to traditional tactile learning methods. Additionally, digital platforms provide real-time feedback and personalized learning paths, optimizing individual progress and skill development.
Advantages of Tactile Learning
Tactile learning enhances memory retention and comprehension by engaging multiple senses, allowing learners to physically interact with materials for deeper understanding. This method improves motor skills and coordination, which digital learning often cannot provide. Studies show that tactile experiences foster better problem-solving abilities and creativity compared to solely screen-based education.
Challenges Faced in Digital Environments
Digital learning often faces challenges such as reduced hands-on interaction, which can hinder kinesthetic and tactile learners who benefit from physical manipulation and sensory feedback. Issues like screen fatigue, distractions, and limited social engagement further impact student motivation and retention in online settings. Furthermore, technological barriers, including unreliable internet access and inadequate digital literacy, exacerbate difficulties in fully engaging with digital learning platforms.
Limitations of Tactile Learning Methods
Tactile learning methods are limited by their reliance on physical materials, which can restrict the range of accessible concepts and scalability in diverse educational environments. These approaches often lack adaptability for students with sensory impairments or fine motor skill challenges, reducing inclusivity. Furthermore, tactile learning may not efficiently support abstract or theoretical knowledge acquisition compared to digital learning platforms that offer interactive simulations and instant feedback.
Comparing Learning Outcomes: Digital vs Tactile
Digital learning enhances access to diverse multimedia resources, promoting rapid information absorption and adaptability across various subjects. Tactile learning strengthens memory retention through hands-on experiences, fostering deeper understanding and skill acquisition in practical tasks. Comparative studies reveal that while digital learning excels in theory-based knowledge, tactile methods yield superior results in kinesthetic and experiential mastery.
Hybrid Models: Integrating Digital and Tactile Techniques
Hybrid learning models combine the strengths of digital learning platforms and tactile, hands-on techniques to enhance educational outcomes. These models leverage interactive digital tools, such as simulations and virtual labs, alongside physical activities like experiments and manipulatives to address diverse learning styles. Research shows that integrating digital resources with tactile experiences improves engagement, retention, and critical thinking skills among students across various subjects.
Future Trends in Education: Balancing Both Approaches
Future trends in education emphasize a hybrid model that integrates digital learning tools with tactile, hands-on experiences to foster comprehensive skill development. Advances in augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) are enhancing immersive digital environments, while makerspaces and interactive labs support kinesthetic learning, promoting engagement and retention. Educational institutions increasingly leverage data analytics to personalize learning paths, balancing technology-driven content delivery with tactile activities to cater to diverse learning styles and improve educational outcomes.
Digital Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com