Assessment evaluates your skills, knowledge, and performance to identify strengths and areas for improvement. It plays a crucial role in personal development, education, and professional growth by providing actionable feedback. Explore the rest of the article to understand different assessment methods and how they can benefit you.
Table of Comparison
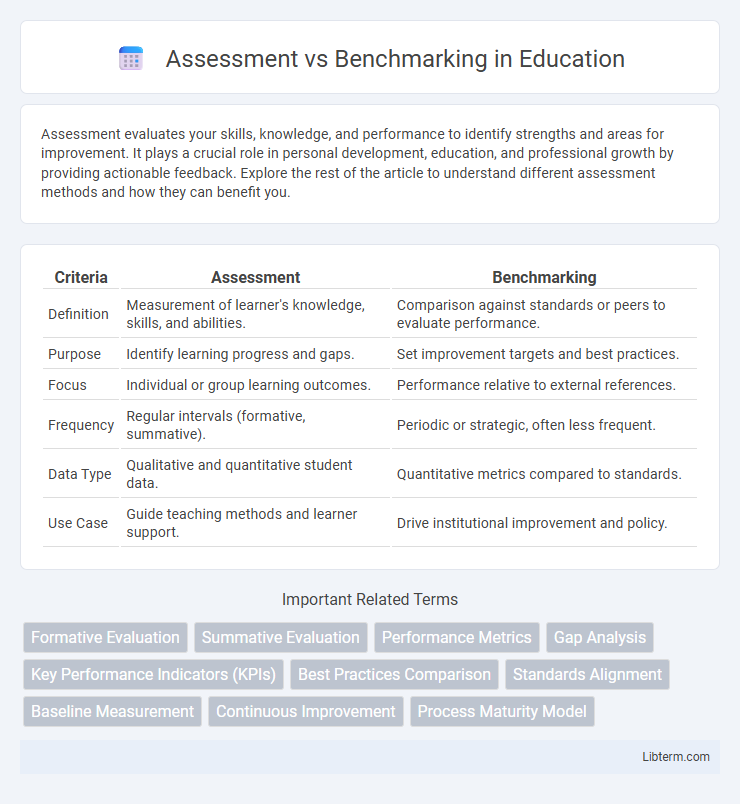
| Criteria | Assessment | Benchmarking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measurement of learner's knowledge, skills, and abilities. | Comparison against standards or peers to evaluate performance. |
| Purpose | Identify learning progress and gaps. | Set improvement targets and best practices. |
| Focus | Individual or group learning outcomes. | Performance relative to external references. |
| Frequency | Regular intervals (formative, summative). | Periodic or strategic, often less frequent. |
| Data Type | Qualitative and quantitative student data. | Quantitative metrics compared to standards. |
| Use Case | Guide teaching methods and learner support. | Drive institutional improvement and policy. |
Understanding Assessment and Benchmarking
Assessment involves evaluating individual or organizational performance against predefined criteria to identify strengths and areas for improvement. Benchmarking compares these performance metrics with industry standards or competitors to set realistic goals and drive continuous improvement. Understanding assessment focuses on measuring internal capabilities, while benchmarking emphasizes external comparison for strategic enhancement.
Key Differences Between Assessment and Benchmarking
Assessment measures current performance levels by evaluating specific criteria within an organization or process, providing a snapshot of strengths and weaknesses. Benchmarking compares these performance metrics against industry standards or competitors to identify gaps and best practices for improvement. While assessment is inward-focused and diagnostic, benchmarking is outward-focused and strategic, aimed at driving continuous enhancement.
Purpose and Objectives of Assessments
Assessments primarily aim to evaluate individual or organizational performance by identifying strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement, guiding targeted development efforts. Their objectives include measuring knowledge, skills, or processes against predefined criteria to support decision-making and enhance effectiveness. Unlike benchmarking, which compares performance against external standards or competitors, assessments focus on internal evaluation for growth and quality assurance.
Purpose and Objectives of Benchmarking
Benchmarking serves to identify best practices and performance standards by comparing processes and outcomes against industry leaders, aiming to drive continuous improvement and competitive advantage. Its primary objective is to analyze gaps in performance, set realistic targets, and implement strategies that enhance efficiency and effectiveness. Assessment, in contrast, focuses on evaluating current performance levels without necessarily providing external comparisons or actionable improvement plans.
Types of Assessments in Organizations
Organizations utilize various types of assessments, including formative assessments aimed at ongoing performance evaluation and summative assessments that provide comprehensive reviews after project completion or fiscal periods. Diagnostic assessments identify gaps and potential areas for improvement, supporting targeted development strategies. Meanwhile, benchmarking compares organizational processes and performance metrics against industry standards or competitors to establish best practices and drive continuous improvement.
Types of Benchmarking Techniques
Assessment evaluates current processes or performance levels to identify strengths and weaknesses, while benchmarking compares these metrics against industry standards or best practices. Types of benchmarking techniques include internal benchmarking, which compares processes within the same organization; competitive benchmarking, focusing on direct competitors' performance; functional benchmarking, analyzing similar functions across different industries; and generic benchmarking, which looks at broader business processes regardless of industry. Each technique helps organizations identify gaps and implement improvements based on data-driven comparisons.
Methodologies: Assessment vs Benchmarking
Assessment methodologies focus on evaluating current processes, performance, or skills using qualitative and quantitative data to identify strengths and weaknesses within an organization. Benchmarking methodologies involve comparing these internal metrics against industry standards or best practices to understand competitive positioning and identify improvement opportunities. Both approaches utilize data collection and analysis but differ in scope; assessments are introspective evaluations, while benchmarking is external comparison-driven.
Benefits of Assessment and Benchmarking
Assessment provides a comprehensive evaluation of current performance, identifying strengths and areas for improvement to guide targeted development. Benchmarking enables comparison against industry standards or competitors, fostering strategic insights that drive operational excellence and innovation. Combining both approaches enhances decision-making by aligning internal capabilities with external best practices, accelerating growth and competitiveness.
Challenges in Implementing Assessment and Benchmarking
Implementing assessment and benchmarking often faces challenges such as data inconsistency, which hinders accurate comparison across departments or organizations. Limited resources and lack of expertise impede the effective collection, analysis, and interpretation of performance metrics. Resistance to change and insufficient stakeholder engagement can further obstruct the successful adoption of these evaluative processes.
Best Practices for Integrating Assessment and Benchmarking
Integrating assessment and benchmarking involves aligning internal performance evaluations with external industry standards to identify gaps and opportunities for improvement. Best practices include establishing clear metrics, using data-driven analysis to compare organizational outcomes against top competitors, and continuously refining processes based on benchmarking insights. Effective integration fosters strategic decision-making, driving enhanced efficiency and competitive advantage.
Assessment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com