Lecture-based learning offers a structured environment where complex concepts are delivered directly by an expert. This traditional method effectively conveys large amounts of information and promotes note-taking for better retention. Explore the rest of this article to discover how lecture-based learning can enhance your educational experience.
Table of Comparison
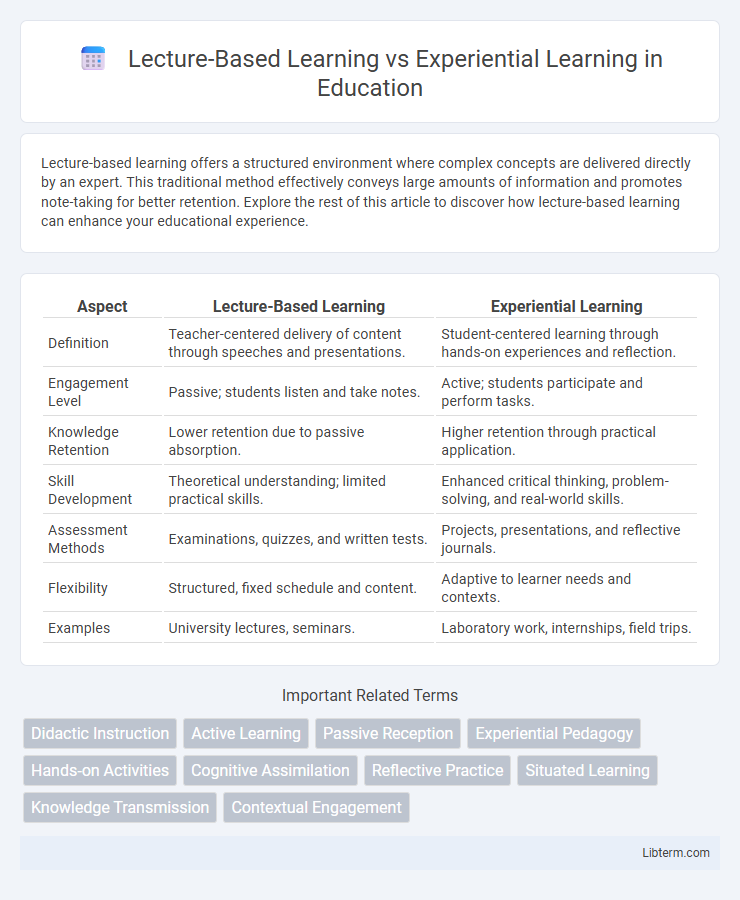
| Aspect | Lecture-Based Learning | Experiential Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Teacher-centered delivery of content through speeches and presentations. | Student-centered learning through hands-on experiences and reflection. |
| Engagement Level | Passive; students listen and take notes. | Active; students participate and perform tasks. |
| Knowledge Retention | Lower retention due to passive absorption. | Higher retention through practical application. |
| Skill Development | Theoretical understanding; limited practical skills. | Enhanced critical thinking, problem-solving, and real-world skills. |
| Assessment Methods | Examinations, quizzes, and written tests. | Projects, presentations, and reflective journals. |
| Flexibility | Structured, fixed schedule and content. | Adaptive to learner needs and contexts. |
| Examples | University lectures, seminars. | Laboratory work, internships, field trips. |
Introduction to Learning Methodologies
Lecture-Based Learning primarily involves passive information delivery through instructor-led presentations, emphasizing theoretical knowledge acquisition. Experiential Learning engages students actively by immersing them in practical tasks and real-world scenarios, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Both methodologies serve distinct educational purposes, with Lecture-Based Learning benefiting foundational understanding and Experiential Learning enhancing application and retention.
Defining Lecture-Based Learning
Lecture-Based Learning is a traditional educational approach where instructors deliver structured content through verbal presentations to an audience, emphasizing passive student reception of information. This method prioritizes the transmission of theoretical knowledge and factual data, often supported by visual aids such as slides or handouts. It is widely used in higher education settings for efficiently covering extensive curricula and establishing foundational understanding.
What is Experiential Learning?
Experiential learning is an educational approach that emphasizes active participation and direct experience to foster deeper understanding and skill acquisition, contrasting with passive lecture-based learning. This method engages learners in hands-on activities, real-world problem-solving, and reflective practices to enhance critical thinking and retention. Key components include concrete experience, reflective observation, abstract conceptualization, and active experimentation, which collectively promote meaningful and practical knowledge development.
Key Differences Between Lecture-Based and Experiential Learning
Lecture-based learning centers on instructor-led presentations where students passively absorb information, prioritizing theoretical knowledge and structured content delivery. Experiential learning emphasizes active participation, hands-on experiences, and real-world application, fostering deeper understanding through practical engagement. Key differences include the passive reception of information in lectures versus the interactive, reflective processes integral to experiential learning environments.
Advantages of Lecture-Based Learning
Lecture-based learning offers a structured environment that efficiently delivers foundational knowledge to large groups, making it ideal for standardized curricula and theoretical subjects. This method enhances information retention through systematic presentation and allows for expert-led clarification of complex concepts. Its scalability and cost-effectiveness make it a preferred choice in institutions with limited resources or time constraints.
Benefits of Experiential Learning
Experiential learning enhances retention by engaging multiple senses and fostering active participation, which promotes deeper understanding compared to passive lecture-based methods. It develops critical thinking, problem-solving, and adaptability by immersing learners in real-world scenarios, preparing them for practical challenges. This hands-on approach also boosts motivation and confidence, as learners directly apply knowledge and receive immediate feedback.
Challenges of Each Learning Approach
Lecture-based learning often faces challenges such as limited student engagement, passive information absorption, and difficulty in addressing diverse learning paces, which may hinder deep understanding. Experiential learning encounters obstacles including resource intensity, logistical complexities, and potential inconsistency in learning outcomes due to varying levels of practical experience. Both approaches require strategic adaptation to balance theoretical knowledge and practical application for effective education.
Impact on Student Engagement and Retention
Lecture-based learning often results in passive student engagement and lower retention rates due to limited interaction and application of knowledge. Experiential learning, by involving hands-on activities, real-world problem-solving, and reflection, significantly enhances engagement and improves long-term retention of material. Research shows that students participating in experiential learning retain up to 75% of information compared to 5-10% through traditional lectures.
Integrating Both Methods in Modern Education
Integrating lecture-based learning with experiential learning fosters a balanced educational approach that enhances knowledge retention and practical application. Modern education leverages lectures to deliver foundational theories while incorporating hands-on projects, simulations, and collaborative activities to deepen understanding and critical thinking skills. This hybrid methodology aligns with cognitive science principles, promoting active engagement and personalized learning pathways that address diverse student needs.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Approach
Selecting the appropriate educational approach depends on learning objectives, content complexity, and learner preferences. Lecture-based learning excels in delivering structured information efficiently, while experiential learning fosters deep understanding through active engagement and real-world application. Integrating both methods often yields optimal educational outcomes by balancing theoretical knowledge with practical experience.
Lecture-Based Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com