Homeroom serves as a daily gathering point where students receive important announcements, settle administrative tasks, and prepare for the day's academic activities. This brief session fosters a sense of community and helps teachers monitor attendance and address student needs efficiently. Explore the rest of the article to discover how maximizing homeroom time can enhance your overall school experience.
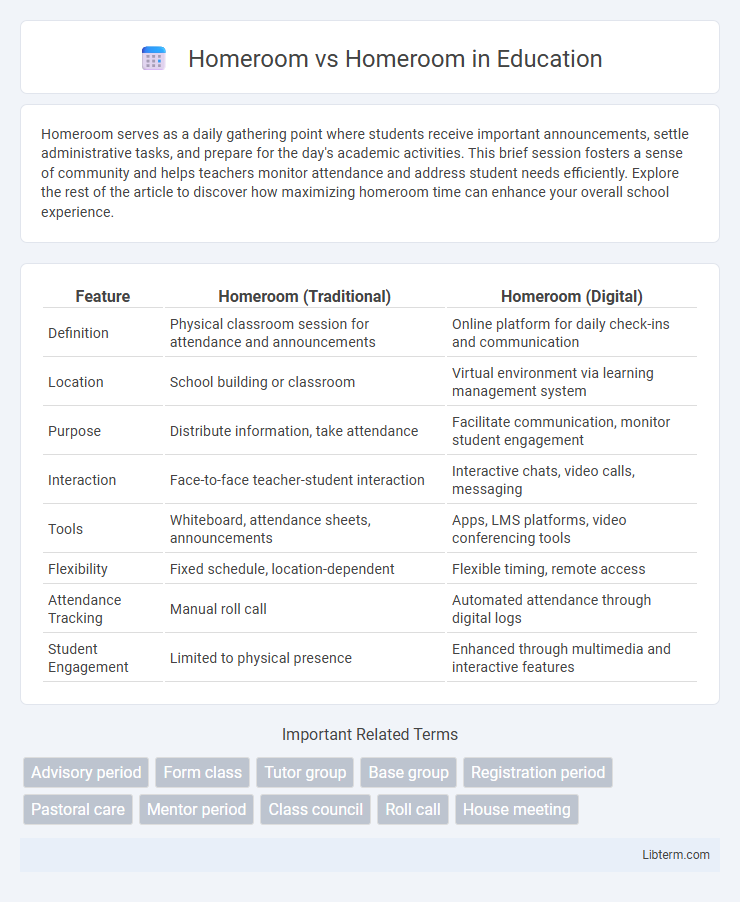
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Homeroom (Traditional) | Homeroom (Digital) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Physical classroom session for attendance and announcements | Online platform for daily check-ins and communication |
| Location | School building or classroom | Virtual environment via learning management system |
| Purpose | Distribute information, take attendance | Facilitate communication, monitor student engagement |
| Interaction | Face-to-face teacher-student interaction | Interactive chats, video calls, messaging |
| Tools | Whiteboard, attendance sheets, announcements | Apps, LMS platforms, video conferencing tools |
| Flexibility | Fixed schedule, location-dependent | Flexible timing, remote access |
| Attendance Tracking | Manual roll call | Automated attendance through digital logs |
| Student Engagement | Limited to physical presence | Enhanced through multimedia and interactive features |
Understanding the Concept of Homeroom
Homeroom serves as a daily gathering space where students receive important announcements, organize materials, and build a classroom community. It functions as both an administrative checkpoint and a social hub, fostering student engagement and timely communication. Understanding homeroom highlights its role in supporting academic routines and enhancing school climate.
Origins and Evolution of Homeroom
Homeroom originated in early 20th century American schools as a daily gathering period for administrative tasks and attendance, evolving from informal student assemblies into a structured time for announcements, distribution of materials, and pastoral care. Over time, its role expanded to include advisory functions, fostering student-teacher relationships and providing academic support tailored to individual student needs. The evolution of homeroom reflects broader educational shifts emphasizing personalized learning environments and the holistic development of students.
Different Models of Homeroom Worldwide
Different models of homerooms vary significantly worldwide, reflecting diverse educational systems and cultural practices. In Japan, homerooms serve as a central daily gathering where teachers handle attendance, disciplinary issues, and emotional support, creating a strong student-teacher bond. In contrast, U.S. homerooms often function primarily for administrative tasks like attendance, with less emphasis on pastoral care, highlighting variations in the holistic roles homerooms play globally.
Primary Functions of a Homeroom
A homeroom primarily serves as a centralized space for administrative tasks such as attendance tracking, distributing announcements, and organizing daily schedules. It provides a consistent environment for student-teacher interaction, fostering community and social-emotional support in primary education. Homerooms also function as a base for academic coordination, enabling teachers to monitor student progress and communicate with parents effectively.
Homeroom Teacher Roles and Responsibilities
Homeroom teachers serve as the primary point of contact between students, parents, and school administration, facilitating communication and fostering a supportive learning environment. Their responsibilities include taking attendance, monitoring student behavior, and addressing individual academic or social needs to ensure overall student well-being. They also coordinate with subject teachers to track progress, assist with administrative tasks, and promote a positive classroom culture that supports student engagement and development.
Student Experience in Homeroom Settings
Student experience in homeroom settings varies significantly between traditional and digital homerooms, with traditional homerooms fostering face-to-face social interaction and personalized teacher support that enhances student engagement and emotional well-being. Digital homerooms offer flexible access to resources and allow for differentiated instruction through technology, though they may challenge the development of peer relationships and real-time communication. Effective homerooms integrate both approaches, leveraging technology for individualized learning while maintaining the community atmosphere critical for student motivation and academic success.
Benefits of Homeroom for School Communities
Homeroom fosters a strong sense of community by providing students with consistent peer groups, which enhances social bonding and peer support. It allows teachers to monitor attendance, distribute important information, and address student needs promptly, promoting a structured and secure learning environment. Regular interaction in homeroom cultivates student accountability and improves communication between staff, students, and families, strengthening overall school community engagement.
Challenges in Homeroom Implementation
Challenges in homeroom implementation include maintaining student engagement and managing diverse student needs within limited time frames. Inconsistent teacher training and unclear objectives contribute to reduced effectiveness and variability in student support. Technology integration and resource allocation also pose significant hurdles, impacting the overall success of homeroom programs.
Homeroom vs. Advisory Programs
Homeroom and advisory programs both provide structured time for student support, but homerooms typically serve administrative functions such as attendance and announcements, while advisory programs focus on personalized guidance, mentoring, and social-emotional learning. Advisory programs often foster stronger student-teacher relationships and promote goal-setting, academic planning, and peer collaboration, enhancing overall student well-being more than homerooms. Schools implementing advisory programs report improved student engagement, motivation, and a supportive learning environment compared to traditional homeroom models.
The Future of the Homeroom Model
The future of the homeroom model centers on personalized learning environments that leverage digital tools to enhance student engagement and teacher-student interaction. Emerging trends emphasize adaptive curricula and integrated technology platforms that transform homerooms into dynamic, collaborative spaces fostering social-emotional development. Data-driven insights and hybrid learning approaches are reshaping homeroom structures to better meet diverse student needs and prepare learners for a rapidly evolving educational landscape.
Homeroom Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com