Synthesis is the process of combining different ideas, information, or elements to form a coherent whole that offers new insights or solutions. This skill is essential for critical thinking, effective problem-solving, and creating innovative content in academic, professional, and creative contexts. Explore the rest of the article to discover practical strategies for mastering synthesis and enhancing your analytical abilities.
Table of Comparison
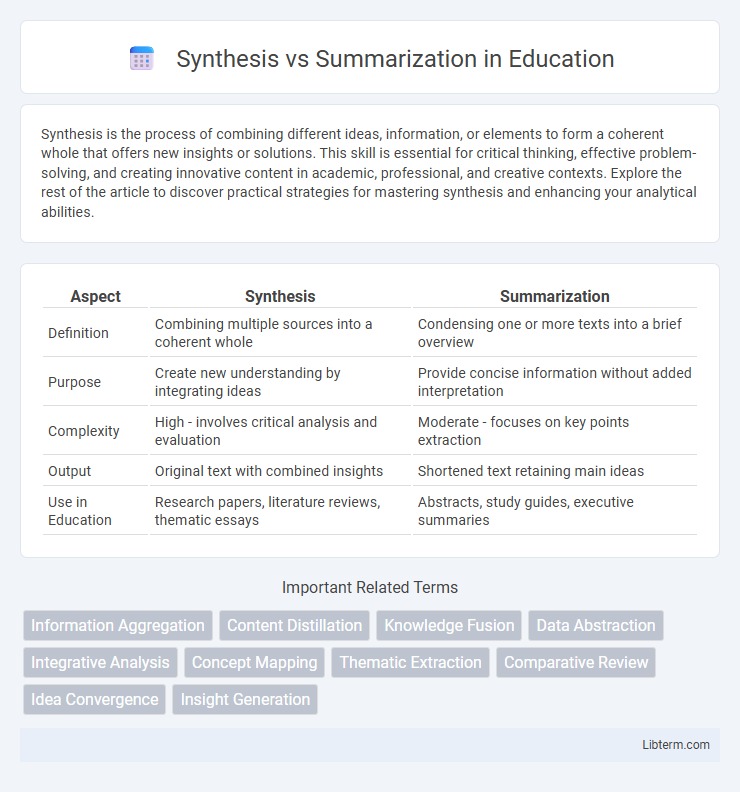
| Aspect | Synthesis | Summarization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combining multiple sources into a coherent whole | Condensing one or more texts into a brief overview |
| Purpose | Create new understanding by integrating ideas | Provide concise information without added interpretation |
| Complexity | High - involves critical analysis and evaluation | Moderate - focuses on key points extraction |
| Output | Original text with combined insights | Shortened text retaining main ideas |
| Use in Education | Research papers, literature reviews, thematic essays | Abstracts, study guides, executive summaries |
Understanding Synthesis and Summarization
Synthesis involves combining information from multiple sources to create a new, cohesive understanding or perspective, while summarization distills core ideas from a single source into a concise form. Understanding synthesis requires analytical skills to identify relationships and integrate diverse viewpoints. Summarization prioritizes clarity and brevity, focusing on key points without adding interpretation or new insights.
Key Differences Between Synthesis and Summarization
Synthesis involves combining information from multiple sources to create new insights or perspectives, whereas summarization condenses a single text into a concise version highlighting main points. Unlike summarization, which is primarily focused on reducing content, synthesis requires critical analysis and integration to produce an original understanding. Effective synthesis synthesizes diverse data to establish connections and original conclusions, while summarization simply captures essential ideas without adding interpretation.
The Purpose of Synthesis in Writing
Synthesis in writing serves to combine multiple sources or ideas to create a cohesive, original perspective that offers deeper insight or understanding beyond individual contributions. It aims to connect themes, identify relationships, and build an integrated argument that supports a specific thesis or research question. Unlike summarization, which condenses content into a brief overview, synthesis actively interprets and evaluates evidence to advance critical thinking and knowledge creation.
The Role of Summarization in Communication
Summarization plays a crucial role in communication by condensing large volumes of information into concise and clear messages, enhancing understanding and retention. It distills essential points from complex texts, enabling efficient information transfer across diverse contexts such as academic, professional, and digital communication. Effective summarization improves clarity, facilitates decision-making, and supports faster cognitive processing for both senders and receivers.
Techniques for Effective Synthesis
Effective synthesis techniques involve integrating information from multiple sources to create a cohesive understanding, emphasizing identifying common themes and relationships. Using concept mapping and thematic coding facilitates organizing key ideas and connecting them logically. Paraphrasing and critical evaluation enhance synthesis by rephrasing information in original terms while assessing source credibility and relevance.
Strategies for Accurate Summarization
Effective strategies for accurate summarization include identifying key points, maintaining the original meaning, and using concise language to convey essential information. Employing techniques such as highlighting main ideas, eliminating redundant details, and organizing content logically enhances clarity and coherence. Leveraging tools like semantic analysis and natural language processing can further improve summary precision and relevance.
Common Challenges in Synthesis vs Summarization
Synthesis and summarization both require critical evaluation of multiple sources but differ in complexity and purpose, posing unique challenges in each. Synthesizing demands integrating diverse perspectives into a coherent new understanding, often complicated by conflicting information and varying data formats. Summarization focuses on condensing content while preserving key ideas, frequently challenged by identifying essential points without losing context or nuance.
When to Use Synthesis Instead of Summarization
Synthesis is ideal when combining multiple sources to create a new perspective or comprehensive understanding, especially in research or academic writing where analyzing relationships and contrasting viewpoints is essential. Use synthesis to generate original insights by merging diverse information, rather than merely condensing content as in summarization. This approach enhances critical thinking and supports argument development beyond the scope of simple summary.
Practical Applications in Academic and Professional Fields
Synthesis integrates information from multiple sources to create new insights, essential for research papers and literature reviews where combining diverse perspectives enhances understanding. Summarization condenses large texts into concise overviews, facilitating quick comprehension of key points in reports, executive summaries, and briefings. Both techniques improve decision-making and knowledge management in academic and professional environments by streamlining information processing.
Tips for Improving Both Synthesis and Summarization Skills
To improve synthesis and summarization skills, focus on identifying key ideas and themes across multiple sources, ensuring accurate representation of the original meaning. Practice organizing information logically, using clear and concise language to convey complex concepts effectively. Enhance these skills by regularly reviewing and refining drafts, seeking feedback to improve clarity and coherence.
Synthesis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com