Solo programming enhances focus and productivity by eliminating distractions and allowing you to control the workflow entirely. This method fosters deep problem-solving and a personalized pace, ideal for tackling complex coding tasks efficiently. Discover how solo programming can transform your development process by exploring the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
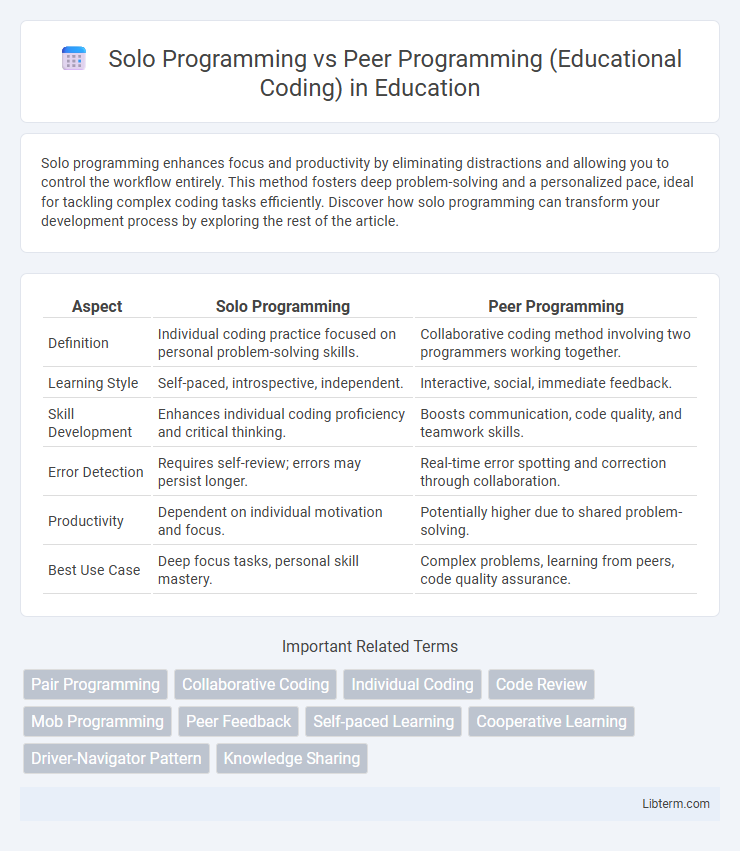
| Aspect | Solo Programming | Peer Programming |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Individual coding practice focused on personal problem-solving skills. | Collaborative coding method involving two programmers working together. |
| Learning Style | Self-paced, introspective, independent. | Interactive, social, immediate feedback. |
| Skill Development | Enhances individual coding proficiency and critical thinking. | Boosts communication, code quality, and teamwork skills. |
| Error Detection | Requires self-review; errors may persist longer. | Real-time error spotting and correction through collaboration. |
| Productivity | Dependent on individual motivation and focus. | Potentially higher due to shared problem-solving. |
| Best Use Case | Deep focus tasks, personal skill mastery. | Complex problems, learning from peers, code quality assurance. |
Introduction to Solo and Peer Programming in Education
Solo programming encourages individual problem-solving skills and independent coding practice, allowing students to develop a deeper personal understanding of programming concepts. Peer programming, often implemented as pair programming, promotes collaboration, real-time feedback, and knowledge sharing, enhancing communication and teamwork abilities in educational settings. Integrating both methods can balance self-reliance and collaborative skills, essential for comprehensive coding education.
Defining Solo Programming: Benefits and Challenges
Solo programming enhances individual problem-solving skills and fosters deep code comprehension by allowing uninterrupted focus on coding tasks. Key benefits include increased creativity, personalized pacing, and the development of autonomous coding proficiency. Challenges involve limited real-time feedback, potential isolation, and reduced opportunities for collaborative learning compared to peer programming environments.
Understanding Peer Programming: Collaboration in Learning
Peer programming enhances educational coding by fostering active collaboration, enabling learners to share diverse problem-solving approaches and immediate feedback. This interactive process boosts comprehension and retention compared to solo programming, where the learner works independently without real-time input. By engaging in paired coding, students develop communication skills and collective reasoning, critical for mastering complex programming concepts.
Cognitive Advantages of Solo Programming
Solo programming enhances deep focus and cognitive processing by allowing learners to engage with coding challenges independently, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills. It promotes personalized learning paces, enabling cognitive schemas to form without external interruptions. This concentrated practice strengthens memory retention and coding fluency, crucial for mastering complex programming concepts in educational settings.
Social and Emotional Impact of Peer Programming
Peer programming in educational coding enhances social interaction by fostering collaboration, communication, and mutual support among students, which improves emotional well-being and sense of belonging. The shared problem-solving experience reduces anxiety and builds confidence, promoting positive attitudes towards learning complex programming concepts. Solo programming lacks this dynamic, potentially leading to isolation and decreased motivation, whereas peer programming creates an engaging and emotionally supportive environment that benefits cognitive and social development.
Skill Development: Independent vs Team-Based Learning
Solo programming enhances problem-solving and self-reliance by allowing learners to independently explore coding concepts and debug errors, fostering deep technical skills and confidence. Peer programming encourages collaboration, communication, and collective problem-solving, which builds interpersonal abilities and exposes learners to diverse coding styles and strategies. Combining solo and peer programming enables a balanced development of both individual technical proficiency and teamwork skills essential for real-world software development.
Code Quality: Individual Focus vs Group Refinement
Solo programming allows developers to maintain individual focus, resulting in code that reflects personal coding style and immediate understanding but may lack diverse perspectives. Peer programming incorporates continuous collaborative refinement through real-time feedback, often enhancing code quality by identifying errors and improving design collectively. Both approaches impact code quality differently: solo work emphasizes clarity for the individual, while peer programming fosters shared ownership and collective code improvement.
Overcoming Common Challenges in Both Approaches
Solo programming enhances individual problem-solving skills but may lead to isolation and limited feedback, requiring disciplined self-review and use of code analysis tools to overcome errors. Peer programming fosters collaboration and real-time knowledge sharing, yet challenges like conflicting ideas and communication barriers necessitate establishing clear roles and effective communication strategies. Combining solo efforts with peer review sessions balances independent thinking and collaborative learning, addressing challenges inherent in both educational coding approaches.
Choosing the Right Method for Different Learners
Selecting the right programming method depends on learners' individual needs and goals; solo programming fosters self-discipline, deep concentration, and personal problem-solving skills, ideal for students who thrive independently. Peer programming enhances collaborative skills, immediate feedback, and shared knowledge, benefiting learners who excel through interaction and real-time communication. Educators should assess student personality, learning style, and project complexity to balance solo and peer programming effectively for optimal educational outcomes.
Conclusion: Blending Solo and Peer Programming for Success
Blending solo programming with peer programming enhances educational coding by combining independent problem-solving skills and collaborative learning benefits. Solo programming fosters deep individual focus and self-reliance, while peer programming encourages knowledge sharing, diverse perspectives, and immediate feedback. Integrating both methods creates a balanced approach that maximizes student engagement, coding proficiency, and overall academic success.
Solo Programming Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com