Flipped classroom methods transform traditional teaching by delivering instructional content outside of class, allowing in-person time to focus on interactive activities. This approach enhances student engagement, promotes deeper understanding, and supports personalized learning experiences. Discover how you can implement a flipped classroom to maximize educational outcomes in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
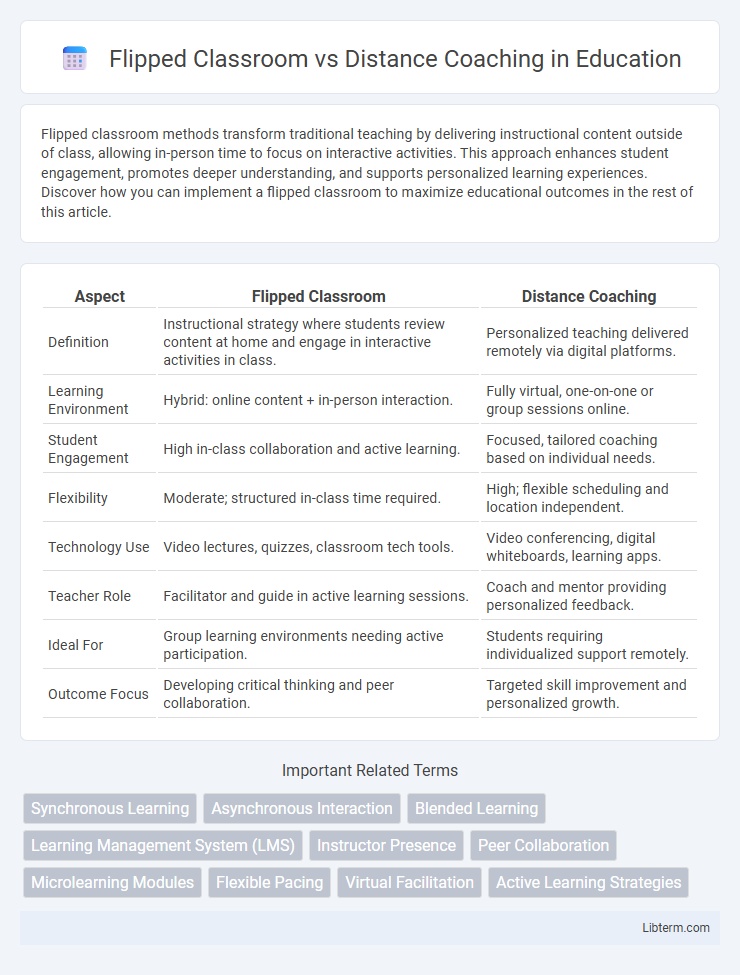
| Aspect | Flipped Classroom | Distance Coaching |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Instructional strategy where students review content at home and engage in interactive activities in class. | Personalized teaching delivered remotely via digital platforms. |
| Learning Environment | Hybrid: online content + in-person interaction. | Fully virtual, one-on-one or group sessions online. |
| Student Engagement | High in-class collaboration and active learning. | Focused, tailored coaching based on individual needs. |
| Flexibility | Moderate; structured in-class time required. | High; flexible scheduling and location independent. |
| Technology Use | Video lectures, quizzes, classroom tech tools. | Video conferencing, digital whiteboards, learning apps. |
| Teacher Role | Facilitator and guide in active learning sessions. | Coach and mentor providing personalized feedback. |
| Ideal For | Group learning environments needing active participation. | Students requiring individualized support remotely. |
| Outcome Focus | Developing critical thinking and peer collaboration. | Targeted skill improvement and personalized growth. |
Introduction to Flipped Classroom and Distance Coaching
Flipped Classroom reverses traditional teaching by delivering instructional content, often online, outside of the classroom while engaging students in interactive activities during class time to enhance comprehension. Distance Coaching leverages virtual platforms to provide personalized guidance and skill development remotely, enabling flexible learning independent of location. Both methods prioritize learner-centered approaches but differ in delivery and interaction dynamics.
Key Concepts and Definitions
Flipped Classroom involves students engaging with instructional content, such as video lectures, outside of traditional class time while class sessions are utilized for interactive activities and personalized support. Distance Coaching refers to remote guidance and skill development delivered via digital platforms, emphasizing real-time communication and tailored feedback without physical presence. Both approaches leverage technology for flexible learning but differ in structure: Flipped Classroom redefines classroom time usage, whereas Distance Coaching replaces in-person mentoring entirely.
Historical Evolution of Both Methods
The flipped classroom originated in the early 2000s as educators sought to enhance student engagement by delivering instructional content online for pre-class study, followed by active learning during class sessions. Distance coaching dates back to correspondence courses in the 19th century, evolving through radio, television, and now digital platforms to provide remote education and personalized instruction. Both methods have progressively integrated technology, transforming traditional teaching into more interactive and accessible learning experiences over time.
Core Differences in Teaching Strategies
Flipped Classroom reverses traditional teaching by delivering instructional content online before class, enabling in-person sessions for interactive activities and personalized support. Distance Coaching emphasizes real-time virtual interaction with coaches or mentors, focusing on individualized guidance and immediate feedback through digital platforms. The core difference lies in Flipped Classroom's blend of asynchronous content with synchronous application, while Distance Coaching relies primarily on synchronous, personalized mentorship.
Technology Integration: Tools and Platforms
Flipped Classroom leverages video lectures, interactive quizzes, and collaborative platforms like Moodle and Edmodo to foster active learning before class. Distance Coaching utilizes real-time communication tools such as Zoom, Microsoft Teams, and Tutor LMS to provide personalized instruction remotely. Both approaches integrate Learning Management Systems (LMS) and multimedia resources, but Flipped Classroom emphasizes asynchronous content delivery while Distance Coaching prioritizes synchronous interaction.
Student Engagement and Participation
Flipped Classroom models increase student engagement by promoting active learning through pre-class video lectures and in-class interactive activities, fostering deeper participation. Distance Coaching relies on real-time digital communication tools to maintain interaction but may face challenges with student motivation and consistent involvement. Studies show flipped classrooms generally yield higher rates of student participation due to structured, peer-collaborative environments.
Effectiveness in Learning Outcomes
Flipped Classroom models enhance learning outcomes by promoting active engagement through pre-class content review and interactive in-class problem-solving, resulting in higher retention and comprehension rates. Distance Coaching offers personalized, flexible learning experiences that cater to individual pacing and immediate feedback, which significantly improves skill acquisition and learner satisfaction. Comparative studies indicate that combining elements of both methodologies maximizes knowledge retention and application, especially in complex subjects requiring practical demonstration and continuous support.
Flexibility and Accessibility Comparison
Flipped Classroom offers students flexibility by allowing them to learn lecture content at their own pace before engaging in interactive, in-person sessions, enhancing comprehension and retention. Distance Coaching provides greater accessibility by enabling learners to participate from any location with internet access, accommodating varied schedules and eliminating geographical barriers. Both methods optimize flexible learning environments, but Distance Coaching uniquely supports real-time, remote interaction tailored to individual needs.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
Flipped classroom challenges include student self-motivation, reliable access to digital content, and the need for effective in-class facilitation to maximize engagement. Distance coaching faces limitations such as potential technical issues, reduced personal interaction, and difficulties in providing immediate, personalized feedback. Both approaches require adaptive strategies to overcome barriers related to technology dependence and learner accountability.
Future Trends in Education Delivery
Flipped Classroom models leverage interactive, pre-recorded content to foster in-class engagement, while Distance Coaching emphasizes personalized, real-time virtual mentorship using advanced communication tools. Future trends in education delivery highlight the integration of AI-driven analytics and immersive technologies like AR/VR to enhance both flipped and remote learning environments. Hybrid approaches combining synchronous mentoring with asynchronous content will drive adaptive, learner-centered experiences, optimizing outcomes in diverse educational settings.
Flipped Classroom Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com