Decontextualized tasks focus on skills or knowledge assessed outside of their usual context, promoting abstract thinking and generalization. Such tasks enhance your ability to apply learning flexibly across varied situations. Explore the rest of this article to understand how decontextualized tasks can boost cognitive development and practical application.
Table of Comparison
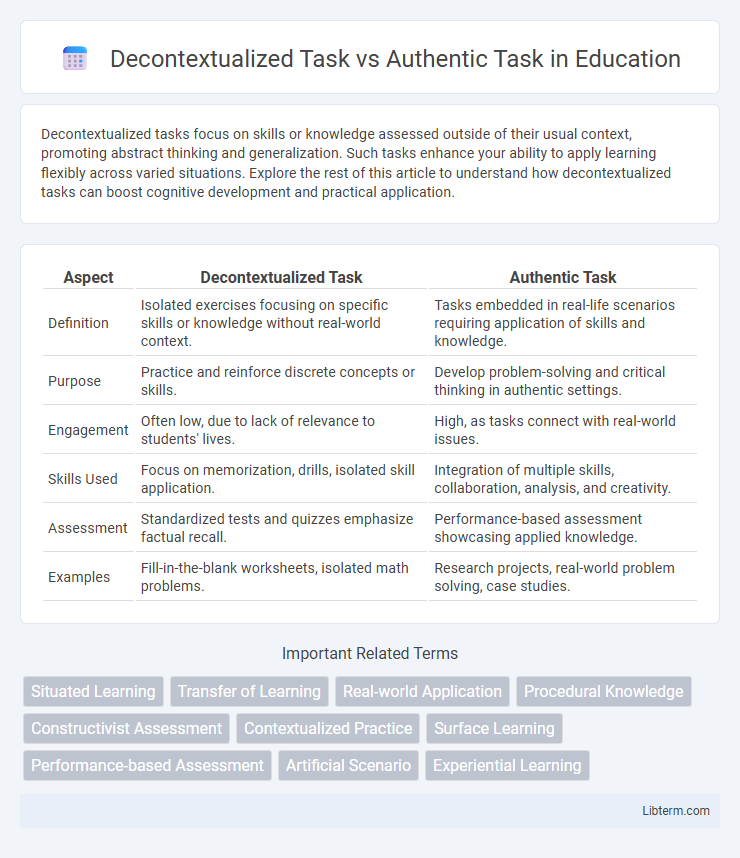
| Aspect | Decontextualized Task | Authentic Task |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Isolated exercises focusing on specific skills or knowledge without real-world context. | Tasks embedded in real-life scenarios requiring application of skills and knowledge. |
| Purpose | Practice and reinforce discrete concepts or skills. | Develop problem-solving and critical thinking in authentic settings. |
| Engagement | Often low, due to lack of relevance to students' lives. | High, as tasks connect with real-world issues. |
| Skills Used | Focus on memorization, drills, isolated skill application. | Integration of multiple skills, collaboration, analysis, and creativity. |
| Assessment | Standardized tests and quizzes emphasize factual recall. | Performance-based assessment showcasing applied knowledge. |
| Examples | Fill-in-the-blank worksheets, isolated math problems. | Research projects, real-world problem solving, case studies. |
Understanding Decontextualized and Authentic Tasks
Decontextualized tasks involve abstract, context-free problems that require learners to apply knowledge or skills without real-world cues, often emphasizing memorization and theoretical understanding. Authentic tasks simulate real-life scenarios demanding critical thinking, problem-solving, and the application of interdisciplinary knowledge, promoting deeper engagement and practical comprehension. Understanding the distinction between these tasks highlights the importance of context in learning, where authentic tasks foster meaningful learning experiences beyond rote knowledge acquisition.
Key Characteristics of Decontextualized Tasks
Decontextualized tasks are characterized by their focus on isolated skills or knowledge without real-world context, often emphasizing abstract reasoning and procedural execution. These tasks typically involve structured, controlled environments where variables are minimized to assess specific cognitive or academic abilities. They lack the situational cues that authentic tasks provide, which makes them less representative of everyday problem-solving or applied learning scenarios.
Defining Features of Authentic Tasks
Authentic tasks are characterized by their relevance to real-world contexts, requiring learners to apply knowledge and skills in meaningful and practical situations. These tasks often involve complex problem-solving, collaboration, and critical thinking that mirror professional or everyday challenges. Unlike decontextualized tasks, authentic tasks promote deep understanding through engagement with authentic materials, scenarios, and outcomes.
Educational Theories Supporting Each Task Type
Decontextualized tasks align with behaviorist theory by emphasizing repetitive practice and reinforcement of isolated skills, promoting mastery through drill and recall. Authentic tasks are supported by constructivist and situated learning theories, which advocate for meaningful, context-rich activities that reflect real-world challenges, encouraging critical thinking and knowledge application. Vygotsky's social development theory also underpins authentic tasks by highlighting the importance of social interaction and scaffolding in learning processes.
Benefits of Decontextualized Tasks in Learning
Decontextualized tasks offer the benefit of isolating specific skills or knowledge, enabling focused practice and mastery without the complexity of real-world distractions. These tasks promote cognitive flexibility, allowing learners to transfer core concepts across various contexts and disciplines. By simplifying learning environments, decontextualized tasks facilitate clearer assessment of individual competencies and support targeted instruction.
Advantages of Authentic Tasks for Real-World Application
Authentic tasks enhance real-world application by mirroring genuine situations, which promotes critical thinking and problem-solving skills relevant to everyday challenges. These tasks engage learners in meaningful contexts, boosting motivation and ensuring knowledge transfer beyond the classroom. Research shows that authentic tasks improve retention and prepare individuals for complex, unpredictable environments in professional and personal settings.
Challenges in Implementing Decontextualized vs Authentic Tasks
Implementing decontextualized tasks often faces challenges such as reduced learner engagement and difficulty in applying abstract knowledge to real-world situations, which can result in limited practical skill development. Authentic tasks, while promoting meaningful learning and real-world application, present obstacles including increased complexity in design, higher resource demands, and the necessity for tailored assessment methods. Balancing cognitive load and ensuring alignment with curriculum standards further complicate the integration of both task types in educational settings.
Impact on Student Engagement and Motivation
Decontextualized tasks often lead to lower student engagement and motivation because they lack real-world relevance and connection to students' interests, making learning feel abstract and disconnected. Authentic tasks, by integrating meaningful, real-life scenarios, enhance intrinsic motivation and active participation by showing students the practical application of skills and knowledge. Studies indicate that learners involved in authentic tasks demonstrate higher persistence, deeper cognitive processing, and improved academic outcomes compared to those restricted to decontextualized exercises.
Assessment and Evaluation: Decontextualized vs Authentic Tasks
Decontextualized tasks assess isolated skills or knowledge through standardized tests, emphasizing accuracy and recall without real-world context. Authentic tasks evaluate learners' ability to apply knowledge in practical, meaningful situations, promoting critical thinking and problem-solving skills. The evaluation of authentic tasks often involves performance-based assessments, rubrics, and reflective evidence to measure deeper understanding and transferable competencies.
Choosing the Appropriate Task Type for Learning Outcomes
Selecting the appropriate task type hinges on the desired learning outcomes, where decontextualized tasks emphasize isolated skills and authentic tasks foster real-world application and critical thinking. Decontextualized tasks are effective for foundational knowledge and procedural accuracy, while authentic tasks enhance problem-solving, creativity, and transferability to practical situations. Aligning task choice with educational goals ensures targeted skill development and meaningful learner engagement.
Decontextualized Task Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com