A balanced portfolio combines a mix of asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and cash equivalents, to optimize risk and return. This strategic allocation helps you safeguard your investments against market volatility while pursuing steady growth over time. Explore the rest of the article to discover how to create and maintain a balanced portfolio tailored to your financial goals.
Table of Comparison
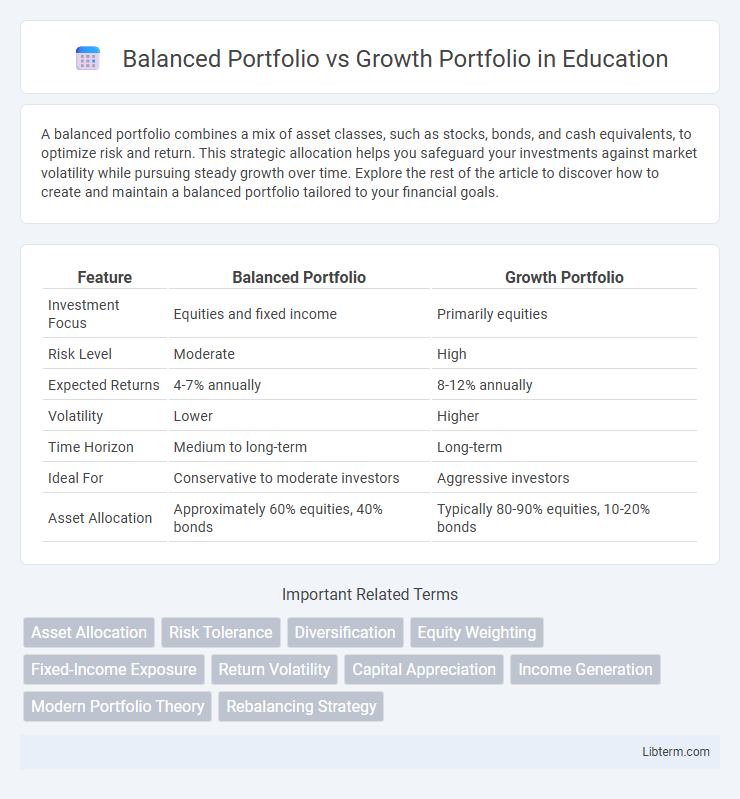
| Feature | Balanced Portfolio | Growth Portfolio |
|---|---|---|
| Investment Focus | Equities and fixed income | Primarily equities |
| Risk Level | Moderate | High |
| Expected Returns | 4-7% annually | 8-12% annually |
| Volatility | Lower | Higher |
| Time Horizon | Medium to long-term | Long-term |
| Ideal For | Conservative to moderate investors | Aggressive investors |
| Asset Allocation | Approximately 60% equities, 40% bonds | Typically 80-90% equities, 10-20% bonds |
Introduction to Portfolio Strategies
A balanced portfolio strategically combines equities and fixed-income securities to manage risk while aiming for moderate growth and income. Growth portfolios prioritize higher allocations in equities to maximize capital appreciation, accepting increased volatility for potential long-term returns. Understanding the risk tolerance and investment horizon is essential when choosing between balanced and growth portfolio strategies.
Defining Balanced and Growth Portfolios
A balanced portfolio typically allocates investments roughly equally between stocks and bonds to reduce risk while aiming for moderate growth. A growth portfolio primarily invests in equities and high-risk assets with the goal of maximizing capital appreciation over time. Understanding the asset allocation and risk tolerance associated with each portfolio type is essential for aligning investment strategies with financial goals.
Investment Objectives: Stability vs. Aggressive Growth
A Balanced Portfolio aims to provide stability by combining a mix of stocks, bonds, and other assets to reduce risk while generating moderate returns. In contrast, a Growth Portfolio focuses on aggressive growth by allocating a higher percentage to equities and high-risk investments, targeting maximum capital appreciation. Investors prioritizing capital preservation typically choose Balanced Portfolios, whereas those seeking rapid portfolio expansion prefer Growth Portfolios.
Asset Allocation in Balanced Portfolios
Balanced portfolios typically allocate 40-60% of assets to equities and 40-60% to fixed income, aiming for moderate risk and steady returns. This diversification reduces volatility by blending growth potential from stocks with the stability of bonds. In contrast, growth portfolios emphasize a higher equity allocation, often exceeding 70%, to maximize capital appreciation with increased risk exposure.
Asset Allocation in Growth Portfolios
Growth portfolios primarily allocate a higher percentage of assets to equities, often between 70% to 90%, to maximize capital appreciation over time. These portfolios emphasize stocks with strong growth potential, including emerging markets and technology sectors, while maintaining a smaller allocation to bonds and cash to mitigate risk. In contrast, balanced portfolios allocate assets more evenly, typically around 50% equities and 50% fixed income, aiming for moderate growth with reduced volatility.
Risk Tolerance: Assessing Your Comfort Level
Risk tolerance is crucial when choosing between a balanced portfolio and a growth portfolio, as it dictates an investor's capacity to withstand market fluctuations. A balanced portfolio typically combines equities and fixed-income securities, offering moderate risk and steady returns suitable for conservative to moderate investors. Growth portfolios, dominated by equities with higher volatility, appeal to risk-tolerant investors aiming for significant capital appreciation over the long term.
Expected Returns and Volatility
A balanced portfolio typically offers moderate expected returns with lower volatility by diversifying between equities and fixed income assets, aiming to reduce risk while achieving steady growth. Growth portfolios, heavily weighted in equities, target higher expected returns but come with increased volatility and greater exposure to market fluctuations. Investors seeking stable income and capital preservation may prefer balanced portfolios, whereas those prioritizing capital appreciation often opt for growth portfolios despite the higher risk.
Ideal Investors for Each Portfolio Type
Balanced portfolios suit investors seeking moderate risk and steady income through a mix of equities and fixed income, ideal for those approaching retirement or conservative growth goals. Growth portfolios target investors willing to accept higher volatility for significant capital appreciation, often younger individuals with longer investment horizons. Understanding risk tolerance and investment timeline is crucial for selecting the appropriate portfolio type.
Rebalancing and Portfolio Maintenance
Rebalancing a balanced portfolio involves adjusting asset allocations regularly to maintain a targeted mix of equities and fixed income, preserving risk tolerance and stability. Growth portfolios require more frequent rebalancing to capitalize on market opportunities while controlling volatility in higher equity exposure. Portfolio maintenance for both types includes monitoring performance, managing tax implications, and aligning with evolving investment goals to ensure long-term growth and risk management.
Choosing the Right Portfolio for Your Goals
Selecting the right portfolio depends on your financial goals and risk tolerance, where a balanced portfolio offers moderate risk with diversified investments in equities and bonds, aiming for steady growth and capital preservation. In contrast, a growth portfolio concentrates heavily on equities and higher-risk assets to maximize long-term capital appreciation, suitable for investors with a longer time horizon and higher risk appetite. Evaluating your investment timeline, income needs, and market volatility comfort ensures alignment of your portfolio choice with achieving specific financial objectives.
Balanced Portfolio Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com