Liberal arts education fosters critical thinking, creativity, and communication skills essential for navigating diverse career paths and complex global issues. It integrates humanities, social sciences, and natural sciences to cultivate a well-rounded understanding of the world. Discover how a liberal arts degree can uniquely empower your personal and professional growth in the full article.
Table of Comparison
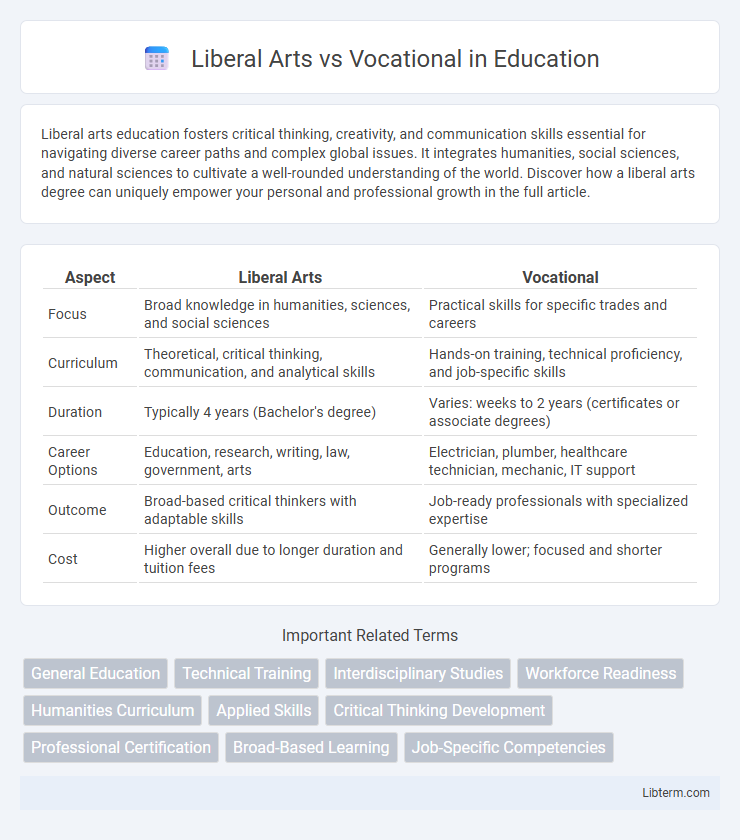
| Aspect | Liberal Arts | Vocational |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Broad knowledge in humanities, sciences, and social sciences | Practical skills for specific trades and careers |
| Curriculum | Theoretical, critical thinking, communication, and analytical skills | Hands-on training, technical proficiency, and job-specific skills |
| Duration | Typically 4 years (Bachelor's degree) | Varies: weeks to 2 years (certificates or associate degrees) |
| Career Options | Education, research, writing, law, government, arts | Electrician, plumber, healthcare technician, mechanic, IT support |
| Outcome | Broad-based critical thinkers with adaptable skills | Job-ready professionals with specialized expertise |
| Cost | Higher overall due to longer duration and tuition fees | Generally lower; focused and shorter programs |
Understanding Liberal Arts Education
Liberal arts education emphasizes a broad interdisciplinary curriculum that cultivates critical thinking, communication skills, and intellectual curiosity, preparing students for diverse career paths and lifelong learning. It integrates humanities, social sciences, and natural sciences to foster well-rounded knowledge and adaptability in a rapidly changing job market. Understanding the core values of liberal arts highlights its role in developing versatile problem-solvers and ethical leaders beyond specific technical skills.
Defining Vocational Training
Vocational training refers to specialized education designed to prepare individuals for specific trades, crafts, or careers at various skill levels. It emphasizes hands-on experience, practical skills, and direct application in industries such as healthcare, manufacturing, information technology, and skilled trades. This form of training contrasts with liberal arts education, which focuses more on broad intellectual development, critical thinking, and a wide-ranging curriculum in humanities, sciences, and social sciences.
Core Differences Between Liberal Arts and Vocational Paths
Liberal arts education emphasizes broad critical thinking, communication, and analytical skills across disciplines like humanities, sciences, and social sciences, fostering intellectual flexibility. Vocational education targets specific trades or careers, providing practical skills and hands-on training for immediate workforce entry in fields such as healthcare, technology, or skilled trades. The core difference lies in liberal arts promoting versatile knowledge and lifelong learning, while vocational education prioritizes specialized expertise and job-ready competencies.
Curriculum Focus: Broad vs. Specialized Skills
Liberal arts education emphasizes a broad curriculum encompassing humanities, social sciences, and natural sciences, fostering critical thinking, communication, and analytical skills. Vocational education concentrates on specialized skills and practical training tailored to specific careers, such as healthcare, engineering, or skilled trades. This focused approach equips students with hands-on expertise directly applicable to industry demands.
Career Opportunities and Job Market Outcomes
Liberal arts degrees develop critical thinking, communication, and problem-solving skills that are highly valued in diverse industries such as education, healthcare, and business administration. Vocational programs provide specialized training tailored to specific trades like plumbing, electrical work, or culinary arts, leading to faster entry into the workforce and often higher initial salaries. Job market outcomes for vocational graduates tend to show strong demand in skilled labor sectors, while liberal arts graduates benefit from greater career flexibility and leadership opportunities across various fields.
Cost and Return on Investment
Liberal arts degrees typically incur higher tuition costs but may lead to diverse career paths with varying income potentials, making their return on investment (ROI) less predictable. Vocational programs often require lower upfront expenses and provide specialized skills aligned with high-demand job markets, resulting in quicker entry into the workforce and more immediate ROI. Evaluating cost against long-term earning potential and employment stability is crucial when choosing between liberal arts and vocational education.
Critical Thinking vs. Practical Skill Development
Liberal arts education emphasizes the development of critical thinking, analytical reasoning, and problem-solving skills through a broad interdisciplinary curriculum in humanities, social sciences, and natural sciences. Vocational training prioritizes practical skill development and hands-on experience tailored to specific trades or professions such as healthcare, technology, or skilled trades. Students in liberal arts programs tend to cultivate adaptability and theoretical knowledge, while vocational students gain job-specific competencies that enable immediate workforce entry.
Flexibility and Adaptability in the Workplace
Liberal arts education fosters critical thinking, problem-solving, and communication skills, providing flexibility to adapt across various industries and roles. Vocational training offers specialized technical skills tailored to specific trades, delivering immediate job readiness but limited versatility. Employers increasingly value adaptability, making liberal arts graduates more capable of navigating changing workplace demands.
Societal Perceptions and Cultural Value
Liberal arts education is often perceived as fostering critical thinking, creativity, and broad cultural awareness, which are highly valued in societies that emphasize intellectual development and civic engagement. Vocational training is culturally associated with practical skills and immediate job readiness, holding significant value in communities prioritizing economic stability and skilled labor. These differing societal perceptions influence education policies and individual career choices, reflecting the balance between cultural ideals of knowledge and economic demands.
Choosing the Right Path: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right path between liberal arts and vocational education depends on career goals, learning style, and job market demands. Liberal arts programs emphasize critical thinking, communication, and broad knowledge, ideal for careers in education, research, and management. Vocational training focuses on practical skills and hands-on experience, preparing students for technical roles in industries like healthcare, manufacturing, and technology.
Liberal Arts Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com