Experiential learning enhances knowledge retention by engaging learners through hands-on activities and real-world experiences, fostering deeper understanding beyond traditional methods. This approach develops critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and adaptability, preparing individuals for practical challenges. Discover how incorporating experiential learning can transform your educational or training programs by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
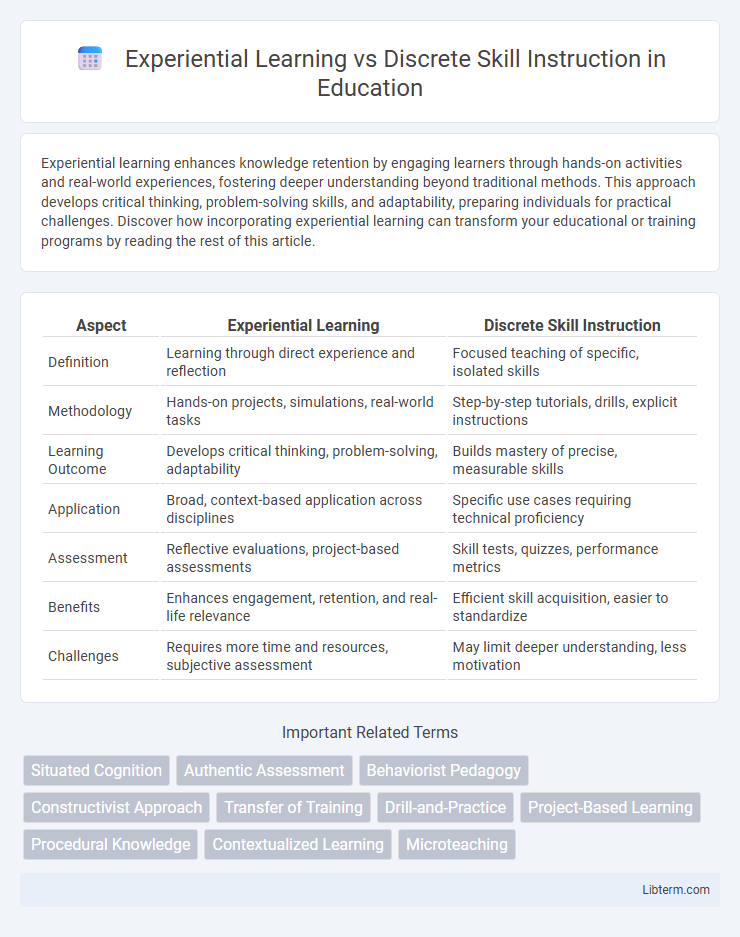
| Aspect | Experiential Learning | Discrete Skill Instruction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Learning through direct experience and reflection | Focused teaching of specific, isolated skills |
| Methodology | Hands-on projects, simulations, real-world tasks | Step-by-step tutorials, drills, explicit instructions |
| Learning Outcome | Develops critical thinking, problem-solving, adaptability | Builds mastery of precise, measurable skills |
| Application | Broad, context-based application across disciplines | Specific use cases requiring technical proficiency |
| Assessment | Reflective evaluations, project-based assessments | Skill tests, quizzes, performance metrics |
| Benefits | Enhances engagement, retention, and real-life relevance | Efficient skill acquisition, easier to standardize |
| Challenges | Requires more time and resources, subjective assessment | May limit deeper understanding, less motivation |
Understanding Experiential Learning
Experiential learning emphasizes immersive, hands-on experiences that promote critical thinking and problem-solving skills, allowing learners to apply theoretical knowledge in real-world contexts. This approach fosters deeper cognitive connections and retention by engaging multiple senses and encouraging active participation. Unlike discrete skill instruction, which targets isolated competencies, experiential learning cultivates holistic understanding and adaptability through reflection and iterative practice.
Defining Discrete Skill Instruction
Discrete skill instruction involves teaching specific, well-defined abilities through structured repetition and clear step-by-step guidance. This method emphasizes measurable outcomes and mastery of individual tasks, such as learning to type or solve algebraic equations. Targeted feedback and practice sessions ensure that learners refine precision and accuracy in each discrete skill.
Key Differences Between Experiential and Discrete Approaches
Experiential learning emphasizes immersive, hands-on experiences that foster critical thinking and problem-solving through real-world application, while discrete skill instruction targets the acquisition of specific, isolated skills in a structured, repetitive manner. Experiential methods promote deeper understanding by engaging learners in contexts that simulate actual challenges, contrasting with discrete instruction's focus on mastery of individual competencies without broader contextual integration. The key difference lies in experiential learning's holistic, integrative approach versus discrete instruction's segmented, skill-specific emphasis.
Core Principles of Experiential Learning
Experiential learning emphasizes active participation, reflection, and real-world context, fostering deeper understanding and retention compared to traditional discrete skill instruction. Core principles involve learning through direct experience, critical thinking, and continuous feedback loops that integrate practical application with theoretical knowledge. This approach enhances adaptability and problem-solving skills by engaging learners in authentic challenges rather than isolated skill drills.
Advantages of Discrete Skill Instruction
Discrete Skill Instruction offers targeted learning by isolating specific skills, allowing for precise assessment and rapid mastery. This method enhances retention through focused repetition and immediate feedback, optimizing skill acquisition efficiency. It supports scalable curriculum design, enabling educators to systematically build complex competencies from foundational elements.
Cognitive Theories Supporting Each Method
Experiential learning is grounded in constructivist cognitive theories such as Kolb's Experiential Learning Model, emphasizing active engagement and reflection to develop deeper understanding and critical thinking skills. Discrete skill instruction aligns with behaviorist theories, notably Skinner's operant conditioning, focusing on repetition and reinforcement to master specific, measurable tasks. Cognitive load theory supports both methods by advocating for instructional designs that optimize working memory capacity according to the complexity of learning objectives.
Impact on Student Engagement and Motivation
Experiential learning enhances student engagement and motivation by providing hands-on, real-world experiences that foster deeper understanding and intrinsic interest. In contrast, discrete skill instruction often leads to rote memorization and limited application, which can reduce student enthusiasm and long-term retention. Studies indicate that integrating experiential methods results in higher levels of participation, creativity, and sustained motivation among learners.
Suitability for Diverse Learning Styles
Experiential learning offers adaptability for diverse learning styles by engaging multiple senses and promoting active participation, making it suitable for kinesthetic, visual, and auditory learners. Discrete skill instruction, while more structured, benefits learners who thrive on clear, focused objectives and repetitive practice, particularly procedural or sequential learners. Combining both approaches can address a broader spectrum of learning preferences, enhancing overall educational effectiveness.
Measuring Outcomes and Assessment Strategies
Measuring outcomes in experiential learning emphasizes qualitative assessment methods such as reflective journals, project-based evaluations, and peer reviews to capture deeper understanding and skill application. Discrete skill instruction relies heavily on quantitative assessments, including standardized tests, quizzes, and skill demonstrations, which provide clear metrics for proficiency measurement. Effective assessment strategies integrate formative feedback and real-world performance tasks to align learning objectives with measurable outcomes in both approaches.
Integrating Both Approaches for Effective Education
Integrating experiential learning with discrete skill instruction enhances educational outcomes by combining hands-on experiences with targeted skill development, fostering deeper understanding and retention. Experiential learning encourages critical thinking and problem-solving through real-world application, while discrete skill instruction ensures mastery of specific competencies essential for academic and professional success. Blending both approaches creates a balanced curriculum that addresses cognitive, emotional, and practical dimensions, resulting in more effective and comprehensive education.
Experiential Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com