Residency programs provide intensive, hands-on training essential for developing specialized medical expertise and clinical skills. These programs play a crucial role in transitioning medical graduates into competent healthcare professionals ready to manage patient care effectively. Explore the full article to understand how residency shapes your medical career path and opportunities.
Table of Comparison
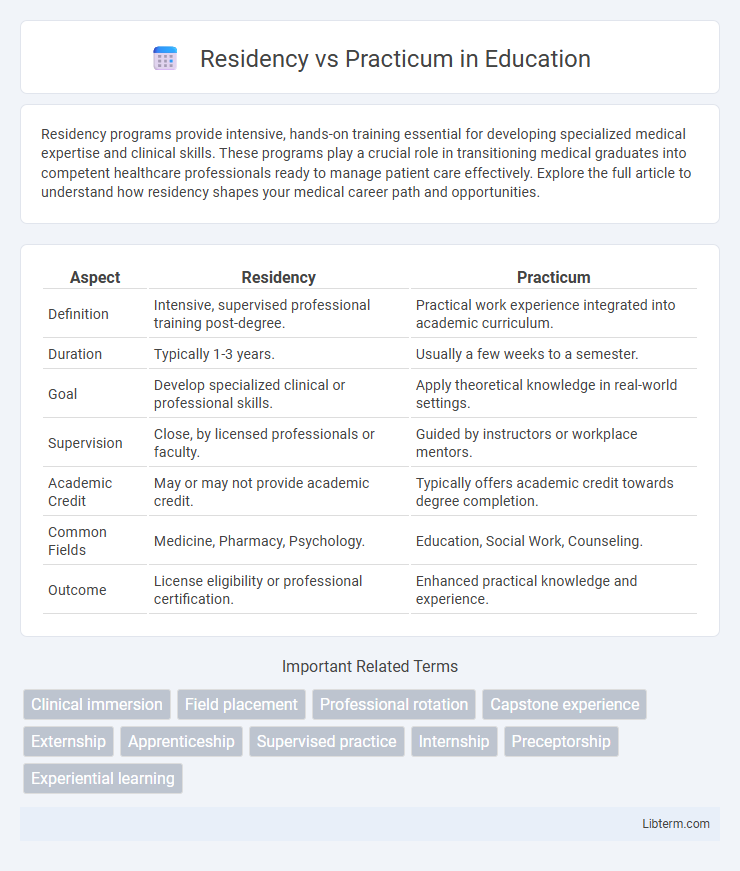
| Aspect | Residency | Practicum |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Intensive, supervised professional training post-degree. | Practical work experience integrated into academic curriculum. |
| Duration | Typically 1-3 years. | Usually a few weeks to a semester. |
| Goal | Develop specialized clinical or professional skills. | Apply theoretical knowledge in real-world settings. |
| Supervision | Close, by licensed professionals or faculty. | Guided by instructors or workplace mentors. |
| Academic Credit | May or may not provide academic credit. | Typically offers academic credit towards degree completion. |
| Common Fields | Medicine, Pharmacy, Psychology. | Education, Social Work, Counseling. |
| Outcome | License eligibility or professional certification. | Enhanced practical knowledge and experience. |
Understanding Residency and Practicum: An Overview
Residency programs offer immersive, hands-on training in clinical settings that enable medical graduates to develop specialized skills under supervision, typically lasting three to seven years depending on the specialty. Practicums provide shorter, supervised practical experiences within academic programs aimed at enhancing students' applied knowledge and professional competencies. Both residency and practicum serve as crucial pathways for transitioning theoretical education into real-world practice, with residency focusing on advanced professional preparation and practicum emphasizing foundational exposure.
Key Differences Between Residency and Practicum
Residency programs typically involve immersive, full-time clinical training in a specialized healthcare setting, offering hands-on patient care under supervision for an extended period. Practicums are shorter, often part-time experiences designed to provide students with practical exposure and skill development in specific professional environments. Key differences include duration, depth of clinical responsibility, and level of supervision, with residencies emphasizing independent practice readiness and practicums focusing on foundational learning.
Goals and Objectives of Residency Programs
Residency programs aim to develop advanced clinical skills through supervised, hands-on patient care, fostering autonomy and decision-making in real-world settings. The primary goals include enhancing specialty-specific competencies, ensuring readiness for independent practice, and promoting evidence-based clinical reasoning. Objectives focus on comprehensive patient management, interdisciplinary collaboration, and preparing residents for board certification and professional responsibilities.
Purpose and Structure of Practicum Experiences
Practicum experiences are designed to provide students with hands-on, supervised training in real-world settings, emphasizing skill development and practical application of theoretical knowledge. Structured with specific learning objectives, scheduled hours, and direct mentorship from industry professionals, practicums ensure students gain competency and reflective learning opportunities in their field. These experiences serve as a bridge between academic coursework and professional practice, fostering readiness for future career responsibilities.
Duration and Commitment: Residency vs Practicum
Residency programs typically last one to three years and require full-time commitment with extensive clinical hours, providing immersive hands-on experience in a medical specialty. Practicums, often part of academic courses, last a few weeks to several months and demand part-time involvement, focusing on supervised practical training aligned with curriculum objectives. The significant difference in duration and intensity reflects residency's role in professional certification compared to practicum's function in educational exposure.
Supervision and Mentorship in Both Pathways
Supervision in residency programs typically involves direct, structured oversight by experienced professionals, ensuring adherence to clinical standards and patient safety while fostering skill development. Practicum supervision is often more flexible, emphasizing mentorship and hands-on guidance tailored to individual learning objectives in real-world settings. Both pathways prioritize mentorship, but residencies focus on formal evaluation and competency milestones, whereas practicums cultivate experiential learning and personalized professional growth.
Types of Skills Developed in Residency vs Practicum
Residency programs emphasize advanced clinical skills, including decision-making, patient management, and specialized procedural expertise essential for independent medical practice. Practicums focus on foundational skills such as observation, basic patient interactions, and applying theoretical knowledge in supervised, real-world settings. Both develop critical professional competencies, but residencies deepen hands-on technical proficiencies, while practicums prioritize introductory clinical exposure and skill-building.
Career Outcomes: Which Pathway Suits Your Goals?
Residency programs offer intensive, specialized training that enhances clinical expertise, making them ideal for healthcare professionals seeking advanced practice roles or academic careers. Practicum experiences provide practical, hands-on learning in real-world settings, benefiting those aiming for direct entry into the workforce or roles requiring immediate application of skills. Evaluating career goals based on desired expertise level, job market demands, and professional development opportunities helps determine whether residency or practicum aligns best with your aspirations.
Admission Requirements and Eligibility Criteria
Residency programs typically require candidates to have completed a relevant degree such as an MD, DO, or equivalent medical qualification and pass licensing exams like the USMLE or COMLEX for admission eligibility. Practicum placements usually admit students enrolled in academic programs, requiring current enrollment status and prerequisites specific to the field, such as coursework or prior experience. Both pathways demand verification of credentials, but residency emphasizes licensure and clinical readiness, whereas practicum focuses on educational progress and foundational skills.
Choosing Between a Residency and a Practicum: Decision Factors
Choosing between a residency and a practicum depends on career goals, duration, and hands-on experience requirements. Residencies typically offer in-depth clinical training for medical or specialized fields over an extended period, while practicums provide shorter, supervised practical experience focusing on applying theoretical knowledge. Evaluating program structure, certification needs, and future employment opportunities is essential to make an informed decision.
Residency Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com