Blended learning combines traditional face-to-face instruction with online educational materials, offering a flexible and personalized approach to education. This method enhances student engagement by integrating interactive digital content with direct teacher support, improving learning outcomes and retention. Explore the rest of this article to discover how blended learning can transform Your educational experience and boost academic success.
Table of Comparison
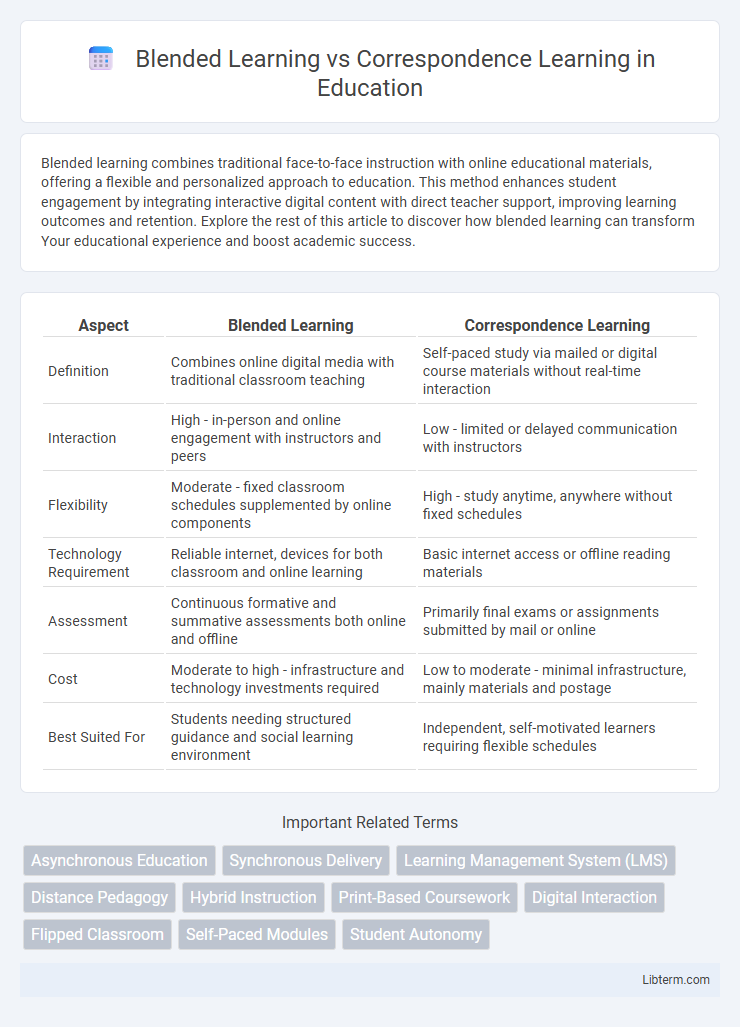
| Aspect | Blended Learning | Correspondence Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combines online digital media with traditional classroom teaching | Self-paced study via mailed or digital course materials without real-time interaction |
| Interaction | High - in-person and online engagement with instructors and peers | Low - limited or delayed communication with instructors |
| Flexibility | Moderate - fixed classroom schedules supplemented by online components | High - study anytime, anywhere without fixed schedules |
| Technology Requirement | Reliable internet, devices for both classroom and online learning | Basic internet access or offline reading materials |
| Assessment | Continuous formative and summative assessments both online and offline | Primarily final exams or assignments submitted by mail or online |
| Cost | Moderate to high - infrastructure and technology investments required | Low to moderate - minimal infrastructure, mainly materials and postage |
| Best Suited For | Students needing structured guidance and social learning environment | Independent, self-motivated learners requiring flexible schedules |
Introduction to Blended and Correspondence Learning
Blended learning combines traditional face-to-face instruction with online educational materials, enhancing flexibility and engagement through interactive digital content and real-time teacher support. Correspondence learning, rooted in remote education, relies primarily on sending educational materials by mail or electronic media, allowing students to study independently at their own pace without synchronous interaction. Both methods aim to accommodate diverse learning preferences, but blended learning emphasizes integration of technology and classroom experiences, while correspondence learning focuses on self-directed, distance-based study.
Historical Evolution of Learning Modalities
Blended learning emerged in the late 20th century, integrating traditional face-to-face instruction with digital platforms to enhance engagement and accessibility. Correspondence learning, dating back to the 19th century, was pioneered through postal systems allowing remote education before the advent of digital communication. Over time, blended learning evolved with technological advances, while correspondence learning laid the foundational framework for modern distance education methodologies.
Defining Blended Learning
Blended learning combines traditional face-to-face instruction with online educational materials and interactive digital tools, creating a dynamic and flexible learning environment. It emphasizes personalized learning paths, real-time feedback, and the integration of technology to enhance student engagement and outcomes. Defining blended learning highlights its hybrid nature, merging the advantages of in-person teaching with the accessibility and convenience of online education.
Understanding Correspondence Learning
Correspondence learning involves remote education where students receive instructional materials via mail or online platforms, allowing self-paced study without real-time interaction. This method is ideal for learners requiring flexible schedules and limited access to traditional classrooms but may lack immediate feedback and peer engagement found in blended learning. Understanding correspondence learning highlights its reliance on autonomous study habits and clear communication between instructors and students for effective knowledge acquisition.
Key Differences Between Blended and Correspondence Learning
Blended learning combines online digital media with traditional classroom methods, offering interactive and real-time engagement, whereas correspondence learning relies primarily on self-paced study through mailed or digital materials without immediate instructor interaction. Blended learning provides structured schedules and collaborative opportunities, enhancing student participation and feedback, while correspondence learning emphasizes flexibility and independent study suitable for remote learners. Key differences include levels of student-teacher interaction, learning pace control, and integration of multimedia resources, making blended learning more dynamic compared to the solitary nature of correspondence courses.
Advantages of Blended Learning
Blended learning combines online digital media with traditional classroom methods, offering greater flexibility and personalized learning experiences compared to correspondence learning, which relies solely on mailed materials. This approach enhances student engagement by integrating interactive content and real-time feedback, facilitating better knowledge retention and skill development. Furthermore, blended learning allows for immediate communication between instructors and students, promoting timely support and collaboration that correspondence learning lacks.
Benefits of Correspondence Learning
Correspondence learning offers flexibility by allowing students to study at their own pace without the constraints of fixed schedules, ideal for those balancing work or personal commitments. It provides accessible education to remote or underserved areas, ensuring learners receive quality instruction without geographical barriers. Cost-effectiveness and reduced need for physical facilities make correspondence learning an affordable and scalable option for diverse populations.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
Blended learning faces challenges such as the need for reliable technology infrastructure, potential digital divide issues, and the difficulty of maintaining student engagement both online and in-person. Correspondence learning struggles with limited immediate feedback, lack of hands-on support, and potential feelings of isolation that can hinder motivation and comprehension. Both approaches require careful planning to address their inherent limitations in fostering effective learner interaction and ensuring equitable access.
Suitability for Different Learner Profiles
Blended learning combines online digital media with traditional classroom methods, making it highly suitable for learners who thrive on interaction and require flexible pacing. Correspondence learning, delivered primarily through mail or online without real-time interaction, caters well to self-motivated individuals who benefit from independent study and time management. Each approach aligns with distinct learner profiles, with blended learning favoring social and active learners, while correspondence learning suits those with strong autonomy and discipline.
Future Trends in Learning Delivery Methods
Blended learning integrates digital tools with traditional classroom instruction, enabling personalized, flexible, and interactive education that adapts to diverse learner needs. Correspondence learning, primarily based on self-paced study through mailed or online materials, faces challenges in engagement and real-time interaction but remains valuable for remote and independent learners. Future trends emphasize immersive technologies such as AI-driven platforms and virtual reality, enhancing blended learning by offering adaptive feedback and collaborative experiences, while correspondence models evolve by incorporating digital communication to increase accessibility and learner support.
Blended Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com