Distance learning offers flexible education options that allow you to study from anywhere, adapting to your schedule and pace. It integrates advanced technology and interactive platforms to create engaging and accessible content for diverse learners. Explore the article to discover how distance learning can transform your educational experience.
Table of Comparison
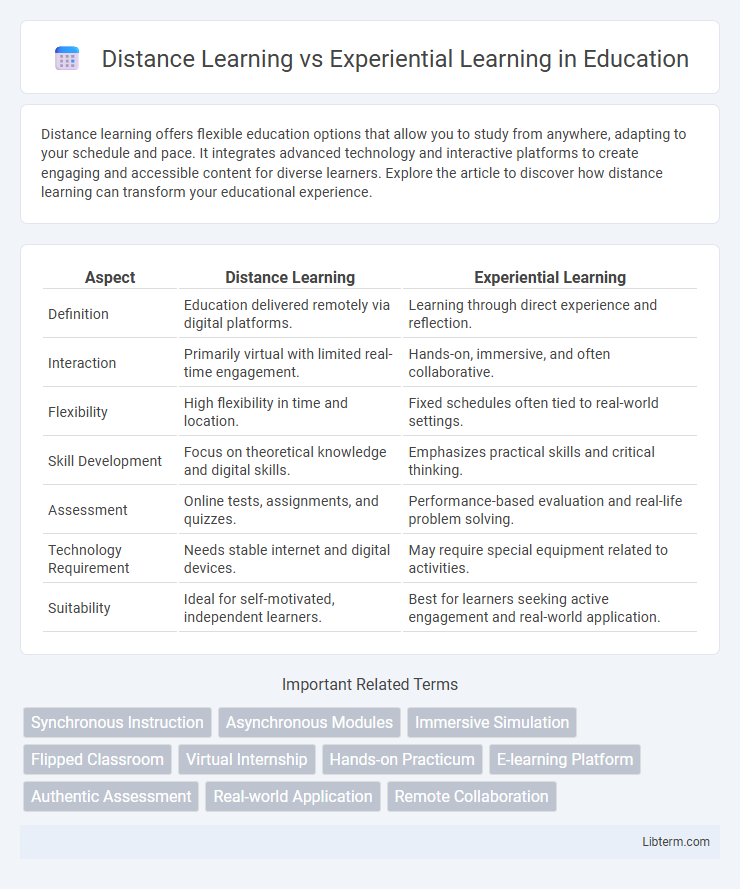
| Aspect | Distance Learning | Experiential Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Education delivered remotely via digital platforms. | Learning through direct experience and reflection. |
| Interaction | Primarily virtual with limited real-time engagement. | Hands-on, immersive, and often collaborative. |
| Flexibility | High flexibility in time and location. | Fixed schedules often tied to real-world settings. |
| Skill Development | Focus on theoretical knowledge and digital skills. | Emphasizes practical skills and critical thinking. |
| Assessment | Online tests, assignments, and quizzes. | Performance-based evaluation and real-life problem solving. |
| Technology Requirement | Needs stable internet and digital devices. | May require special equipment related to activities. |
| Suitability | Ideal for self-motivated, independent learners. | Best for learners seeking active engagement and real-world application. |
Introduction to Distance Learning and Experiential Learning
Distance learning leverages digital platforms and online resources to provide flexible education accessible from anywhere, promoting self-paced study and broader reach. Experiential learning emphasizes hands-on activities, real-world experiences, and reflection to deepen understanding and skill acquisition through active participation. Both methods cater to diverse learning preferences, with distance learning prioritizing accessibility and convenience, while experiential learning focuses on immersive, practical engagement.
Key Characteristics of Distance Learning
Distance learning offers flexible scheduling, allowing learners to access course materials and lectures remotely via the internet, accommodating diverse time zones and personal commitments. It leverages digital platforms for content delivery, assessments, and communication, promoting self-paced learning and autonomy. Key characteristics include asynchronous participation, limited physical interaction, and reliance on multimedia tools to facilitate knowledge acquisition.
Core Elements of Experiential Learning
Experiential learning centers on active engagement, reflection, and real-world application, differentiating it from distance learning's reliance on virtual instruction and independent study. Core elements include concrete experience, reflective observation, abstract conceptualization, and active experimentation, enabling learners to internalize knowledge through direct involvement. This hands-on approach fosters deeper understanding and skill development by intertwining practical challenges with critical analysis.
Flexibility and Accessibility Compared
Distance learning offers unparalleled flexibility by enabling students to access coursework anytime and anywhere, accommodating diverse schedules and geographical barriers. Experiential learning, while highly engaging, often requires physical presence and scheduled activities, limiting immediate accessibility for remote or non-traditional learners. Combining the convenience of distance learning with the hands-on nature of experiential education can optimize both flexibility and accessibility in modern educational models.
Engagement and Interactivity in Learning
Distance learning utilizes digital platforms to deliver content, often incorporating multimedia tools and interactive quizzes to enhance student engagement. Experiential learning emphasizes hands-on activities and real-world experiences that foster active participation and deeper cognitive processing. Interactive elements in both methods, such as virtual simulations in distance learning and collaborative projects in experiential learning, significantly boost learner motivation and retention.
Learning Outcomes: Theory vs. Practice
Distance learning emphasizes theoretical knowledge acquisition through structured online modules, enabling flexible access to diverse academic content. Experiential learning prioritizes practical skills development by engaging learners in real-world challenges, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving abilities. Combining both approaches enhances learning outcomes by integrating foundational theory with hands-on experience for comprehensive understanding.
Technology’s Role in Shaping Education
Technology revolutionizes distance learning by providing interactive platforms, virtual classrooms, and real-time assessments that enhance accessibility and engagement for students worldwide. Experiential learning benefits from immersive technologies such as augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR), enabling hands-on practice and simulations in fields like medicine, engineering, and environmental science. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in both modalities offers personalized feedback and adaptive learning paths, driving improved educational outcomes.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Method
Distance learning often faces challenges such as limited student engagement, technological barriers, and reduced opportunities for hands-on practice, which can hinder skill development and real-time interaction. Experiential learning's limitations include high resource requirements, logistical complexities, and the difficulty of scaling in diverse or remote settings. Both methods require strategic adaptation to address their respective constraints while maximizing educational effectiveness.
Suitability for Different Types of Learners
Distance learning suits self-motivated learners who excel in independent study and time management, offering flexibility and access to diverse resources. Experiential learning benefits hands-on, kinesthetic learners who thrive through real-world engagement and active problem-solving, enhancing retention and practical skills. Matching these approaches to learner preferences and goals maximizes educational effectiveness and personal development.
Future Trends in Distance and Experiential Learning
Future trends in distance learning emphasize the integration of AI-powered adaptive platforms and immersive technologies such as virtual reality to create personalized and engaging educational experiences. Experiential learning is increasingly augmented by mixed reality and real-time data analytics, enabling learners to apply skills in simulated environments that mirror real-world scenarios. The convergence of these modalities predicts a hybrid educational landscape where digital convenience and hands-on engagement coalesce to optimize learning outcomes.
Distance Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com