Time-based progression enhances user engagement by pacing challenges and content according to real-world time intervals, creating a consistent and immersive experience. This mechanic encourages players to return regularly, fostering long-term interaction and satisfaction without feeling rushed. Discover how implementing time-based progression can transform your game's dynamics and keep players invested.
Table of Comparison
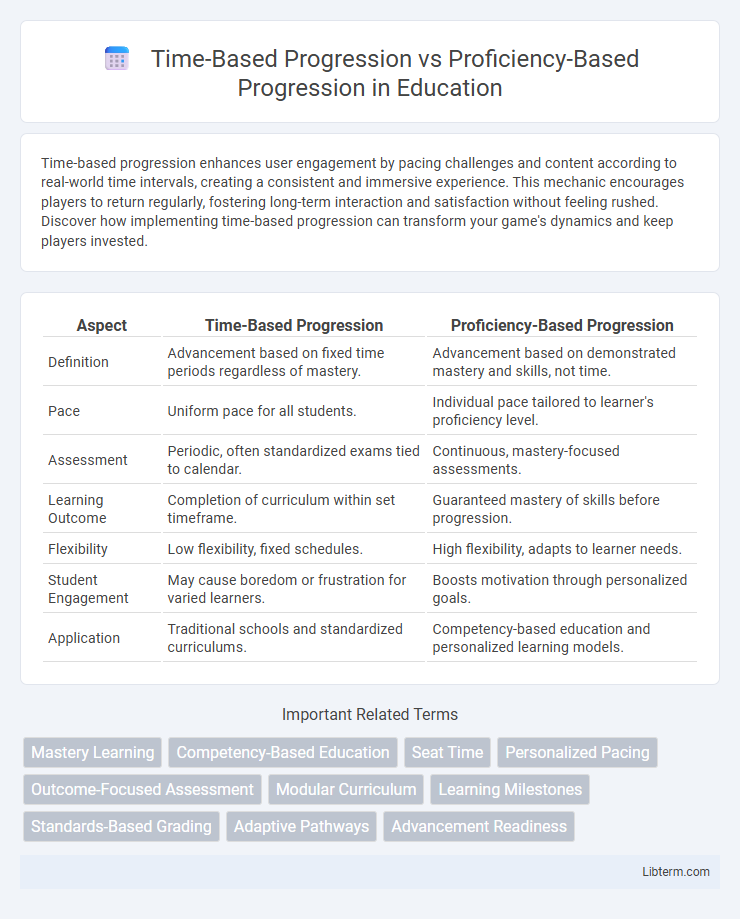
| Aspect | Time-Based Progression | Proficiency-Based Progression |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Advancement based on fixed time periods regardless of mastery. | Advancement based on demonstrated mastery and skills, not time. |
| Pace | Uniform pace for all students. | Individual pace tailored to learner's proficiency level. |
| Assessment | Periodic, often standardized exams tied to calendar. | Continuous, mastery-focused assessments. |
| Learning Outcome | Completion of curriculum within set timeframe. | Guaranteed mastery of skills before progression. |
| Flexibility | Low flexibility, fixed schedules. | High flexibility, adapts to learner needs. |
| Student Engagement | May cause boredom or frustration for varied learners. | Boosts motivation through personalized goals. |
| Application | Traditional schools and standardized curriculums. | Competency-based education and personalized learning models. |
Understanding Time-Based Progression
Time-Based Progression structures education around fixed time intervals, such as semesters or academic years, requiring students to advance after completing set periods regardless of skill mastery. This approach often emphasizes seat time and standardized pacing, potentially leading to gaps in learning if students are not fully proficient before moving forward. Critics argue that it may hinder individualized learning, as it prioritizes schedule over competency development.
Defining Proficiency-Based Progression
Proficiency-Based Progression prioritizes mastery of specific skills and knowledge before advancing, ensuring learners achieve defined competencies regardless of time spent. This approach allows personalized pacing, emphasizing learner understanding and application over seat time. By focusing on measurable outcomes, it supports more effective and targeted educational experiences compared to traditional Time-Based Progression models.
Key Differences Between Time and Proficiency Approaches
Time-based progression structures learning around fixed schedules, where students advance after a set period regardless of skill mastery. Proficiency-based progression requires demonstrating mastery of specific competencies before moving forward, ensuring readiness at each stage. The key difference lies in measurement criteria: time versus demonstrated ability, impacting personalized pacing and learner outcomes.
Historical Context and Evolution
Time-based progression historically became the standard in education systems during the industrial era, emphasizing uniform grade advancement regardless of individual mastery. Proficiency-based progression emerged in the late 20th century as a response to the limitations of fixed timelines, promoting student advancement based on demonstrated competency and skill acquisition. This shift reflects evolving educational philosophies aiming to personalize learning and improve outcomes by accommodating diverse learning paces.
Benefits of Time-Based Progression
Time-based progression ensures a consistent learning schedule, allowing institutions to standardize curriculum delivery and assess students uniformly. This approach supports structured pacing, enabling learners to build foundational knowledge before advancing, which can enhance group collaboration and classroom management. Predictable time frames also facilitate efficient resource allocation and academic planning for educators and administrators.
Advantages of Proficiency-Based Progression
Proficiency-based progression ensures learners advance only after mastering specific skills and knowledge, leading to deeper understanding and retention. It allows personalized pacing, accommodating diverse learning speeds and styles, which increases engagement and reduces frustration. By emphasizing mastery over time, this approach promotes higher competency and readiness for real-world applications.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Model
Time-Based Progression often faces challenges such as limited personalization, where students advance regardless of mastery, leading to gaps in understanding and motivation issues. Proficiency-Based Progression demands accurate and consistent assessment methods, which can be resource-intensive and may delay progression for students struggling to meet benchmarks. Both models encounter limitations in scalability and flexibility, impacting their effectiveness across diverse educational contexts.
Impact on Student Motivation and Outcomes
Time-based progression structures learning around fixed schedules, which can lead to varied student motivation as some may feel rushed or unchallenged, potentially impacting outcomes negatively. Proficiency-based progression allows students to advance upon mastering skills, fostering intrinsic motivation by emphasizing personal achievement and often resulting in improved learning outcomes. Research indicates that proficiency-based models enhance engagement and retention rates by aligning pace with individual learning needs.
Implementing Progression Models in Education
Implementing time-based progression in education requires structured scheduling and fixed instructional periods that advance students uniformly regardless of individual mastery. Proficiency-based progression emphasizes personalized learning pathways, allowing students to advance upon demonstrating mastery of specific competencies, which necessitates adaptive assessment tools and flexible curricular frameworks. Integrating technology and data analytics facilitates tailored feedback and progress tracking critical for successfully adopting proficiency-based models.
Future Trends in Educational Progression
Future trends in educational progression emphasize a shift from traditional Time-Based Progression, which advances students after set periods, to Proficiency-Based Progression, where learners move forward upon mastering skills and competencies. Increasing integration of adaptive learning technologies and data analytics supports personalized learning pathways, enabling educators to tailor instruction to individual proficiency levels. This transformation aims to enhance student outcomes by fostering mastery, reducing learning gaps, and promoting lifelong learning in dynamic educational environments.
Time-Based Progression Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com