Direct Instruction is a highly structured teaching method that emphasizes clear, explicit teaching of academic skills through carefully planned lessons and guided practice. This approach uses systematic instruction, immediate feedback, and consistent review to ensure students master foundational concepts efficiently. Discover how Direct Instruction can transform your teaching strategy by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
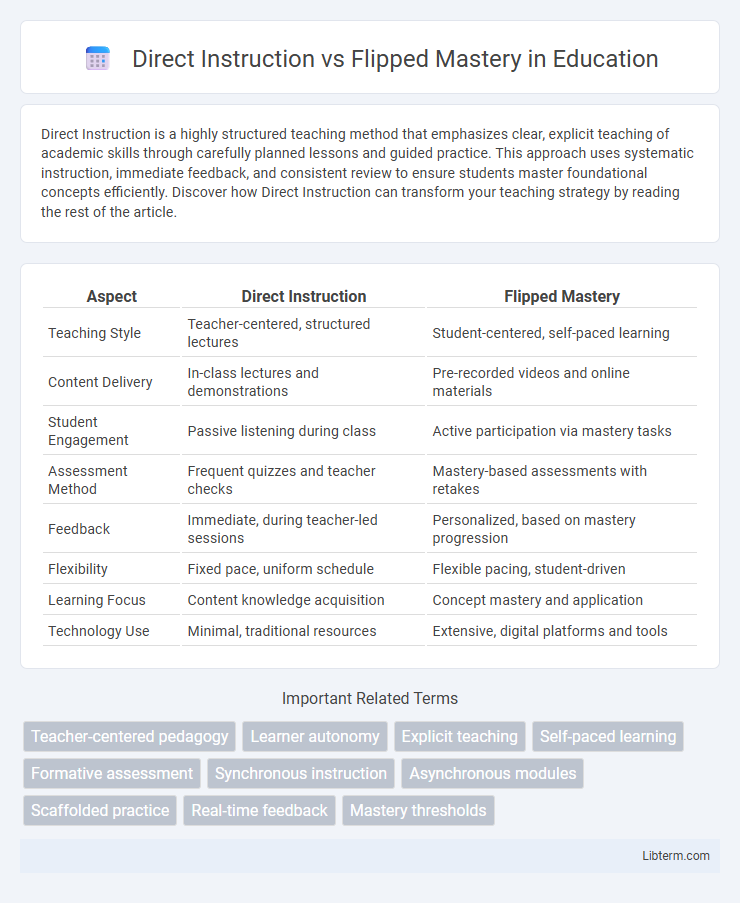
| Aspect | Direct Instruction | Flipped Mastery |
|---|---|---|
| Teaching Style | Teacher-centered, structured lectures | Student-centered, self-paced learning |
| Content Delivery | In-class lectures and demonstrations | Pre-recorded videos and online materials |
| Student Engagement | Passive listening during class | Active participation via mastery tasks |
| Assessment Method | Frequent quizzes and teacher checks | Mastery-based assessments with retakes |
| Feedback | Immediate, during teacher-led sessions | Personalized, based on mastery progression |
| Flexibility | Fixed pace, uniform schedule | Flexible pacing, student-driven |
| Learning Focus | Content knowledge acquisition | Concept mastery and application |
| Technology Use | Minimal, traditional resources | Extensive, digital platforms and tools |
Introduction to Direct Instruction and Flipped Mastery
Direct Instruction is a teacher-centered approach that delivers clear, structured lessons with explicit teaching and immediate feedback to ensure student mastery. Flipped Mastery inverts traditional teaching by having students engage with instructional content at home through videos or readings, allowing classroom time for personalized practice and mastery learning. Both methodologies prioritize mastery but differ in content delivery and classroom dynamics, with Direct Instruction focusing on guided teaching and Flipped Mastery emphasizing student autonomy in initial learning.
Core Principles of Direct Instruction
Direct Instruction emphasizes explicit teaching with scripted lessons, frequent assessments, and immediate corrective feedback to ensure students master foundational skills efficiently. It relies on carefully designed instructional sequences, clear objectives, and active teacher guidance to promote high levels of student engagement and achievement. Mastery checks are integral to Direct Instruction, ensuring that learners achieve proficiency before progressing to more complex concepts.
Foundations of Flipped Mastery Learning
Flipped Mastery Learning centers on students mastering content at their own pace by engaging with instructional videos or resources before class, fostering active in-class problem-solving and personalized teacher support. Unlike Direct Instruction, which follows a rigid, teacher-led approach delivering content sequentially to all students, Flipped Mastery emphasizes individualized progression through foundational skills and concepts. This approach enhances deep understanding and retention by allowing learners to revisit instructional material as needed and demonstrate mastery before advancing.
Teaching Strategies: Direct vs. Flipped Mastery
Direct Instruction employs a teacher-centered approach where concepts are explicitly taught through structured lessons and guided practice, ensuring immediate feedback and skill acquisition. Flipped Mastery reverses traditional teaching by having students engage with instructional content independently before class, allowing in-person time to focus on mastery through individualized support and application. This strategic shift enhances student autonomy and accommodates varying learning paces while maintaining effectiveness through continuous assessment and targeted interventions.
Student Engagement and Participation
Direct Instruction promotes student engagement through structured, teacher-led lessons, ensuring clear learning objectives and immediate feedback, which increases participation by guiding students step-by-step. Flipped Mastery empowers students to engage with content at their own pace outside the classroom, fostering active participation through interactive activities and peer collaboration during class time. Both methods enhance student involvement, with Direct Instruction emphasizing guided practice and Flipped Mastery emphasizing student autonomy and mastery learning.
Assessment and Feedback Methods
Direct Instruction employs frequent formative assessments and teacher-led feedback to monitor student progress, ensuring immediate correction and reinforcement of concepts. Flipped Mastery relies on self-paced assessments and peer or automated feedback within digital platforms, allowing learners to progress upon mastery while fostering autonomy. Both approaches prioritize timely assessment but differ in feedback delivery, with Direct Instruction emphasizing instructor intervention and Flipped Mastery leveraging student-driven review.
Flexibility and Differentiation in Learning
Direct Instruction offers structured, teacher-led lessons that ensure consistent content delivery, but its rigid format limits flexibility in pacing and personalization. In contrast, Flipped Mastery enables students to learn at their own pace by accessing instructional videos and materials outside class, which supports individualized learning paths and greater differentiation. This approach allows educators to focus classroom time on tailored support and enrichment activities that meet diverse learner needs.
Technology Integration in Both Approaches
Direct Instruction leverages technology primarily through interactive whiteboards and video presentations to deliver structured, teacher-led lessons that maintain a steady instructional pace. Flipped Mastery integrates digital platforms and learning management systems to provide students with on-demand video tutorials and personalized assessments, enabling self-paced mastery outside the classroom. Both approaches utilize data analytics tools to track student progress, but Flipped Mastery places greater emphasis on adaptive technology for individualized learning pathways.
Challenges and Limitations
Direct Instruction faces challenges such as limited student engagement and inflexible pacing, which can hinder differentiation for diverse learners. Flipped Mastery encounters limitations including the need for reliable technology access and student self-motivation to manage pre-class learning effectively. Both approaches require careful implementation to address potential gaps in comprehension and participation.
Choosing the Optimal Method for Diverse Learners
Choosing between Direct Instruction and Flipped Mastery hinges on addressing diverse learners' needs by balancing structured guidance with self-paced learning. Direct Instruction offers clear, teacher-led explanations ideal for students needing explicit scaffolding, while Flipped Mastery empowers learners to control their pace, benefiting those who thrive with autonomy and repeated practice. Effective implementation involves assessing learners' abilities, motivation, and access to technology to optimize comprehension, engagement, and mastery outcomes.
Direct Instruction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com