Dual language education fosters bilingualism by teaching students in two languages, enhancing cognitive skills and cultural awareness. This approach supports academic achievement and prepares learners for global communication challenges. Discover how dual language programs can benefit your child's education in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
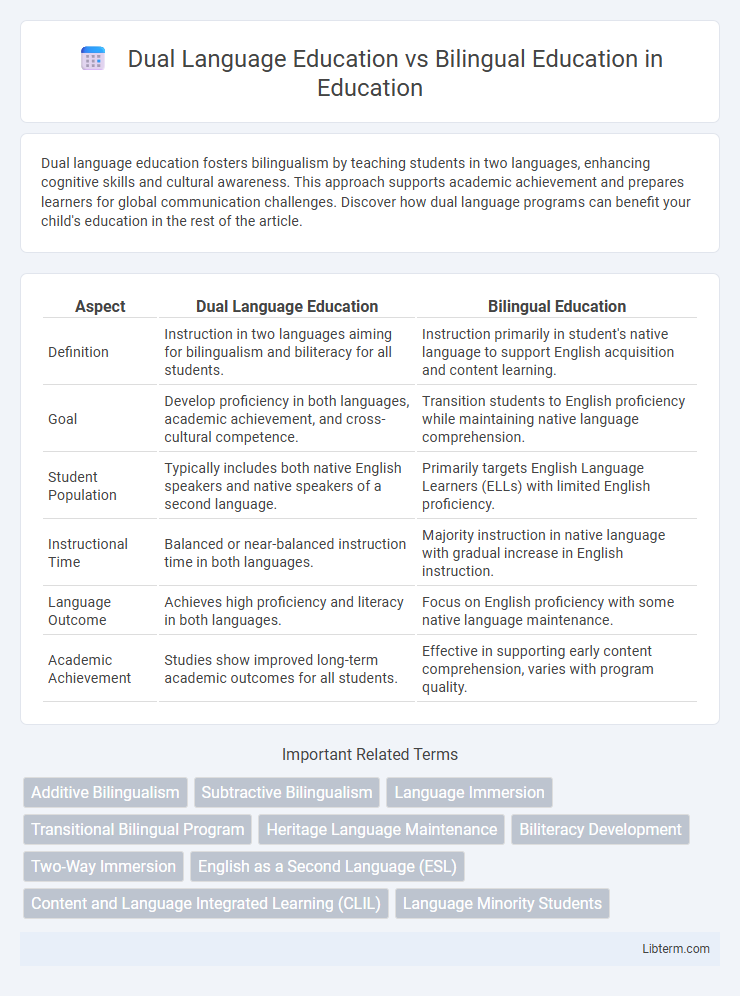
| Aspect | Dual Language Education | Bilingual Education |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Instruction in two languages aiming for bilingualism and biliteracy for all students. | Instruction primarily in student's native language to support English acquisition and content learning. |
| Goal | Develop proficiency in both languages, academic achievement, and cross-cultural competence. | Transition students to English proficiency while maintaining native language comprehension. |
| Student Population | Typically includes both native English speakers and native speakers of a second language. | Primarily targets English Language Learners (ELLs) with limited English proficiency. |
| Instructional Time | Balanced or near-balanced instruction time in both languages. | Majority instruction in native language with gradual increase in English instruction. |
| Language Outcome | Achieves high proficiency and literacy in both languages. | Focus on English proficiency with some native language maintenance. |
| Academic Achievement | Studies show improved long-term academic outcomes for all students. | Effective in supporting early content comprehension, varies with program quality. |
Understanding Dual Language Education
Dual Language Education immerses students in two languages equally, promoting bilingualism and biliteracy by integrating native English speakers and English learners in the same classroom. This approach enhances cognitive skills and academic achievement by fostering cross-cultural competence and language development in both languages. Unlike traditional Bilingual Education, which often focuses on transitioning students to English proficiency, Dual Language Education aims for long-term proficiency in both languages.
What Is Bilingual Education?
Bilingual education is an instructional approach where students are taught literacy and content in two languages, typically their native language and a second language, to foster proficiency and academic achievement in both. This method supports cultural identity and cognitive development by using students' first language as a foundation for learning a new language. It contrasts with dual language education, which aims for full bilingualism and biliteracy by integrating native speakers of both languages in the same classroom.
Key Philosophies: Dual Language vs Bilingual Programs
Dual Language Education emphasizes balanced proficiency in two languages by integrating native and non-native speakers to promote bilingualism and biliteracy across academic subjects. Bilingual Education primarily supports students' native language while gradually transitioning them to English, focusing on language maintenance and English acquisition. The core philosophy of Dual Language centers on additive bilingualism and cultural integration, whereas Bilingual Education often addresses language preservation and remedial language support.
Curriculum Design Differences
Dual Language Education programs design curricula to integrate two languages equally, promoting biliteracy and balanced proficiency for both native English speakers and English language learners. Bilingual Education curricula typically prioritize proficiency in the native language first, gradually transitioning to English instruction, aiming to support language development sequentially. Dual Language curricula emphasize cultural inclusivity and content mastery in both languages simultaneously, whereas Bilingual Education often focuses on language preservation and English acquisition as distinct phases.
Language Proficiency Goals
Dual Language Education aims to develop high proficiency and literacy in two languages by integrating native speakers of both languages in a balanced instructional model, promoting additive bilingualism. Bilingual Education primarily focuses on supporting students' transition from their native language to English proficiency, often prioritizing English acquisition while maintaining the home language. Language proficiency goals in Dual Language programs emphasize equal competency and academic achievement in both languages, whereas Bilingual Education may prioritize English dominance with varying levels of native language retention.
Classroom Structure and Student Demographics
Dual Language Education integrates native English speakers and English language learners in the same classroom, promoting bilingualism and biliteracy through balanced instruction in two languages. Bilingual Education typically separates students by language proficiency, providing instruction mainly in the students' native language to support English acquisition. Classroom structure in Dual Language programs fosters interaction among diverse linguistic backgrounds, while Bilingual Education classrooms often serve predominantly non-English-speaking students, aiming to transition them to English proficiency.
Academic Outcomes and Achievement
Dual Language Education consistently promotes higher academic outcomes by integrating both languages across all subjects, fostering balanced bilingualism and biliteracy. Research indicates that students in dual language programs outperform peers in bilingual education on standardized tests, especially in reading and math proficiency. The sustained exposure to academic content in two languages enhances cognitive flexibility and long-term achievement compared to traditional bilingual education models that often prioritize one language over another.
Cultural Awareness and Development
Dual Language Education fosters cultural awareness by integrating two languages in instruction, promoting bilingualism and biliteracy while encouraging students to appreciate and respect cultural diversity. Bilingual Education primarily supports language development for non-native speakers, often focusing on English proficiency, which may limit the depth of cultural engagement. Emphasizing cultural development, Dual Language programs create immersive environments where students experience and understand multiple cultural perspectives, enhancing social cohesion and global competence.
Challenges and Criticisms of Each Approach
Dual Language Education faces challenges such as resource allocation, teacher proficiency in both languages, and balancing language exposure to prevent dominance of one language over the other. Bilingual Education often encounters criticisms related to insufficient support for content learning in the second language and potential delays in English proficiency. Both approaches require careful program design to address equity, cultural relevance, and effective assessment methods.
Choosing the Right Program for Your Community
Choosing the right program for your community depends on understanding the goals of Dual Language Education versus Bilingual Education. Dual Language Education promotes fluency and literacy in two languages by maintaining balanced instruction, benefiting both native English speakers and English language learners through integrated cultural awareness. Bilingual Education primarily supports students in acquiring English proficiency while maintaining their native language, often emphasizing transitional language development rather than full bilingualism.
Dual Language Education Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com