Push-in support technology streamlines the installation process by allowing wires to be quickly and securely connected without the need for screws or additional tools. This innovation enhances efficiency and reliability in electrical setups, reducing installation time and minimizing the risk of loose connections. Discover how push-in support can optimize your next project by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
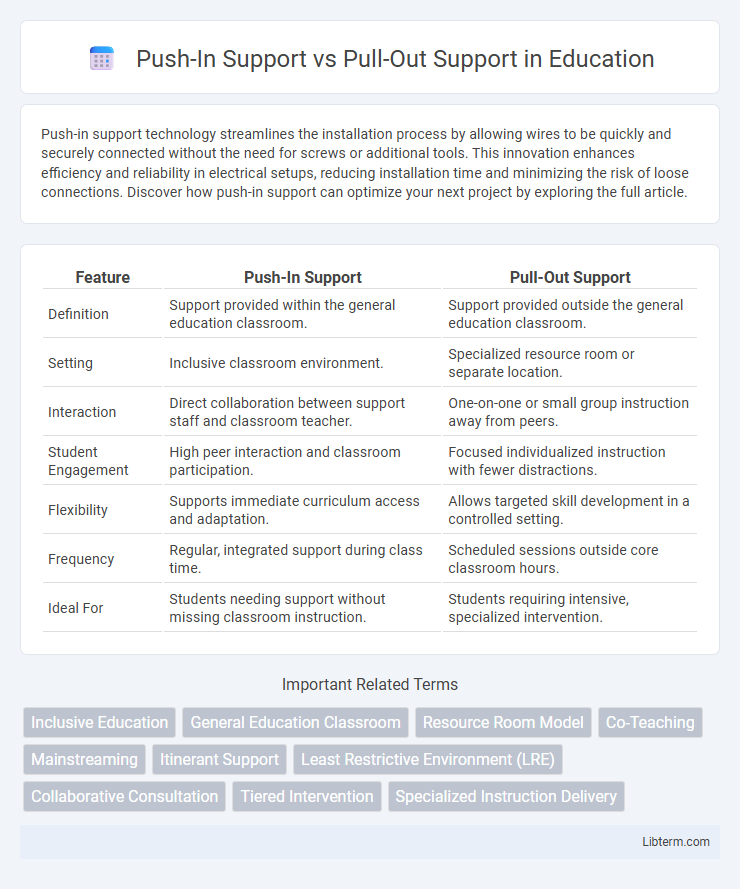
| Feature | Push-In Support | Pull-Out Support |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Support provided within the general education classroom. | Support provided outside the general education classroom. |
| Setting | Inclusive classroom environment. | Specialized resource room or separate location. |
| Interaction | Direct collaboration between support staff and classroom teacher. | One-on-one or small group instruction away from peers. |
| Student Engagement | High peer interaction and classroom participation. | Focused individualized instruction with fewer distractions. |
| Flexibility | Supports immediate curriculum access and adaptation. | Allows targeted skill development in a controlled setting. |
| Frequency | Regular, integrated support during class time. | Scheduled sessions outside core classroom hours. |
| Ideal For | Students needing support without missing classroom instruction. | Students requiring intensive, specialized intervention. |
Introduction to Push-In and Pull-Out Support
Push-in support provides stabilization by inserting reinforcement bars into existing concrete elements, enhancing structural integrity and load transfer. Pull-out support involves embedding anchors or rods that resist extraction forces, commonly used to counteract tensile stresses in construction joints. Both techniques optimize reinforcement strategies for different load conditions and structural requirements.
Defining Push-In Support
Push-in support refers to a method where attention or resources are integrated directly into ongoing activities, allowing specialists to assist within the existing environment without removing individuals from their primary setting. This approach promotes real-time guidance and immediate intervention, enhancing collaborative problem-solving and skill development. Push-in support is commonly used in educational settings to provide inclusive assistance while maintaining student participation in general instruction.
Defining Pull-Out Support
Pull-out support is a structural reinforcement technique designed to resist forces that attempt to dislodge an element from its anchorage, ensuring stability under tensile loads. This method is crucial in applications such as retaining walls, anchoring systems, and foundation supports where resistance to extraction forces is paramount. Unlike push-in support, which counteracts compressive forces, pull-out support prevents components from being pulled away, enhancing overall structural integrity.
Key Differences Between Push-In and Pull-Out Support
Push-In support involves inserting components, such as connectors or fasteners, directly into a housing or panel, providing a quick and secure attachment without additional tools. Pull-Out support relies on the force required to remove these components once inserted, with design elements like friction or locking mechanisms ensuring stability under stress. The key differences lie in the insertion method and retention force, where push-in support prioritizes ease and speed of assembly, while pull-out support emphasizes resistance to disengagement under load.
Advantages of Push-In Support
Push-In Support offers superior ease of installation and reduced labor costs by allowing components to be quickly secured without the need for additional tools. This method enhances stability and vibration resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring reliable mechanical retention. Furthermore, Push-In Support provides better space efficiency and simplifies maintenance, contributing to improved system performance and longevity.
Advantages of Pull-Out Support
Pull-Out Support offers superior accessibility for maintenance and troubleshooting, allowing equipment to be easily removed without disassembling surrounding structures. This type of support enhances safety by minimizing downtime and reducing the risk of damage during servicing. Its modular design also accommodates heavier loads and complex machinery, making it ideal for industrial applications requiring frequent inspections.
Challenges Faced in Push-In Support
Push-in support faces challenges such as the risk of damaging delicate components during insertion, limited accessibility in tight spaces, and the need for precise alignment to ensure secure connections. This method often requires specialized tools and skilled technicians to avoid misalignment or incomplete engagement, which can compromise system integrity. High insertion forces may also cause wear or deformation over time, reducing the reliability of push-in connections in dynamic environments.
Challenges Faced in Pull-Out Support
Pull-out support in underground utility installations faces challenges such as increased risk of cable damage due to excessive pulling force and potential misalignment during extraction, which can compromise system integrity. Managing friction and tension requires precise calculation and careful monitoring to avoid insulation abrasion or conductor deformation. Furthermore, limited workspace and environmental factors like soil composition exacerbate difficulties in executing pull-out procedures efficiently and safely.
Choosing the Right Support Model for Students
Choosing the right support model for students involves evaluating their individual learning needs and engagement styles. Push-in support integrates specialists directly into the general classroom, promoting immediate assistance and inclusive learning, while pull-out support removes students from the standard setting for targeted, intensive intervention. Educators should consider factors such as student self-regulation, social skills, and academic goals to determine which approach maximizes learning outcomes and fosters independence.
Conclusion: Push-In vs Pull-Out Support
Push-In support offers greater stability and strength in retaining structural components compared to Pull-Out support, making it ideal for heavy-load applications. Pull-Out support, while easier to install, may lack the same level of reliability under dynamic or high-stress conditions. Selecting Push-In support ensures enhanced durability and safety in construction and mechanical systems.
Push-In Support Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com