Inclusive education fosters a learning environment where students of all abilities learn together, promoting diversity and equal opportunities. This approach benefits not only students with disabilities but also cultivates empathy and collaboration among all classmates. Discover how inclusive education can transform your classroom by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
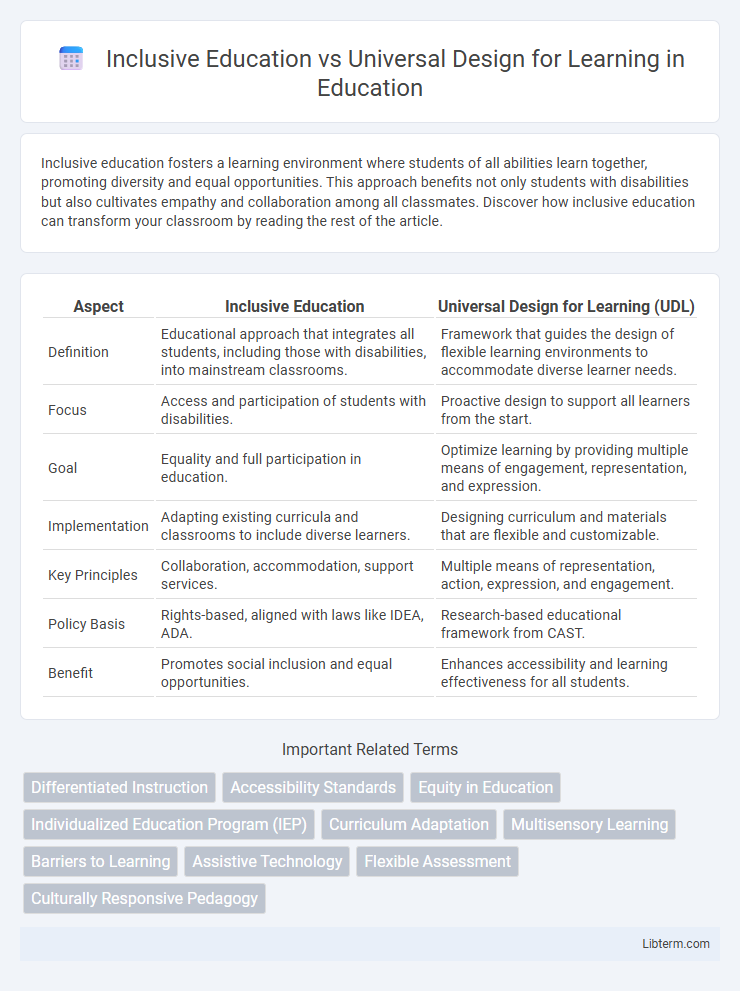
| Aspect | Inclusive Education | Universal Design for Learning (UDL) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Educational approach that integrates all students, including those with disabilities, into mainstream classrooms. | Framework that guides the design of flexible learning environments to accommodate diverse learner needs. |
| Focus | Access and participation of students with disabilities. | Proactive design to support all learners from the start. |
| Goal | Equality and full participation in education. | Optimize learning by providing multiple means of engagement, representation, and expression. |
| Implementation | Adapting existing curricula and classrooms to include diverse learners. | Designing curriculum and materials that are flexible and customizable. |
| Key Principles | Collaboration, accommodation, support services. | Multiple means of representation, action, expression, and engagement. |
| Policy Basis | Rights-based, aligned with laws like IDEA, ADA. | Research-based educational framework from CAST. |
| Benefit | Promotes social inclusion and equal opportunities. | Enhances accessibility and learning effectiveness for all students. |
Understanding Inclusive Education
Inclusive education emphasizes adapting teaching methods and learning environments to meet the diverse needs of all students, including those with disabilities, ensuring equal access to education. It promotes collaboration among educators, families, and communities to remove barriers and foster a supportive learning atmosphere. Understanding inclusive education involves recognizing its commitment to diversity, equity, and personalized support within mainstream classrooms.
Defining Universal Design for Learning (UDL)
Universal Design for Learning (UDL) is a research-based educational framework that guides the development of flexible learning environments to accommodate individual learning differences. UDL principles emphasize multiple means of representation, expression, and engagement to ensure all students, including those with disabilities, have equal opportunities to learn. By proactively designing curriculum and assessments, UDL aims to remove barriers and foster inclusive education through adaptable teaching methods.
Core Principles of Inclusive Education
Inclusive Education emphasizes the core principles of equity, diversity, and learner-centered approaches to ensure all students, regardless of ability or background, have access to quality education. It promotes participation, respect for differences, and the removal of barriers within the educational environment. Universal Design for Learning (UDL) supports these principles by providing flexible learning methods that accommodate diverse learning styles and needs.
Key Concepts of Universal Design for Learning
Universal Design for Learning (UDL) emphasizes multiple means of representation, engagement, and expression to accommodate diverse learner needs, promoting flexibility in teaching methods and materials. Unlike traditional Inclusive Education that often adapts existing curricula, UDL proactively designs curricula to be accessible and effective for all students from the outset. Key UDL principles include providing varied ways to access information, motivating learners with multiple engagement options, and allowing diverse methods for students to demonstrate understanding.
Similarities Between Inclusive Education and UDL
Inclusive Education and Universal Design for Learning (UDL) both emphasize creating accessible learning environments tailored to diverse student needs, ensuring equal opportunities for all learners. They prioritize flexibility in teaching methods and materials to accommodate different learning styles and abilities, fostering engagement and participation. Both frameworks advocate for proactive adjustments rather than reactive accommodations, promoting equity and reducing barriers to learning from the outset.
Distinct Differences in Approach
Inclusive Education emphasizes adapting existing educational frameworks to accommodate diverse learners by modifying curricula, teaching strategies, and assessment methods to ensure all students participate fully. Universal Design for Learning (UDL) proactively creates flexible learning environments and materials from the outset, using multiple means of representation, engagement, and expression to address learner variability. While Inclusive Education often reacts to student needs, UDL integrates accessibility as a foundational principle, promoting equity through intentional design rather than retrospective adjustments.
Benefits of Inclusive Education
Inclusive education fosters equitable learning environments by integrating diverse students, including those with disabilities, promoting social interaction and reducing stigma. It enhances academic outcomes by providing personalized support and encouraging collaboration among peers with varying abilities. Schools implementing inclusive education experience improved empathy, mutual respect, and a sense of community, benefiting all students academically and socially.
Advantages of Universal Design for Learning
Universal Design for Learning (UDL) offers significant advantages by creating flexible learning environments that accommodate diverse student needs and promote equitable access to education. UDL principles emphasize multiple means of engagement, representation, and expression, which support personalized learning pathways and improve student motivation and achievement. By proactively addressing barriers, UDL reduces the need for individual accommodations and fosters inclusive educational practices benefiting all learners.
Integrating Inclusive Education and UDL in Practice
Integrating Inclusive Education and Universal Design for Learning (UDL) in practice enhances accessibility by implementing flexible teaching methods and materials tailored to diverse learner needs, promoting equitable participation and reducing barriers. Effective collaboration between educators, specialists, and families supports personalized learning environments that accommodate cognitive, sensory, and physical differences. Combining Inclusive Education frameworks with UDL principles leads to comprehensive strategies that foster student engagement, improve academic outcomes, and exemplify commitment to diversity and inclusion in educational settings.
Future Directions for Equitable Learning
Future directions for equitable learning emphasize integrating Universal Design for Learning (UDL) principles within inclusive education frameworks to accommodate diverse learner needs and promote accessibility. Advancements in educational technology and personalized learning analytics support adaptive teaching methods that align with UDL's focus on multiple means of engagement, representation, and expression. Policy development and teacher training increasingly prioritize equity-driven strategies that bridge systemic gaps, ensuring all students benefit from inclusive environments enhanced by universal design principles.
Inclusive Education Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com