A subject-based curriculum focuses on organizing education around specific disciplines such as mathematics, science, and history, promoting deep knowledge in each area. This approach helps students build a strong foundation by concentrating on core subjects, enhancing critical thinking and expertise. Discover how adopting a subject-based curriculum can benefit your learning experience by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
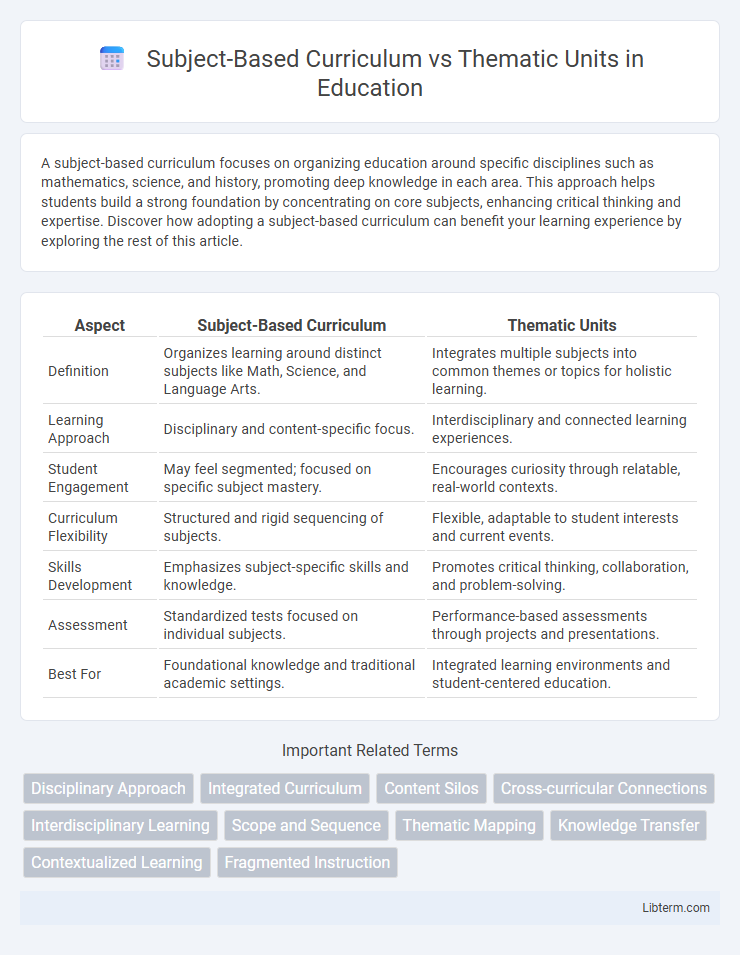
| Aspect | Subject-Based Curriculum | Thematic Units |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Organizes learning around distinct subjects like Math, Science, and Language Arts. | Integrates multiple subjects into common themes or topics for holistic learning. |
| Learning Approach | Disciplinary and content-specific focus. | Interdisciplinary and connected learning experiences. |
| Student Engagement | May feel segmented; focused on specific subject mastery. | Encourages curiosity through relatable, real-world contexts. |
| Curriculum Flexibility | Structured and rigid sequencing of subjects. | Flexible, adaptable to student interests and current events. |
| Skills Development | Emphasizes subject-specific skills and knowledge. | Promotes critical thinking, collaboration, and problem-solving. |
| Assessment | Standardized tests focused on individual subjects. | Performance-based assessments through projects and presentations. |
| Best For | Foundational knowledge and traditional academic settings. | Integrated learning environments and student-centered education. |
Introduction to Curriculum Design Approaches
Subject-based curriculum organizes learning around distinct disciplines such as math, science, or history, promoting in-depth subject mastery and clear content progression. Thematic units integrate multiple subjects around a central theme, fostering connections across disciplines and enhancing critical thinking and engagement. Curriculum design approaches must consider educational goals, student needs, and content coherence when choosing between subject-based structure and thematic integration.
Defining Subject-Based Curriculum
Subject-based curriculum organizes educational content around distinct disciplines such as mathematics, science, language arts, and social studies, providing a structured framework for sequential knowledge acquisition. This approach emphasizes in-depth mastery of subject-specific skills and concepts to build a strong foundational expertise. By separating content into discrete subjects, it enables targeted assessments and systematic progression within each academic domain.
Understanding Thematic Units
Thematic units organize curriculum around central themes that integrate multiple subject areas, promoting deeper understanding and real-world connections. This approach encourages students to apply knowledge across disciplines such as science, literacy, and social studies, enhancing critical thinking and engagement. By focusing on meaningful themes, thematic units facilitate holistic learning experiences that foster creativity and collaboration.
Key Differences Between Subject-Based and Thematic Curricula
Subject-based curricula organize learning content around distinct disciplines such as math, science, and history, emphasizing in-depth knowledge and skill development within each subject area. Thematic units integrate multiple subjects through common themes or big ideas, promoting interdisciplinary connections and real-world applications. Key differences include the focus on isolated subject mastery in subject-based curricula versus the holistic, context-driven approach of thematic units that foster critical thinking and synthesis across topics.
Advantages of Subject-Based Curriculum
Subject-Based Curriculum offers clear advantages such as in-depth knowledge acquisition and specialization in specific academic disciplines, enhancing students' expertise and critical thinking skills. It promotes structured learning with well-defined objectives and assessment criteria, ensuring consistent academic standards across subjects. This approach prepares students effectively for higher education and specialized career paths by fostering a strong foundation in core subjects like mathematics, science, and literature.
Benefits of Thematic Units
Thematic units promote interdisciplinary learning by integrating multiple subjects around a central theme, enhancing student engagement and making lessons more relevant to real-world contexts. They foster deeper critical thinking and creativity by encouraging connections across concepts and allowing students to explore topics more holistically. This approach supports differentiated instruction, addressing diverse learning styles and promoting collaboration through shared projects and discussions.
Challenges of Each Curriculum Model
Subject-based curriculum faces challenges such as compartmentalized learning, where students struggle to see connections across different disciplines, leading to limited critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Thematic units often encounter difficulties in ensuring comprehensive content coverage and maintaining academic rigor, as the integration of themes may dilute subject-specific depth. Both models require careful balancing of student engagement and curriculum standards, posing challenges for educators in lesson planning and assessment design.
Impact on Student Learning and Engagement
Subject-Based Curriculum structures learning by isolating disciplines, fostering deep knowledge in specific areas like mathematics and science, which enhances critical thinking skills within those domains. Thematic Units integrate multiple subjects around central themes, increasing student engagement through relevant, real-world connections that promote interdisciplinary understanding and creativity. Research indicates that thematic approaches often lead to higher motivation and better retention, while subject-based methods support mastery of foundational content and skill development.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Classroom
Selecting the right educational framework depends on your classroom goals and student needs. Subject-Based Curriculum offers structured content mastery in discrete disciplines, ideal for reinforcing foundational skills in math, science, and language arts. Thematic Units integrate multiple subjects around central themes, promoting critical thinking and real-world connections, which suits diverse learning styles and encourages deeper engagement.
Conclusion: Balancing Curriculum Models for Effective Education
Balancing subject-based curriculum and thematic units fosters a comprehensive educational approach, enhancing student engagement and knowledge retention. Integrating focused subject expertise with interconnected thematic learning supports diverse cognitive skills and real-world application. Effective education emerges through flexible curriculum design that aligns academic standards with meaningful, context-rich experiences.
Subject-Based Curriculum Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com