Credit transfer allows students to apply previously earned academic credits toward a new degree program, saving time and reducing educational costs. Understanding the specific policies and limits of credit transfer at your institution can maximize your academic progress. Explore the article to learn how to navigate credit transfer effectively and make the most of your prior learning.
Table of Comparison
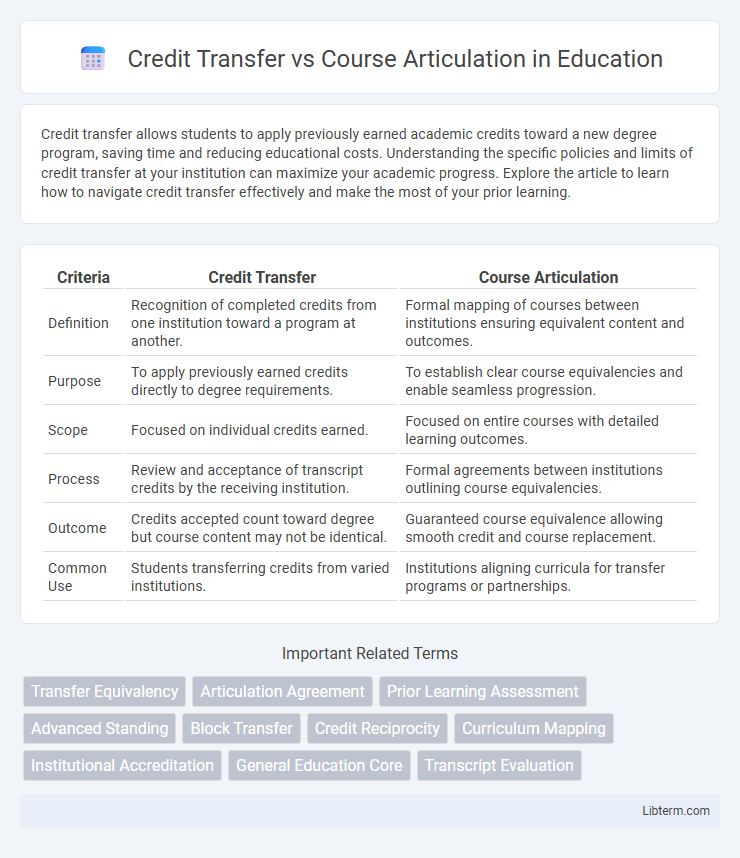
| Criteria | Credit Transfer | Course Articulation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Recognition of completed credits from one institution toward a program at another. | Formal mapping of courses between institutions ensuring equivalent content and outcomes. |
| Purpose | To apply previously earned credits directly to degree requirements. | To establish clear course equivalencies and enable seamless progression. |
| Scope | Focused on individual credits earned. | Focused on entire courses with detailed learning outcomes. |
| Process | Review and acceptance of transcript credits by the receiving institution. | Formal agreements between institutions outlining course equivalencies. |
| Outcome | Credits accepted count toward degree but course content may not be identical. | Guaranteed course equivalence allowing smooth credit and course replacement. |
| Common Use | Students transferring credits from varied institutions. | Institutions aligning curricula for transfer programs or partnerships. |
Understanding Credit Transfer: Definition and Purpose
Credit transfer enables students to apply previously earned academic credits from one institution toward requirements at another, facilitating educational continuity and reducing redundancy. It primarily serves to recognize and validate past coursework, ensuring that students do not repeat similar courses and can progress efficiently through their degree programs. Understanding credit transfer involves grasping its role in academic mobility and degree acceleration within higher education systems.
What is Course Articulation?
Course articulation is the formal process that establishes equivalency between courses offered by different institutions, enabling students to receive credit for completed coursework when transferring schools. It involves evaluating course content, learning outcomes, and credit hours to ensure alignment and maintain academic standards. This system facilitates smoother transitions for students by clearly defining which courses satisfy specific program requirements at the receiving institution.
Key Differences Between Credit Transfer and Course Articulation
Credit transfer allows students to receive academic credit for courses completed at one institution when enrolling at another, primarily focusing on credit equivalency without detailed course content comparison. Course articulation involves a comprehensive evaluation of course learning outcomes, ensuring specific courses from one institution meet the curriculum requirements of another before granting credit. The key difference lies in credit transfer emphasizing credit recognition broadly, while course articulation ensures precise content alignment for seamless academic progression.
How Credit Transfer Works in Higher Education
Credit transfer in higher education allows students to apply previously earned academic credits from one institution toward the requirements of a degree program at another institution, streamlining the path to graduation. The process involves evaluating the equivalency of courses, credit hours, and learning outcomes based on institutional policies and accreditation standards. Transferable credits often depend on course content relevance, grade minimums, and formal articulation agreements between universities and colleges.
The Course Articulation Process Explained
The course articulation process involves evaluating and matching courses from different institutions to establish equivalency, ensuring transferred credits meet program requirements accurately. Academic advisors and articulation officers systematically analyze course content, learning outcomes, and credit hours to determine compatibility. This process guarantees students receive appropriate credit recognition, facilitating a smooth transition without redundant coursework.
Common Challenges in Credit Transfer
Common challenges in credit transfer include discrepancies in course content, varying grading standards, and differences in institutional policies, which often result in non-equivalent credits. Students frequently face delays due to lack of standardized evaluation criteria and insufficient communication between sending and receiving institutions. These issues contribute to credit loss, extended time to degree completion, and increased educational costs.
Benefits of Course Articulation for Students
Course articulation ensures a clear, formal agreement between institutions guaranteeing that specific courses fulfill program requirements, thereby reducing the risk of credit loss for students. It accelerates degree completion by allowing seamless acceptance of pre-approved coursework, minimizing administrative hurdles and duplicated efforts. Students benefit from enhanced academic planning and confidence that their prior learning aligns with their current educational trajectory, optimizing time and financial resources.
Institutional Policies Impacting Credit Transfer
Institutional policies significantly impact credit transfer by determining the criteria for evaluating and accepting external coursework, affecting students' academic progress and graduation timelines. Clear articulation agreements streamline credit recognition by establishing predefined equivalencies between courses across institutions, reducing administrative barriers and inconsistencies. Variations in policy, including GPA requirements, course content alignment, and accreditation standards, directly influence the ease and success rate of credit transfer processes.
Tips for a Smooth Credit Transfer or Course Articulation
Ensure thorough evaluation of course syllabi and institutional policies to align course content accurately for credit transfer or course articulation. Maintain clear communication between sending and receiving institutions to verify credit equivalencies and prevent academic discrepancies. Organize all academic records, transcripts, and prerequisite documentation meticulously to facilitate a seamless transfer process.
Frequently Asked Questions: Credit Transfer vs Course Articulation
Credit transfer involves accepting previously earned academic credits from one institution to count toward a degree at another, streamlining the transfer process and reducing time to graduation. Course articulation refers to formal agreements that specify which courses from one institution are equivalent to courses at another, ensuring clear, pre-approved credit recognition. Frequently asked questions often address differences in eligibility, application procedures, and how credits affect degree requirements.
Credit Transfer Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com