Holistic learning integrates emotional, social, and cognitive experiences to enhance retention and understanding. It emphasizes connecting concepts across subjects, encouraging deeper engagement and meaningful application. Explore the rest of the article to discover how holistic learning can transform your educational journey.
Table of Comparison
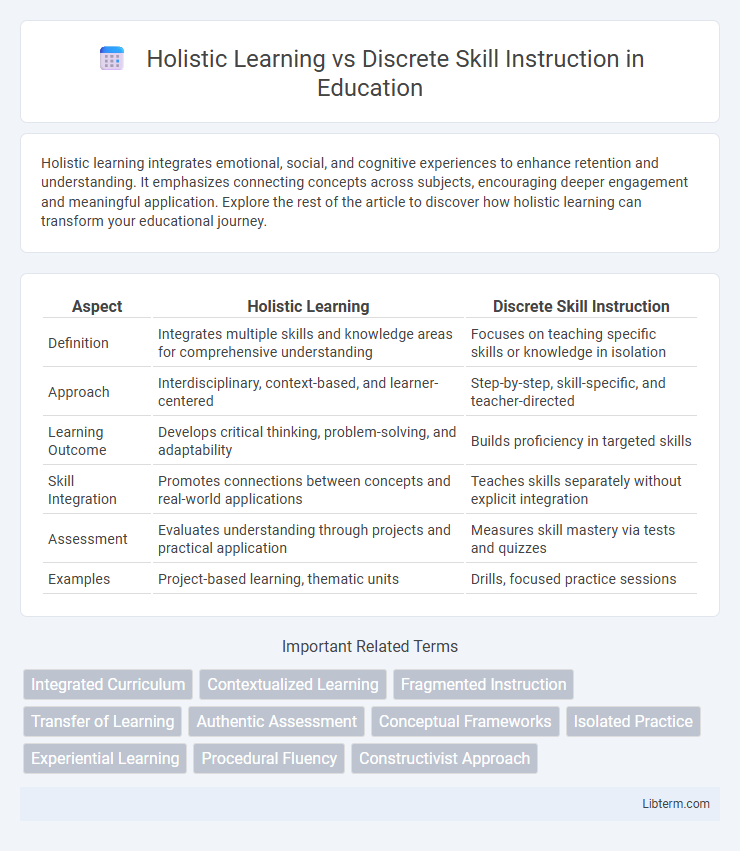
| Aspect | Holistic Learning | Discrete Skill Instruction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integrates multiple skills and knowledge areas for comprehensive understanding | Focuses on teaching specific skills or knowledge in isolation |
| Approach | Interdisciplinary, context-based, and learner-centered | Step-by-step, skill-specific, and teacher-directed |
| Learning Outcome | Develops critical thinking, problem-solving, and adaptability | Builds proficiency in targeted skills |
| Skill Integration | Promotes connections between concepts and real-world applications | Teaches skills separately without explicit integration |
| Assessment | Evaluates understanding through projects and practical application | Measures skill mastery via tests and quizzes |
| Examples | Project-based learning, thematic units | Drills, focused practice sessions |
Introduction to Holistic Learning and Discrete Skill Instruction
Holistic learning integrates multiple skills and concepts simultaneously to foster deeper understanding and real-world application, emphasizing connections and comprehensive knowledge building. Discrete skill instruction isolates specific abilities or tasks, promoting focused practice and mastery through repetition and drills. Balancing holistic approaches with targeted skill instruction optimizes cognitive development and skill acquisition in educational settings.
Defining Holistic Learning Approaches
Holistic learning approaches emphasize integrating multiple skills and concepts simultaneously, fostering deeper understanding and real-world application by connecting knowledge across disciplines. This method contrasts with discrete skill instruction, which isolates specific abilities for focused practice and incremental mastery. Research highlights holistic learning's effectiveness in promoting cognitive flexibility, critical thinking, and long-term retention through context-rich experiences.
Understanding Discrete Skill Instruction Methods
Discrete skill instruction methods emphasize breaking down complex tasks into smaller, manageable components to facilitate focused practice and mastery of individual skills. Techniques such as direct instruction, step-by-step modeling, and repeated drills enable learners to acquire specific abilities with clarity and precision. This approach is particularly effective in contexts requiring measurable skill acquisition and incremental learning progress.
Key Differences Between Holistic and Discrete Instruction
Holistic learning emphasizes understanding entire concepts and their interconnections, fostering deep comprehension and critical thinking, whereas discrete skill instruction targets specific abilities through focused practice and repetition. Holistic methods integrate multiple skills simultaneously within real-world contexts, enhancing adaptability and application, while discrete instruction isolates individual skills for step-by-step mastery. The key difference lies in the scope and integration of learning, with holistic instruction promoting a broad, interconnected knowledge base and discrete instruction emphasizing precision and incremental skill acquisition.
Cognitive Benefits of Holistic Learning
Holistic learning integrates multiple cognitive processes by connecting concepts across disciplines, enhancing memory retention and critical thinking skills. This approach stimulates neural networks more effectively than discrete skill instruction, promoting deeper understanding and flexible problem-solving abilities. Cognitive benefits include improved creativity, better information synthesis, and long-term mastery of complex tasks.
Advantages of Discrete Skill Instruction
Discrete skill instruction offers precise targeting of specific competencies, enhancing focused mastery and measurable progress in subjects such as mathematics and language acquisition. It supports structured learning pathways, enabling efficient identification and remediation of weaknesses through step-by-step skill development. This method facilitates standardized assessment, ensuring consistency and clarity in evaluating student performance and outcomes.
When to Use Holistic Learning in Education
Holistic learning is most effective in education when fostering critical thinking, creativity, and real-world problem-solving skills that require integrating multiple concepts and perspectives. It suits interdisciplinary subjects and project-based learning environments where students benefit from understanding connections rather than memorizing isolated facts. Employ holistic approaches during early education stages and skill development phases to cultivate deeper comprehension and long-term retention.
Situations Favoring Discrete Skill Instruction
Discrete skill instruction is most effective in situations requiring precise mastery of individual components, such as learning mathematical operations, phonics in early reading, or technical tasks in vocational training. This approach promotes focused practice and immediate feedback, enabling learners to develop accuracy and automaticity in foundational skills. Environments demanding clear, measurable progress and skill acquisition, like test preparation or procedural training, particularly favor discrete skill instruction.
Integrating Holistic and Discrete Approaches
Integrating holistic learning with discrete skill instruction enhances cognitive development by combining contextual understanding with targeted practice, fostering deeper mastery of complex concepts and precise skill execution. Research indicates that students exposed to both approaches demonstrate improved problem-solving abilities and adaptability across disciplines, as holistic methods promote meaningful connections while discrete tasks build foundational competencies. Educational frameworks that blend immersive thematic units with isolated skill drills optimize retention and application, resulting in balanced and versatile learners.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Method for Optimal Learning
Holistic learning fosters deeper understanding by integrating knowledge across contexts, while discrete skill instruction targets specific competencies for focused mastery. Optimal learning outcomes depend on balancing these methods to address individual needs and learning objectives. Educators should assess goals, content complexity, and learner preferences to select the most effective approach.
Holistic Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com