Competency-Based Progression focuses on advancing learners based on their demonstrated skills and knowledge rather than time spent in class. This approach personalizes education, allowing Your growth to align with mastery of specific competencies essential for real-world application. Explore this article to uncover how competency-based progression can transform your learning experience.
Table of Comparison
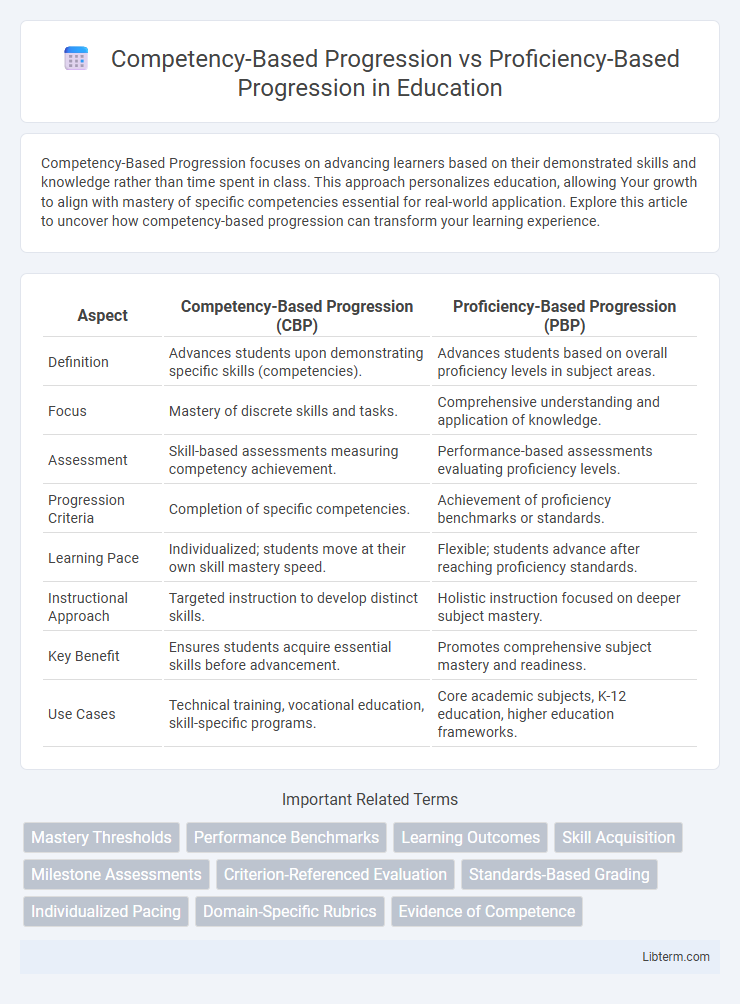
| Aspect | Competency-Based Progression (CBP) | Proficiency-Based Progression (PBP) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Advances students upon demonstrating specific skills (competencies). | Advances students based on overall proficiency levels in subject areas. |
| Focus | Mastery of discrete skills and tasks. | Comprehensive understanding and application of knowledge. |
| Assessment | Skill-based assessments measuring competency achievement. | Performance-based assessments evaluating proficiency levels. |
| Progression Criteria | Completion of specific competencies. | Achievement of proficiency benchmarks or standards. |
| Learning Pace | Individualized; students move at their own skill mastery speed. | Flexible; students advance after reaching proficiency standards. |
| Instructional Approach | Targeted instruction to develop distinct skills. | Holistic instruction focused on deeper subject mastery. |
| Key Benefit | Ensures students acquire essential skills before advancement. | Promotes comprehensive subject mastery and readiness. |
| Use Cases | Technical training, vocational education, skill-specific programs. | Core academic subjects, K-12 education, higher education frameworks. |
Understanding Competency-Based Progression
Competency-Based Progression emphasizes mastering specific skills and knowledge units before advancing, often personalized to a learner's pace and needs. This approach measures progress through demonstrated abilities rather than time spent in class, ensuring practical application and readiness for subsequent challenges. It enhances learner autonomy and aligns education outcomes with real-world competencies required in professional environments.
Defining Proficiency-Based Progression
Proficiency-Based Progression centers on students advancing only after demonstrating mastery of specific skills or knowledge, ensuring a deeper understanding before moving forward. This approach emphasizes clearly defined learning outcomes and personalized pacing tailored to individual progress. In contrast to Competency-Based Progression, Proficiency-Based Progression rigorously measures student ability through assessments aligned with proficiency standards to maintain educational quality and consistency.
Key Differences Between Competency and Proficiency Models
Competency-Based Progression emphasizes mastering specific skills and knowledge units before advancing, while Proficiency-Based Progression measures overall performance levels and readiness. Competency models often use discrete, measurable outcomes tied to job functions, whereas proficiency models assess holistic abilities through continuous evaluation. Key differences include the granularity of assessment and the focus on skill mastery versus demonstrated proficiency in real-world contexts.
Educational Outcomes: Competency vs. Proficiency
Competency-based progression emphasizes the mastery of specific skills and knowledge, ensuring students demonstrate the ability to apply concepts in real-world contexts, which leads to measurable and actionable educational outcomes. Proficiency-based progression focuses on achieving a defined level of understanding or performance, often using standardized assessments to evaluate students' grasp of subject matter. Both approaches aim to improve educational outcomes, but competency-based models prioritize practical application and skill integration, while proficiency-based systems highlight content knowledge and performance benchmarks.
Assessment Strategies in Each Progression Model
Competency-Based Progression relies on assessment strategies that measure specific skills and knowledge mastery through performance tasks, practical exams, and direct observation to ensure learners demonstrate required competencies before advancing. Proficiency-Based Progression employs assessments designed to evaluate overall understanding and application of concepts, often using formative quizzes, summative tests, and rubric-based evaluations aligned with proficiency scales. Both models emphasize tailored feedback and evidence-based evaluations but differ in the granularity and focus of their assessment approaches to support personalized learning trajectories.
Benefits of Competency-Based Progression
Competency-Based Progression accelerates learning by allowing students to advance upon demonstrating specific skills, fostering personalized education tailored to individual strengths and gaps. This model enhances mastery and retention, as learners focus deeply on practical competencies rather than time-bound metrics. Institutions adopting Competency-Based Progression often report improved learner engagement, higher completion rates, and better alignment with workforce demands.
Advantages of Proficiency-Based Progression
Proficiency-Based Progression offers personalized learning paths by allowing students to advance only after demonstrating mastery of specific skills, ensuring a solid understanding before moving forward. This approach enhances long-term retention and reduces knowledge gaps, leading to improved academic outcomes and increased student confidence. Schools implementing Proficiency-Based Progression often see higher engagement and motivation as learners receive targeted feedback aligned with proficiency standards.
Implementation Challenges and Solutions
Implementing Competency-Based Progression (CBP) faces challenges such as inconsistent competency definitions and variable assessment standards, whereas Proficiency-Based Progression (PBP) struggles with setting uniform proficiency benchmarks and ensuring valid skill evaluations. Solutions include adopting standardized competency frameworks like the Common Core State Standards for CBP and utilizing data-driven assessment tools including adaptive testing platforms to enhance PBP accuracy. Both approaches benefit from continuous professional development for educators and integrated learning management systems to monitor and support individual learner progress effectively.
Case Studies: Real-World Applications
Case studies reveal that competency-based progression (CBP) emphasizes mastering specific skills before advancement, as seen in organizations like Amazon, which improves workforce readiness through targeted training modules. Proficiency-based progression (PBP) focuses on demonstrating overall proficiency levels, exemplified by medical residency programs where residents advance after meeting comprehensive benchmarks. These real-world applications highlight CBP's skill-specific approach contrasted with PBP's holistic assessment model, guiding tailored educational and professional development strategies.
Selecting the Right Model for Your Educational Context
Competency-Based Progression emphasizes mastering specific skills and knowledge units before advancing, ideal for vocational and skill-intensive programs requiring measurable competencies; Proficiency-Based Progression focuses on achieving a broader level of understanding and application, suited for academic settings where depth and critical thinking are prioritized. Selecting the right model depends on your educational context's goals, student demographics, and assessment capabilities, ensuring alignment with desired learning outcomes and resource availability. Analyzing program objectives, institutional capacity, and learner needs helps tailor progression models that maximize engagement and educational effectiveness.
Competency-Based Progression Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com