Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS) is a proactive framework designed to improve student behavior through consistent teaching of expectations and reinforcement of positive actions. By focusing on prevention and data-driven decision making, schools create safe and effective learning environments that promote social, emotional, and academic success. Explore the rest of the article to discover how PBIS can transform your school's culture and support every student's growth.
Table of Comparison
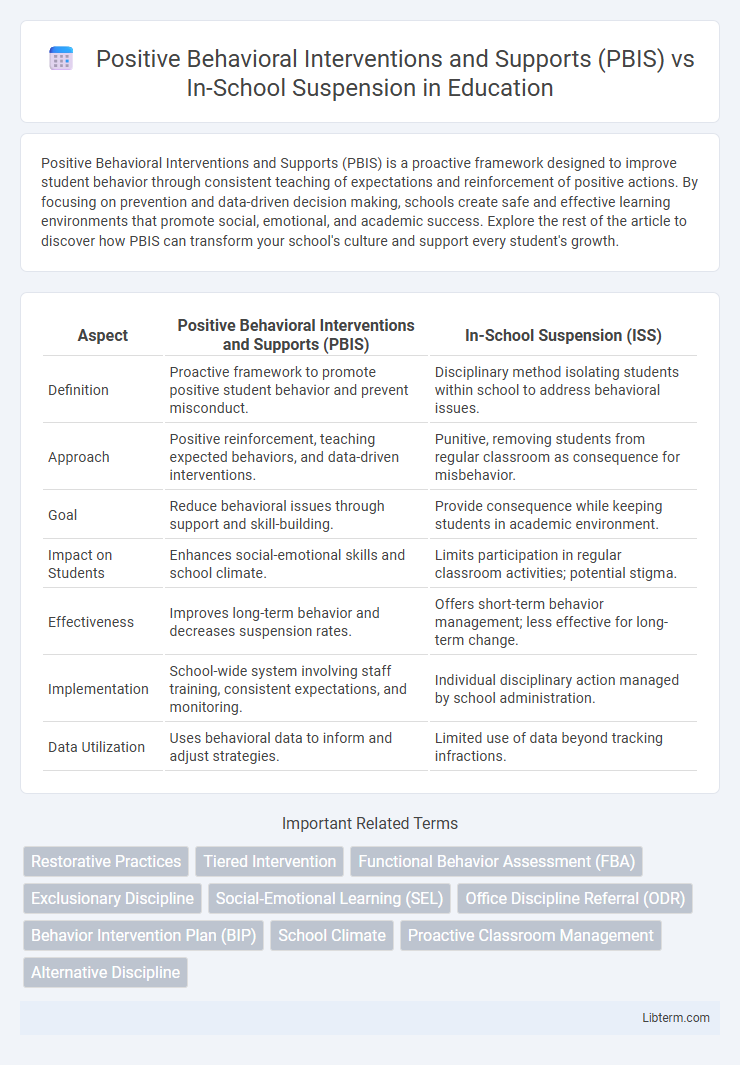
| Aspect | Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS) | In-School Suspension (ISS) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Proactive framework to promote positive student behavior and prevent misconduct. | Disciplinary method isolating students within school to address behavioral issues. |
| Approach | Positive reinforcement, teaching expected behaviors, and data-driven interventions. | Punitive, removing students from regular classroom as consequence for misbehavior. |
| Goal | Reduce behavioral issues through support and skill-building. | Provide consequence while keeping students in academic environment. |
| Impact on Students | Enhances social-emotional skills and school climate. | Limits participation in regular classroom activities; potential stigma. |
| Effectiveness | Improves long-term behavior and decreases suspension rates. | Offers short-term behavior management; less effective for long-term change. |
| Implementation | School-wide system involving staff training, consistent expectations, and monitoring. | Individual disciplinary action managed by school administration. |
| Data Utilization | Uses behavioral data to inform and adjust strategies. | Limited use of data beyond tracking infractions. |
Understanding PBIS: A Proactive Approach
Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS) is a proactive framework emphasizing the prevention of behavioral issues through teaching and reinforcing positive behavior, contrasting with In-School Suspension (ISS), which is a reactive disciplinary method isolating students after misbehavior. PBIS utilizes data-driven strategies to create supportive school climates, promoting social-emotional learning and reducing the need for punitive measures like ISS. By focusing on early intervention and consistent positive reinforcement, PBIS aims to improve student outcomes and decrease behavioral incidents more effectively than traditional suspension practices.
In-School Suspension: Traditional Discipline Explained
In-School Suspension (ISS) is a traditional discipline method where students are removed from the regular classroom but remain within the school environment, typically placed in a separate room for a specified period. This approach aims to isolate disruptive behavior while allowing students to complete academic work, yet it often fails to address underlying behavioral issues or promote positive social skills. Unlike Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS), which emphasize proactive strategies and reinforcement of positive behavior, ISS focuses primarily on punitive measures without integrating supportive interventions for long-term behavioral improvement.
Comparing Goals: PBIS vs. In-School Suspension
Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS) aims to proactively improve student behavior by teaching and reinforcing positive social skills, fostering a supportive school environment that reduces disciplinary incidents. In contrast, In-School Suspension (ISS) primarily serves as a punitive measure to isolate students temporarily, focusing on consequence rather than prevention or skill-building. PBIS emphasizes long-term behavior change and school climate enhancement, whereas ISS centers on immediate discipline and removal from the general classroom setting.
Impact on Student Behavior and Engagement
Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS) enhance student behavior by promoting positive reinforcement and teaching expected behaviors, resulting in increased engagement and reduced disciplinary issues. In contrast, In-School Suspension (ISS) often isolates students, which may temporarily remove disruptive behavior but does not address underlying behavior causes or improve student engagement. Research indicates PBIS fosters long-term behavioral improvements and higher academic participation, whereas ISS primarily serves as a short-term punitive measure with limited impact on student motivation.
Evidence-Based Outcomes: Effectiveness of PBIS
Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS) demonstrate superior evidence-based outcomes compared to In-School Suspension (ISS) by reducing disciplinary incidents and improving student behavior across diverse school settings. Studies show that PBIS implementation leads to a 30-50% decrease in office discipline referrals and fosters a positive school climate, whereas ISS often results in negative academic and social consequences for students. The data underscores PBIS as an effective framework for promoting long-term behavioral improvements and inclusive educational environments.
Limitations of In-School Suspension Programs
In-School Suspension (ISS) programs often fail to address the root causes of behavioral issues and do not provide positive reinforcement that encourages long-term behavioral improvement. Unlike Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS), which emphasize proactive strategies and skill-building, ISS focuses on punitive isolation that can exacerbate feelings of alienation among students. Research indicates that reliance on ISS correlates with increased dropout rates and does not significantly reduce recidivism in negative behaviors.
School Climate and Culture: PBIS vs. Suspension
Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS) fosters a positive school climate by promoting consistent, proactive strategies that reinforce desirable student behaviors and create a supportive learning environment. In contrast, In-School Suspension often contributes to a negative school culture by isolating students, increasing disengagement, and failing to address underlying behavioral issues. Implementing PBIS enhances student engagement and long-term behavioral improvement, whereas suspension tends to perpetuate negative cycles and does little to improve overall school climate.
Equity and Fairness in Disciplinary Practices
Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS) emphasize proactive strategies to promote positive behavior and reduce disciplinary disparities by fostering an inclusive school culture. In contrast, In-School Suspension (ISS) often disproportionately impacts marginalized students, contributing to inequitable disciplinary outcomes and exacerbating achievement gaps. Implementing PBIS frameworks supports fairness by addressing root behavioral causes and providing targeted support, whereas ISS primarily serves as a punitive response with limited focus on equity.
Implementing PBIS: Steps and Challenges
Implementing Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS) requires a strategic framework involving data-driven decision-making, staff training, and consistent reinforcement of expected behaviors across all school settings. Key steps include establishing leadership teams, defining clear behavioral expectations, and using tiered intervention models to address diverse student needs effectively. Challenges often arise from resistance to change, inadequate resources, and difficulties in maintaining fidelity to the PBIS framework, which can undermine the sustainability and success compared to traditional In-School Suspension practices.
Recommendations for School Discipline Reform
Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS) provide a proactive framework that emphasizes teaching and reinforcing positive behaviors, reducing the reliance on punitive measures like In-School Suspension (ISS). Research shows PBIS improves student outcomes by promoting a supportive school climate, whereas ISS often correlates with increased dropout rates and behavioral issues. Recommendations for school discipline reform advocate for expanding PBIS implementation, integrating restorative practices, and minimizing exclusionary punishments to foster equity and enhance overall student engagement.
Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS) Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com