Criterion-referenced assessment measures a student's performance against a fixed set of standards or learning objectives rather than comparing them to peers. This approach helps identify specific knowledge gaps and mastery levels, making it ideal for tailored instruction and targeted improvement. Discover how criterion-referenced assessments can enhance your evaluation strategies by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
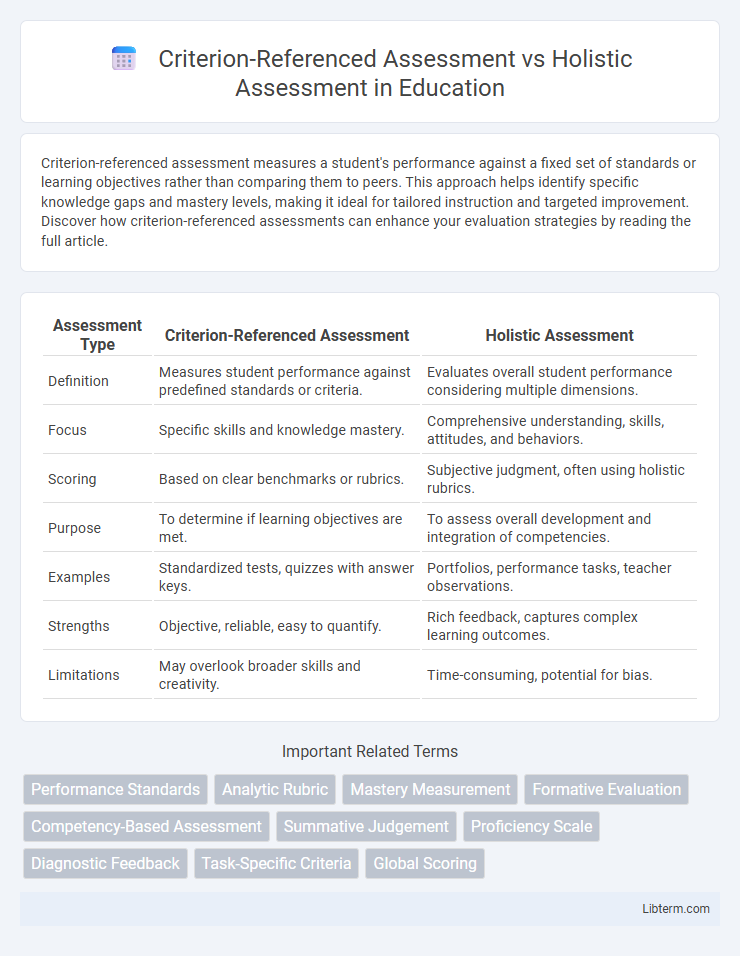
| Assessment Type | Criterion-Referenced Assessment | Holistic Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measures student performance against predefined standards or criteria. | Evaluates overall student performance considering multiple dimensions. |
| Focus | Specific skills and knowledge mastery. | Comprehensive understanding, skills, attitudes, and behaviors. |
| Scoring | Based on clear benchmarks or rubrics. | Subjective judgment, often using holistic rubrics. |
| Purpose | To determine if learning objectives are met. | To assess overall development and integration of competencies. |
| Examples | Standardized tests, quizzes with answer keys. | Portfolios, performance tasks, teacher observations. |
| Strengths | Objective, reliable, easy to quantify. | Rich feedback, captures complex learning outcomes. |
| Limitations | May overlook broader skills and creativity. | Time-consuming, potential for bias. |
Introduction to Assessment Types
Criterion-referenced assessment evaluates a learner's performance against predefined specific criteria or learning standards, providing clear insights into mastery of particular skills or knowledge. Holistic assessment, in contrast, examines overall performance by considering the general quality, coherence, and integration of various competencies in a single, unified judgment. Both assessment types play critical roles in education by offering distinct perspectives on student learning and achievement.
Defining Criterion-Referenced Assessment
Criterion-referenced assessment evaluates a learner's performance against a predetermined set of objectives or criteria, rather than comparing scores with peers. This assessment method measures specific skills or knowledge by determining whether each criterion or learning goal has been met. It provides clear benchmarks for mastery, enabling targeted feedback and instructional adjustments to support individual learning progress.
Understanding Holistic Assessment
Holistic assessment evaluates a learner's overall performance by considering a comprehensive set of criteria, integrating cognitive, emotional, and social aspects rather than isolated skills. This approach emphasizes understanding student progress in real-world contexts, promoting deeper learning and critical thinking. By focusing on the synthesis of knowledge and abilities, holistic assessment supports personalized feedback and fosters lifelong learning habits.
Key Differences Between the Two Approaches
Criterion-referenced assessment evaluates student performance based on specific learning objectives or criteria, providing detailed feedback on individual skill mastery. Holistic assessment, in contrast, judges overall performance by considering the entire work or behavior as a whole, emphasizing general competence and integrated understanding. The key difference lies in criterion-referenced assessment's focus on measurable components, while holistic assessment centers on broad, qualitative evaluation.
Advantages of Criterion-Referenced Assessment
Criterion-referenced assessment offers clear advantages by measuring student performance against specific learning objectives, ensuring precise identification of mastery levels and targeted feedback for improvement. This method promotes consistent evaluation standards, reducing subjectivity and enabling educators to tailor instruction to individual needs effectively. Criterion-referenced assessments also enhance transparency in grading, facilitating better communication between teachers, students, and parents regarding academic progress.
Benefits of Holistic Assessment
Holistic assessment offers a comprehensive evaluation of student performance by considering multiple dimensions such as critical thinking, creativity, and collaboration, rather than isolating specific skills or criteria. This approach supports personalized learning by recognizing individual strengths and areas for growth, fostering deeper understanding and self-reflection. Research indicates holistic assessments improve student engagement and motivation, leading to enhanced long-term academic success and skill development.
Limitations of Each Assessment Type
Criterion-referenced assessment may limit student creativity and fail to capture complex learning processes by focusing solely on specific objectives and predefined criteria. Holistic assessment can be subjective and inconsistent, as it relies on overall impressions rather than measurable standards, leading to potential bias and reduced reliability. Both assessment types face challenges in balancing objectivity, comprehensiveness, and fairness in evaluating learner performance.
Application Scenarios and Use Cases
Criterion-referenced assessment is ideal for evaluating individual performance against specific learning objectives, commonly used in educational settings for standardized testing and skill mastery verification. Holistic assessment suits scenarios requiring overall judgment of complex abilities, such as art evaluations or comprehensive writing assessments, emphasizing the integration of multiple skills and creativity. Use cases for criterion-referenced assessments include certification exams and formative assessments, while holistic assessments are effectively applied in portfolio reviews and performance-based evaluations.
Selecting the Appropriate Assessment Method
Criterion-referenced assessment measures student performance against predefined learning objectives, making it ideal for identifying specific skill mastery and guiding targeted instruction. Holistic assessment evaluates overall learner capabilities and performance quality, best suited for assessing complex tasks and integrative skills. Selecting the appropriate assessment method depends on the instructional goals, with criterion-referenced preferred for clear skill benchmarks and holistic favored for comprehensive evaluations.
Conclusion and Recommendations
Criterion-referenced assessment provides precise measurement of specific learning objectives, ensuring students meet predefined standards, while holistic assessment offers a broader evaluation of overall learner performance and critical thinking. Combining both approaches can enhance instructional effectiveness by balancing detailed criterion-based feedback with comprehensive judgment of student abilities. Implementing integrated assessment strategies that align with curricular goals is recommended to optimize student learning outcomes and support personalized education pathways.
Criterion-Referenced Assessment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com