Creating an effective lesson plan ensures structured teaching and maximizes student engagement by clearly outlining objectives, materials, and activities. It helps educators track progress and adapt methods to meet diverse learning needs. Discover how to design a comprehensive lesson plan that enhances your teaching effectiveness by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
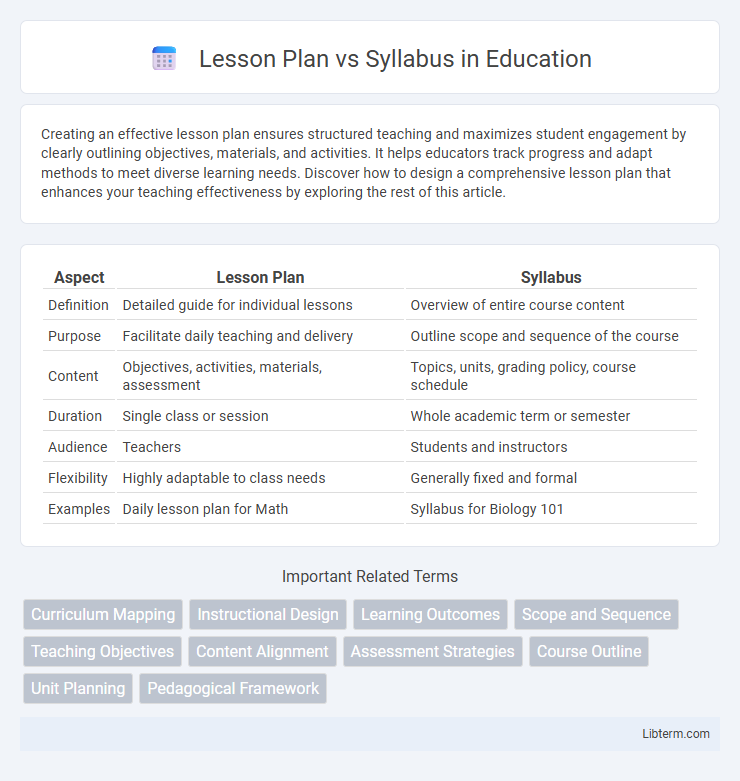
| Aspect | Lesson Plan | Syllabus |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Detailed guide for individual lessons | Overview of entire course content |
| Purpose | Facilitate daily teaching and delivery | Outline scope and sequence of the course |
| Content | Objectives, activities, materials, assessment | Topics, units, grading policy, course schedule |
| Duration | Single class or session | Whole academic term or semester |
| Audience | Teachers | Students and instructors |
| Flexibility | Highly adaptable to class needs | Generally fixed and formal |
| Examples | Daily lesson plan for Math | Syllabus for Biology 101 |
Introduction to Lesson Plans and Syllabi
Lesson plans provide detailed daily or weekly instructional guidance, outlining specific objectives, activities, and assessments tailored to individual lessons. Syllabi serve as comprehensive course overviews, presenting the overall structure, learning goals, grading policies, and schedule for the entire academic term. Understanding the distinctions between lesson plans and syllabi is essential for effective curriculum design and classroom management.
Defining Lesson Plan: Key Elements
A lesson plan is a detailed guide for teachers outlining specific learning objectives, instructional activities, required materials, and assessment methods for each class session. Key elements include the learning objectives that define what students should achieve, instructional strategies designed to facilitate understanding, and evaluation techniques to measure student progress. This structured approach ensures targeted teaching and effective knowledge transfer within individual lessons.
Understanding the Syllabus: Core Components
A syllabus outlines the core components of a course, including objectives, topics, assessment methods, and grading policies, providing a structured roadmap for both instructors and students. It serves as a comprehensive guide to course expectations, timelines, and resources, ensuring clarity and alignment of educational goals. In contrast, a lesson plan breaks down individual class sessions, detailing specific activities, teaching strategies, and materials needed to achieve the syllabus objectives.
Purpose and Objectives: Lesson Plan vs Syllabus
A lesson plan details specific objectives and activities tailored to individual class sessions, ensuring targeted learning outcomes and instructional pacing. A syllabus outlines the overall course structure, including major topics, grading policies, and broad educational goals for the entire term. Together, these documents provide complementary frameworks for delivering and organizing curriculum content effectively.
Structure and Format Differences
A lesson plan typically features a detailed, day-to-day breakdown with specific objectives, materials, activities, and assessment methods designed for individual classes. In contrast, a syllabus provides a broader course outline, including topics covered, grading policies, reading assignments, and important dates, serving as a contract between instructor and students. The lesson plan's micro-level format emphasizes instructional flow and student engagement, while the syllabus presents a macro-level framework for the entire course.
Scope and Timeframe Comparison
A lesson plan outlines specific objectives, activities, and assessments for individual classes or sessions, typically covering a short timeframe such as a day or a week. In contrast, a syllabus provides a comprehensive overview of an entire course, detailing topics, learning outcomes, grading policies, and a timeline that spans the full semester or academic term. The scope of a lesson plan is narrow and focused on immediate instructional goals, while a syllabus encompasses the broader curriculum structure and long-term learning progression.
Roles in Curriculum Development
Lesson plans serve as detailed guides for individual classroom sessions, outlining specific learning objectives, teaching methods, and assessment strategies that align with curriculum goals. Syllabi function as overarching frameworks, organizing course content, timelines, and learning outcomes to ensure coherence across the curriculum. Both tools play crucial roles in curriculum development by translating broad educational standards into actionable teaching steps and structured course progression.
Flexibility and Adaptability
A lesson plan offers greater flexibility and adaptability by allowing educators to modify content, activities, and pacing based on students' needs and real-time classroom dynamics. In contrast, a syllabus provides a fixed outline of the course structure, objectives, and assessment criteria, serving as a roadmap with limited room for spontaneous changes. Emphasizing lesson plans supports personalized learning experiences and immediate responsiveness to diverse learner profiles and engagement levels.
Importance for Teachers and Students
A lesson plan provides teachers with a detailed roadmap for daily instruction, ensuring clear learning objectives and efficient use of class time, which directly enhances student engagement and understanding. A syllabus outlines the overall course structure, essential topics, and assessment schedules, offering students a comprehensive framework to manage their learning progress and expectations. Both tools are crucial for fostering organized teaching and promoting student accountability, leading to improved academic outcomes.
Choosing the Right Tool for Effective Teaching
A lesson plan offers detailed daily objectives and activities tailored to specific class sessions, while a syllabus provides a broader overview of course goals, policies, and timelines. Selecting the right tool depends on teaching needs: lesson plans enhance day-to-day instructional effectiveness, and syllabi guide overall course structure and student expectations. Effective teaching often integrates both, ensuring clear direction and dynamic classroom engagement.
Lesson Plan Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com