A degree signifies the successful completion of an academic program, serving as a key credential that validates your expertise and dedication in a particular field. Earning a degree can open doors to advanced career opportunities, higher earning potential, and personal growth. Discover how selecting the right degree can shape your future by reading the rest of the article.
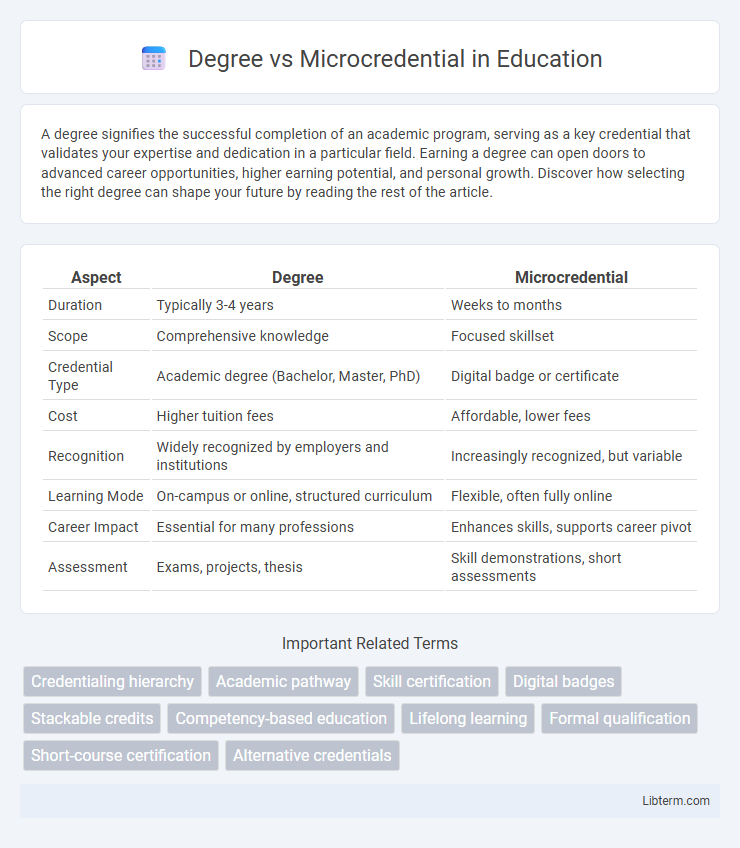
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Degree | Microcredential |
|---|---|---|
| Duration | Typically 3-4 years | Weeks to months |
| Scope | Comprehensive knowledge | Focused skillset |
| Credential Type | Academic degree (Bachelor, Master, PhD) | Digital badge or certificate |
| Cost | Higher tuition fees | Affordable, lower fees |
| Recognition | Widely recognized by employers and institutions | Increasingly recognized, but variable |
| Learning Mode | On-campus or online, structured curriculum | Flexible, often fully online |
| Career Impact | Essential for many professions | Enhances skills, supports career pivot |
| Assessment | Exams, projects, thesis | Skill demonstrations, short assessments |
Introduction: Degree vs Microcredential
A degree typically represents a comprehensive, multi-year academic program that provides in-depth knowledge and a broad skill set in a specific field, often recognized by employers worldwide. Microcredentials, in contrast, are short, targeted certifications that validate specific skills or competencies, offering flexibility and rapid skill acquisition tailored to evolving industry demands. Both pathways serve distinct purposes: degrees emphasize foundational education and career preparation, while microcredentials focus on continuous learning and skill enhancement.
Defining Degrees and Microcredentials
Degrees represent formal educational qualifications typically awarded by universities after completing a comprehensive curriculum over several years, such as bachelor's, master's, or doctoral degrees. Microcredentials are short, focused certifications that validate specific skills or knowledge areas, often aligned with industry needs and completed in a shorter time frame. While degrees provide broad, in-depth education across multiple subjects, microcredentials emphasize targeted expertise and practical competencies.
Key Differences Between Degrees and Microcredentials
Degrees typically require years of full-time study, offer comprehensive theoretical knowledge, and provide widely recognized academic credentials. Microcredentials focus on specific skills or competencies, are usually completed in weeks or months, and offer flexible, targeted learning often recognized by employers for immediate job relevance. The cost and time investment for degrees far exceed those of microcredentials, making microcredentials attractive for skill enhancement without long-term commitment.
Pros and Cons of Earning a Degree
Earning a degree offers comprehensive knowledge and broad career opportunities, often leading to higher earning potential and increased job stability. However, degrees typically require significant time and financial investment, with less flexibility compared to microcredentials. Degrees may also include coursework that is less directly applicable to specific skills demanded by rapidly evolving industries.
Advantages and Limitations of Microcredentials
Microcredentials offer targeted skill development that allows learners to quickly acquire and demonstrate specific competencies, making them highly valuable for career advancement and continuous learning. These credentials are often more affordable and flexible than traditional degrees but may lack the comprehensive knowledge and recognition provided by a full degree program. Employers may value microcredentials for specialized expertise, yet they can still prioritize degrees for roles requiring extensive theoretical foundations and broad academic training.
Costs and Time Commitment Comparison
Microcredentials typically require significantly less time and financial investment compared to traditional degrees, often costing a fraction of the tuition fees associated with bachelor's or master's programs. Degree programs usually span two to four years with comprehensive coursework, while microcredentials can be completed in weeks to a few months, allowing for faster skill acquisition and workforce entry. The lower cost and shorter duration of microcredentials make them an attractive option for professionals seeking targeted knowledge without the extended commitment of full degree programs.
Career Outcomes: Which Option Suits Your Goals?
Degrees typically provide comprehensive education and are valued for long-term career advancement and higher earning potential in fields like engineering, healthcare, and law. Microcredentials offer targeted skills and quicker completion times, appealing to professionals seeking rapid upskilling or career shifts in technology, digital marketing, and data analysis. Choosing between a degree and a microcredential depends on industry demands, job market trends, and the specific career goals aiming for specialized expertise or a broad foundational knowledge.
Industry Recognition and Credibility
Degrees from accredited universities typically hold widespread industry recognition and credibility due to their comprehensive curriculum and established evaluation standards. Microcredentials often focus on specific skills or competencies, earning rapid recognition in niche markets or emerging sectors where up-to-date expertise is critical. Employers increasingly value microcredentials for their agility in reflecting current technologies, but degrees remain dominant for roles requiring deep theoretical knowledge and formal qualification.
Flexibility and Learning Experience
Microcredentials offer greater flexibility by allowing learners to acquire specific skills through short, targeted courses that fit diverse schedules and career goals. Degrees typically require a fixed curriculum and longer time commitment, providing a more comprehensive and structured learning experience. The personalized pace and modular design of microcredentials enhance engagement and immediate applicability compared to traditional degree programs.
Choosing the Right Path: Degree or Microcredential?
Choosing between a traditional degree and a microcredential depends on career goals, time commitment, and industry demands. Degrees offer comprehensive knowledge and are valued for roles requiring deep expertise, while microcredentials provide targeted skills with faster completion tailored to rapidly evolving job markets. Professionals should evaluate employer preferences, desired skill sets, and flexibility needs to select the most effective educational path.
Degree Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com