Project-based learning engages students in real-world challenges that enhance critical thinking, collaboration, and problem-solving skills. This hands-on approach allows Your knowledge to deepen as you apply concepts in practical scenarios, making education more meaningful and memorable. Discover how project-based learning can transform your educational experience by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
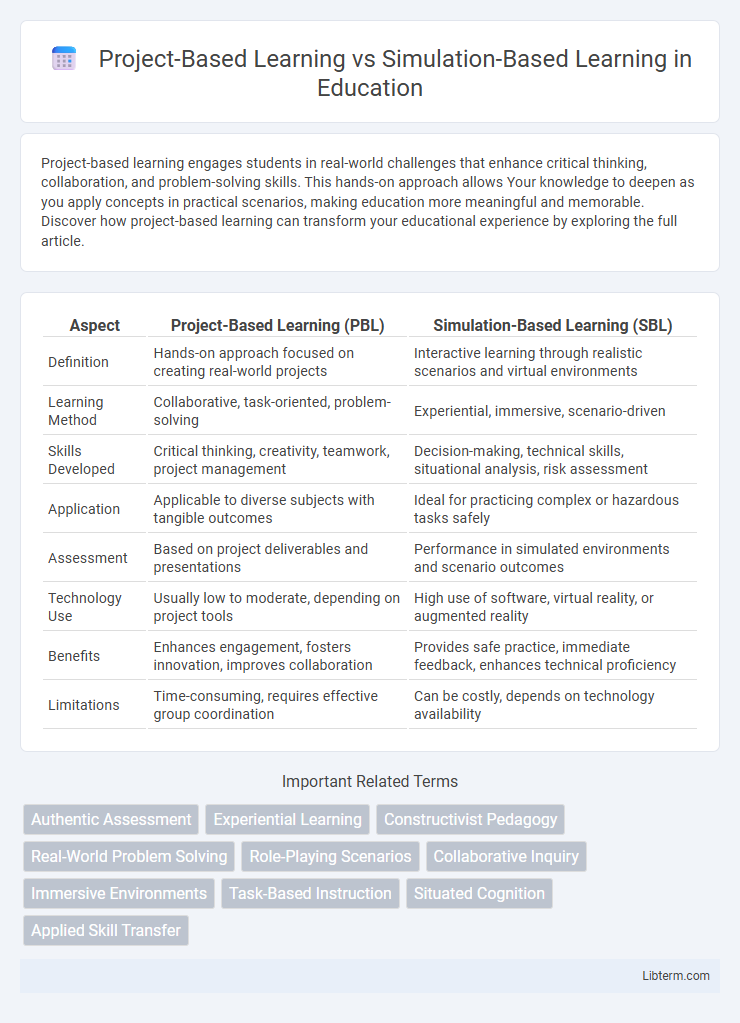
| Aspect | Project-Based Learning (PBL) | Simulation-Based Learning (SBL) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Hands-on approach focused on creating real-world projects | Interactive learning through realistic scenarios and virtual environments |
| Learning Method | Collaborative, task-oriented, problem-solving | Experiential, immersive, scenario-driven |
| Skills Developed | Critical thinking, creativity, teamwork, project management | Decision-making, technical skills, situational analysis, risk assessment |
| Application | Applicable to diverse subjects with tangible outcomes | Ideal for practicing complex or hazardous tasks safely |
| Assessment | Based on project deliverables and presentations | Performance in simulated environments and scenario outcomes |
| Technology Use | Usually low to moderate, depending on project tools | High use of software, virtual reality, or augmented reality |
| Benefits | Enhances engagement, fosters innovation, improves collaboration | Provides safe practice, immediate feedback, enhances technical proficiency |
| Limitations | Time-consuming, requires effective group coordination | Can be costly, depends on technology availability |
Introduction to Experiential Learning Approaches
Project-Based Learning centers on active exploration of real-world problems, encouraging critical thinking and collaborative skills, while Simulation-Based Learning uses virtual or physical models to replicate complex scenarios for hands-on practice and decision-making. Both approaches fall under Experiential Learning, emphasizing knowledge acquisition through direct experience and reflection. These methods enhance engagement and retention by immersing learners in interactive, contextual environments tailored to develop practical competencies.
Defining Project-Based Learning
Project-Based Learning (PBL) is an instructional approach where students actively explore real-world problems and challenges over an extended period, developing critical thinking, collaboration, and problem-solving skills. PBL emphasizes student-driven inquiry, allowing learners to create tangible products or presentations that demonstrate their understanding and application of knowledge. This method fosters deep engagement by integrating interdisciplinary content and authentic tasks that prepare students for practical, real-life situations.
Defining Simulation-Based Learning
Simulation-Based Learning involves immersive, interactive experiences that replicate real-world scenarios using virtual or physical models to enhance knowledge and skill acquisition. This method emphasizes active participation and decision-making within controlled environments, allowing learners to practice complex tasks safely and receive immediate feedback. Unlike Project-Based Learning, which centers on completing extended projects, Simulation-Based Learning prioritizes experiential engagement through realistic simulations to build competency in specific contexts.
Key Differences Between Project-Based and Simulation-Based Learning
Project-Based Learning emphasizes real-world problem-solving through extended projects that integrate multiple disciplines and foster collaboration, critical thinking, and creativity. Simulation-Based Learning focuses on immersive, interactive scenarios that replicate real-life processes or environments to develop specific skills, decision-making, and situational awareness. The key difference lies in Project-Based Learning's broader scope of creating tangible outcomes versus Simulation-Based Learning's targeted practice within controlled, replicable virtual or physical models.
Educational Objectives: PBL vs Simulation-Based Learning
Project-Based Learning (PBL) emphasizes developing critical thinking, problem-solving, and collaborative skills through real-world projects, aligning with objectives centered on creativity and long-term knowledge retention. Simulation-Based Learning targets experiential understanding and practical skill application, focusing on hands-on practice in controlled, risk-free environments to enhance decision-making and procedural proficiency. Both methods aim to improve learner engagement and knowledge transfer but cater to distinct educational objectives--PBL fosters conceptual depth and teamwork, while simulation hones immediate tactical and operational expertise.
Real-World Applications and Context
Project-Based Learning immerses students in real-world tasks that require problem-solving, collaboration, and critical thinking to create tangible outcomes reflecting authentic challenges in fields like engineering, business, or social sciences. Simulation-Based Learning offers immersive, interactive environments that replicate real-world scenarios, enabling learners to practice decision-making, experiment with variables, and experience consequences in a risk-free, controlled setting, particularly effective in medicine, aviation, and emergency response training. Both approaches emphasize contextual understanding and practical application, but project-based learning promotes sustained engagement with complex problems, while simulation-based learning focuses on experiential skill acquisition and immediate feedback.
Student Engagement and Motivation
Project-based learning fosters student engagement by allowing hands-on, real-world problem-solving that enhances intrinsic motivation and deepens understanding through active participation. Simulation-based learning increases motivation by immersing students in authentic scenarios, promoting experiential learning that builds decision-making skills and immediate feedback. Both methods boost engagement but project-based learning emphasizes creativity and collaboration, while simulation-based learning prioritizes practical application and situational adaptability.
Assessment and Evaluation Methods
Project-Based Learning (PBL) uses authentic assessments like portfolios, presentations, and real-world application tasks to evaluate student understanding and skill mastery, emphasizing long-term retention and collaboration. Simulation-Based Learning (SBL) employs scenario-based evaluations, including real-time performance metrics, decision-making accuracy, and immediate feedback mechanisms to assess practical skills and adaptive responses in controlled environments. Both methods utilize formative and summative assessments but differ as PBL focuses on product and process assessment, while SBL prioritizes process and performance metrics.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Method
Project-Based Learning faces challenges such as time-intensive planning, resource allocation, and varying student motivation levels that can impact the depth of engagement. Simulation-Based Learning is limited by the need for advanced technological infrastructure, high costs, and potential gaps between simulated scenarios and real-world complexities. Both methods require skilled facilitation to maximize learning outcomes while addressing issues of scalability and assessment accuracy.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Educational Goals
Project-Based Learning (PBL) excels in fostering critical thinking and real-world problem-solving by engaging students in hands-on, long-term projects that mimic authentic challenges. Simulation-Based Learning (SBL) offers immersive, interactive environments that enhance experiential understanding and skill application through realistic scenarios and immediate feedback. Selecting between PBL and SBL depends on your educational goals; prioritize PBL for developing complex project management and collaboration skills, while SBL is ideal for mastery of technical skills and decision-making in controlled, risk-free settings.
Project-Based Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com