Inquiry-based learning fosters critical thinking by encouraging students to explore questions and problems deeply. This student-centered approach promotes active engagement, creativity, and a deeper understanding of the subject matter. Discover how inquiry-based learning can transform your educational experience by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
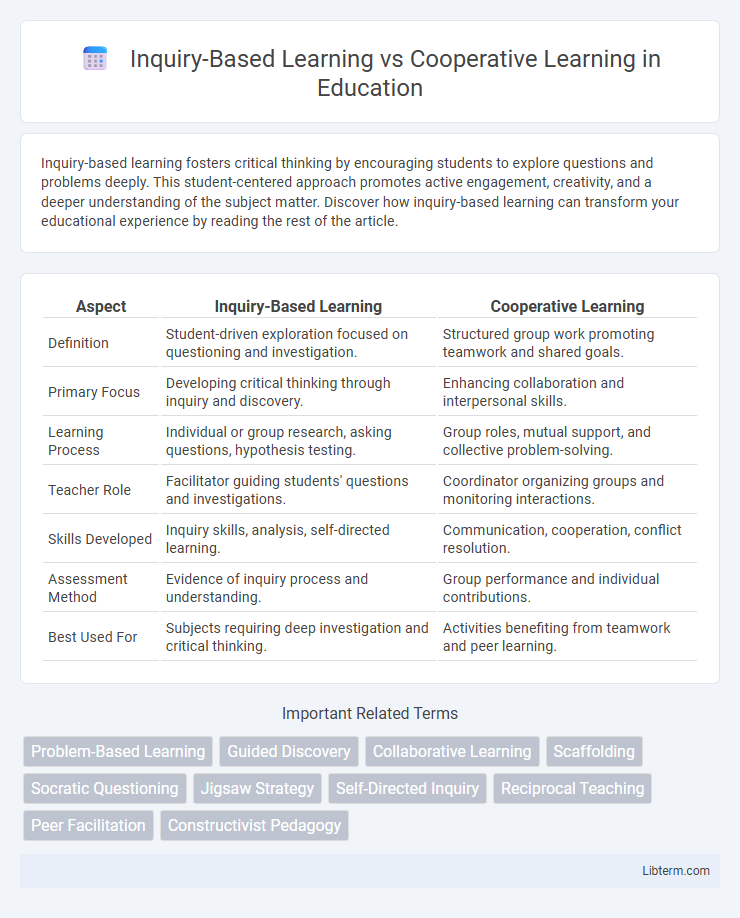
| Aspect | Inquiry-Based Learning | Cooperative Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Student-driven exploration focused on questioning and investigation. | Structured group work promoting teamwork and shared goals. |
| Primary Focus | Developing critical thinking through inquiry and discovery. | Enhancing collaboration and interpersonal skills. |
| Learning Process | Individual or group research, asking questions, hypothesis testing. | Group roles, mutual support, and collective problem-solving. |
| Teacher Role | Facilitator guiding students' questions and investigations. | Coordinator organizing groups and monitoring interactions. |
| Skills Developed | Inquiry skills, analysis, self-directed learning. | Communication, cooperation, conflict resolution. |
| Assessment Method | Evidence of inquiry process and understanding. | Group performance and individual contributions. |
| Best Used For | Subjects requiring deep investigation and critical thinking. | Activities benefiting from teamwork and peer learning. |
Introduction to Inquiry-Based Learning and Cooperative Learning
Inquiry-Based Learning engages students by encouraging exploration, questioning, and investigation to construct their own understanding and knowledge. Cooperative Learning emphasizes structured group activities where learners collaborate, share resources, and support each other to achieve shared academic goals. Both methods foster active participation and critical thinking but differ in focus; Inquiry-Based Learning centers on individual inquiry processes, while Cooperative Learning prioritizes social interaction and teamwork.
Defining Inquiry-Based Learning
Inquiry-Based Learning emphasizes student-driven exploration and critical thinking by engaging learners in asking questions, investigating problems, and constructing knowledge through hands-on experiences. This method fosters deeper understanding and active participation by encouraging curiosity and evidence-based reasoning. Unlike Cooperative Learning, which centers on group collaboration and shared tasks, Inquiry-Based Learning prioritizes individual inquiry processes to develop independent problem-solving skills.
Defining Cooperative Learning
Cooperative learning is an instructional strategy where students work together in small groups to achieve shared learning goals, fostering social interaction and collective problem-solving. This approach emphasizes positive interdependence, individual accountability, and the development of interpersonal skills. Unlike inquiry-based learning, which centers on individual exploration and questioning, cooperative learning prioritizes collaboration and group dynamics to enhance understanding and retention.
Key Principles of Inquiry-Based Learning
Inquiry-Based Learning centers on active student engagement through questioning, exploration, and critical thinking, fostering deep understanding and independent problem-solving skills. It emphasizes the construction of knowledge through investigation, where learners formulate hypotheses, gather evidence, and draw conclusions. This approach contrasts with Cooperative Learning by prioritizing individual inquiry processes over structured group collaboration dynamics.
Core Features of Cooperative Learning
Cooperative learning centers on structured group activities where students work collaboratively to achieve shared academic goals, enhancing communication, social skills, and collective problem-solving. Core features include positive interdependence, individual accountability, face-to-face promotive interaction, and development of interpersonal and small group skills. This approach contrasts with inquiry-based learning by emphasizing group roles and responsibilities rather than individual exploration and questioning.
Differences in Classroom Implementation
Inquiry-Based Learning emphasizes student-driven exploration where learners formulate questions and investigate to construct understanding, often working individually or in small groups. Cooperative Learning involves structured group activities with assigned roles and clear interdependence, promoting collaboration and shared responsibility for learning outcomes. Classroom implementation of Inquiry-Based Learning requires facilitation of open-ended inquiry and critical thinking, while Cooperative Learning focuses on social interaction and teamwork skills to achieve common academic goals.
Student Roles and Interactions
Inquiry-Based Learning positions students as active investigators who formulate questions, conduct research, and construct knowledge individually or collaboratively, promoting critical thinking and autonomy. Cooperative Learning organizes students into structured groups where each member assumes specific roles such as facilitator, recorder, or presenter, fostering interdependence and teamwork skills. Interactions in Inquiry-Based Learning are often exploratory and self-directed, while Cooperative Learning emphasizes coordinated communication and shared responsibility for achieving group goals.
Benefits and Challenges of Each Approach
Inquiry-Based Learning fosters critical thinking and deep understanding by encouraging students to explore questions and problems independently, promoting curiosity and self-directed learning; however, it may pose challenges such as the need for strong facilitation skills and potential student frustration due to ambiguous outcomes. Cooperative Learning enhances social skills and knowledge retention through structured group activities and peer collaboration, supporting diverse learners and increasing engagement, yet it can encounter difficulties like unequal participation and dependency on group dynamics. Both approaches require careful planning and adaptability to maximize student growth and overcome inherent challenges.
Impact on Student Engagement and Achievement
Inquiry-Based Learning fosters student engagement by encouraging curiosity and critical thinking through hands-on exploration of real-world problems, which enhances deep understanding and knowledge retention. Cooperative Learning boosts achievement by promoting collaboration, communication, and peer support, leading to improved social skills and higher collective academic performance. Both approaches significantly increase student motivation and active participation, resulting in positively impacted educational outcomes.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Classroom
Inquiry-Based Learning encourages student curiosity and critical thinking by allowing learners to explore questions and problems independently, making it ideal for fostering deep understanding in subjects requiring analysis and creativity. Cooperative Learning emphasizes collaboration and social skills development by having students work together in structured groups, which enhances communication and teamwork in diverse classroom settings. Selecting the right approach depends on your classroom goals: prioritize Inquiry-Based Learning for promoting autonomy and inquiry, or choose Cooperative Learning to build interpersonal skills and collective problem-solving.
Inquiry-Based Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com