Assessment-centered approaches prioritize evaluating learners' understanding and skills to guide effective instruction and promote meaningful learning outcomes. This method emphasizes continuous feedback and the use of assessments to tailor educational experiences to individual needs. Explore the rest of the article to discover how assessment-centered strategies can enhance your teaching and learning processes.
Table of Comparison
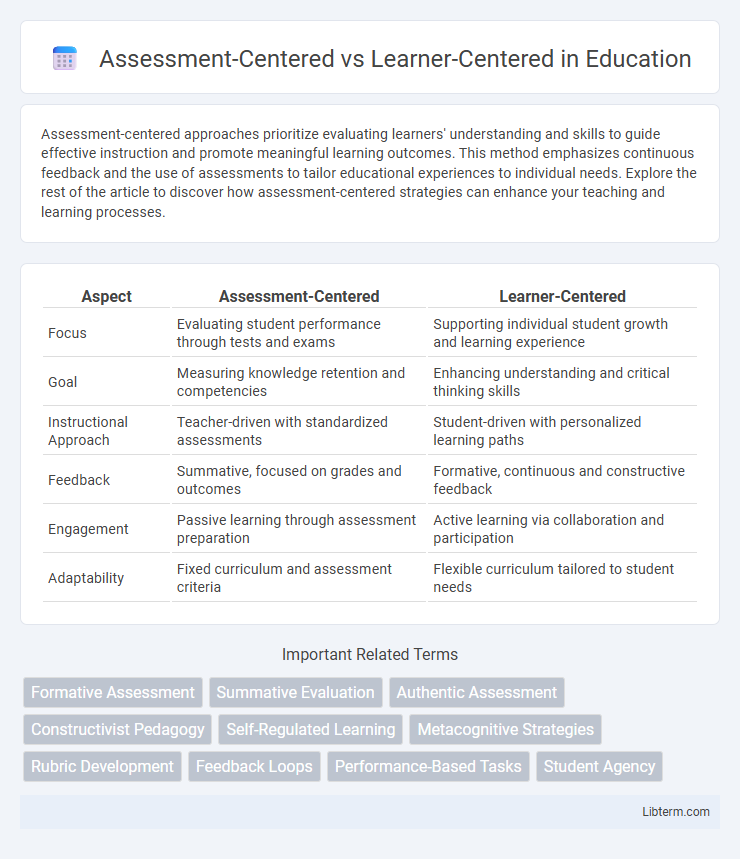
| Aspect | Assessment-Centered | Learner-Centered |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Evaluating student performance through tests and exams | Supporting individual student growth and learning experience |
| Goal | Measuring knowledge retention and competencies | Enhancing understanding and critical thinking skills |
| Instructional Approach | Teacher-driven with standardized assessments | Student-driven with personalized learning paths |
| Feedback | Summative, focused on grades and outcomes | Formative, continuous and constructive feedback |
| Engagement | Passive learning through assessment preparation | Active learning via collaboration and participation |
| Adaptability | Fixed curriculum and assessment criteria | Flexible curriculum tailored to student needs |
Understanding Assessment-Centered and Learner-Centered Approaches
Assessment-centered approaches emphasize the evaluation of student performance through standardized tests and measurable outcomes to ensure alignment with curriculum standards. Learner-centered approaches prioritize individual learning needs, fostering active engagement and personalized feedback to support deeper understanding and skill development. Understanding these frameworks helps educators balance objective assessment metrics with tailored pedagogical strategies that promote both accountability and student growth.
Core Principles of Assessment-Centered Education
Assessment-centered education prioritizes continuous, data-driven feedback to inform instruction and enhance learner performance through formative assessments and performance tasks. Core principles emphasize alignment between learning objectives, instructional activities, and assessments to ensure validity and reliability in measuring student understanding. This approach promotes metacognitive skills by encouraging students to self-assess and reflect on their progress, fostering deeper engagement and mastery.
Key Features of Learner-Centered Classrooms
Learner-centered classrooms emphasize active student engagement, personalized learning paths, and collaborative activities that foster critical thinking and problem-solving skills. These environments prioritize students' prior knowledge, interests, and learning styles to enhance intrinsic motivation and autonomy in the learning process. Technology integration and formative assessments support real-time feedback, enabling continuous adjustment of instruction to meet diverse learner needs.
Comparing Assessment-Centered and Learner-Centered Strategies
Assessment-centered strategies prioritize evaluating student performance through tests, quizzes, and standardized assessments to measure knowledge acquisition and skill development. Learner-centered approaches emphasize personalized learning experiences, adapting instruction to individual student needs, interests, and pace to foster deeper engagement and intrinsic motivation. Comparing the two reveals that assessment-centered methods focus on quantifiable outcomes, while learner-centered strategies center on holistic development and continuous feedback.
Benefits of Assessment-Centered Learning
Assessment-centered learning enhances educational outcomes by providing continuous feedback that helps learners identify strengths and areas for improvement. This approach promotes active engagement and self-regulation, enabling students to take ownership of their learning process. Research indicates that assessment-centered strategies improve knowledge retention and critical thinking skills more effectively than traditional methods.
Advantages of Learner-Centered Approaches
Learner-centered approaches promote active engagement, fostering deeper understanding and retention by tailoring instruction to individual needs and learning styles. This method encourages critical thinking and self-regulation, empowering students to take ownership of their learning process. Enhanced motivation and collaboration are also benefits, as learners feel more connected and invested in meaningful, relevant tasks.
Challenges in Implementing Assessment-Centered Models
Implementing assessment-centered models often faces challenges such as aligning assessments with learning objectives, ensuring reliability and validity in diverse educational contexts, and managing the increased workload for educators in designing and grading frequent, formative assessments. These models require substantial institutional support, including professional development and technological infrastructure, to effectively gather and analyze assessment data for student feedback. Resistance from both teachers and students accustomed to traditional evaluation methods can also hinder the adoption of assessment-centered approaches.
Barriers to Adopting Learner-Centered Education
Barriers to adopting learner-centered education include resistance from educators accustomed to traditional assessment-centered models that prioritize standardized testing and uniform benchmarks. Institutional constraints such as rigid curricula, limited resources, and insufficient professional development hinder the implementation of personalized, active learning strategies. Furthermore, assessment-centered systems often emphasize summative evaluation, reducing opportunities for formative feedback essential in learner-centered environments.
Integrating Both Approaches for Effective Learning
Integrating assessment-centered and learner-centered approaches enhances effective learning by aligning evaluation methods with student needs, promoting active engagement and personalized feedback. Assessment-centered strategies provide clear learning objectives and measurable outcomes, while learner-centered practices foster autonomy and adaptability in diverse learning environments. Combining both ensures comprehensive understanding and continuous improvement, driving higher academic achievement and motivation.
Future Trends in Educational Approaches
Future trends in educational approaches emphasize a shift from assessment-centered models, which prioritize standardized testing and performance metrics, toward learner-centered frameworks that focus on personalized learning, critical thinking, and adaptive technologies. Emerging innovations include AI-driven assessments that tailor feedback to individual student needs and immersive learning environments promoting engagement and creativity. Data analytics and competency-based education will increasingly support continuous, formative evaluation rather than one-time high-stakes exams, fostering lifelong learning skills.
Assessment-Centered Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com