Continuous feedback fosters real-time improvement by allowing you to promptly address performance gaps and adapt strategies efficiently. This ongoing exchange enhances collaboration, drives employee engagement, and cultivates a culture of continuous learning and development. Explore the rest of the article to discover how continuous feedback transforms workplace dynamics and boosts overall productivity.
Table of Comparison
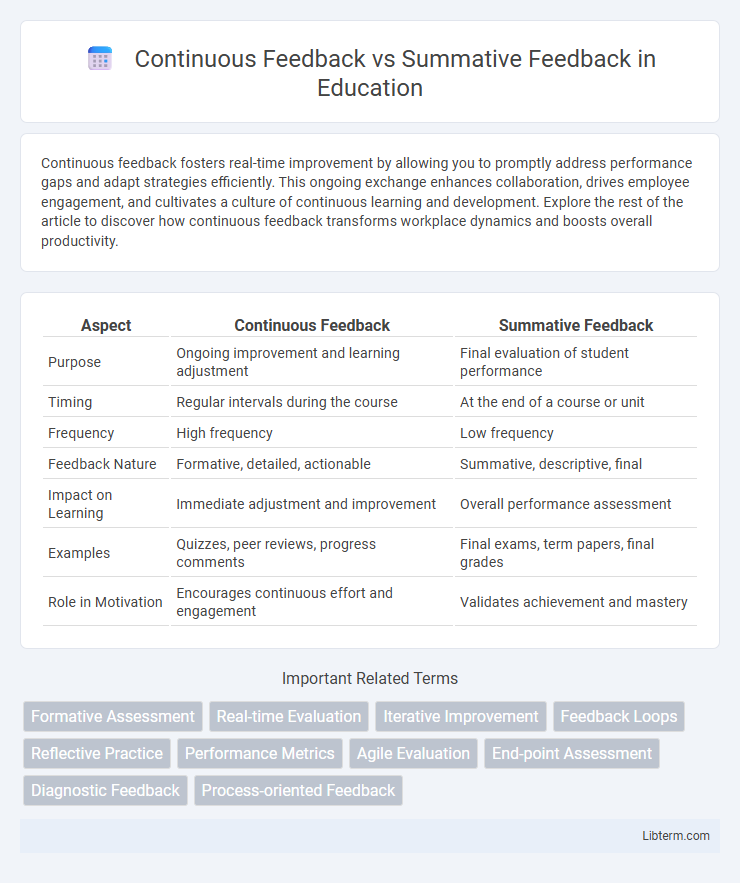
| Aspect | Continuous Feedback | Summative Feedback |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Ongoing improvement and learning adjustment | Final evaluation of student performance |
| Timing | Regular intervals during the course | At the end of a course or unit |
| Frequency | High frequency | Low frequency |
| Feedback Nature | Formative, detailed, actionable | Summative, descriptive, final |
| Impact on Learning | Immediate adjustment and improvement | Overall performance assessment |
| Examples | Quizzes, peer reviews, progress comments | Final exams, term papers, final grades |
| Role in Motivation | Encourages continuous effort and engagement | Validates achievement and mastery |
Introduction to Feedback in Learning and Work
Continuous feedback provides ongoing, real-time insights that help learners and employees adjust their performance promptly, fostering a growth-oriented environment. Summative feedback, typically delivered at the end of a learning period or project, evaluates overall achievement against set criteria, serving as a benchmark for success. Both feedback types are essential in educational and workplace settings, balancing immediate improvement with comprehensive assessment.
Defining Continuous Feedback
Continuous feedback refers to the ongoing process of providing real-time, constructive input during a task or project, enabling immediate improvements and learning. Unlike summative feedback, which occurs after completion and evaluates overall performance, continuous feedback fosters adaptability and personal growth by addressing issues as they arise. This form of feedback enhances engagement and productivity by maintaining open communication between learners or employees and their mentors or supervisors.
Understanding Summative Feedback
Summative feedback provides a comprehensive evaluation of learner performance at the end of an instructional period, highlighting overall achievements and areas requiring improvement. It serves as a benchmark for measuring knowledge retention, skill acquisition, and mastery of subject matter, often used in grading or certification. Effective summative feedback enables educators and learners to identify gaps and inform future instructional strategies.
Key Differences Between Continuous and Summative Feedback
Continuous feedback provides real-time, ongoing insights during the learning or work process, promoting timely adjustments and improvement. Summative feedback occurs after completion, evaluating overall performance to measure achievement against standards. The key difference lies in timing and purpose: continuous feedback supports growth and development moment-to-moment, while summative feedback serves as a final assessment.
Advantages of Continuous Feedback
Continuous feedback offers real-time insights that enable employees to make immediate improvements, enhancing overall performance and productivity. This ongoing communication fosters a culture of growth and development, reducing the anxiety often associated with traditional summative evaluations. Organizations adopting continuous feedback benefit from increased employee engagement and more agile responses to challenges.
Benefits of Summative Feedback
Summative feedback provides a comprehensive evaluation of overall performance at the end of a learning period, offering clear benchmarks and measurable outcomes. It enables learners to understand their proficiency and areas of strength while motivating goal-oriented improvement. Educators benefit from summative assessments by gaining insights into curriculum effectiveness and student achievement trends for future planning.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
Continuous feedback often faces challenges such as time constraints for educators, potential information overload for students, and difficulties in maintaining consistent quality and relevance of feedback throughout a course. Summative feedback is limited by its retrospective nature, often providing insufficient opportunities for students to apply improvements before final evaluations, and may not capture incremental learning progress or address individual learning gaps effectively. Both approaches require balanced implementation to mitigate these limitations while enhancing student development and assessment accuracy.
Best Practices for Implementing Feedback Systems
Continuous feedback systems thrive on real-time, actionable insights that promote ongoing improvement and employee engagement, making frequent, specific, and constructive communication essential. Summative feedback, typically delivered after a performance period, requires clarity, objectivity, and alignment with predefined goals to accurately assess achievements and guide future development. Best practices for implementing effective feedback systems include integrating technology for seamless communication, ensuring training for managers on delivering balanced feedback, and fostering a culture that values transparency and continuous learning.
Choosing the Right Feedback Method for Your Context
Continuous feedback fosters ongoing improvement by providing real-time insights, ideal for dynamic environments requiring agile adjustments. Summative feedback delivers comprehensive evaluations at project milestones, best suited for assessing overall performance and outcomes. Selecting the right feedback method depends on the project's pace, team needs, and desired impact on learning and development.
Future Trends in Feedback Strategies
Continuous feedback leverages real-time data analysis and AI-powered platforms to provide personalized learning paths, enhancing adaptive performance improvement. Summative feedback, traditionally periodic and evaluative, is evolving through integration with analytics dashboards to inform strategic decision-making and long-term skill development. Future trends emphasize hybrid models combining instant feedback loops with comprehensive performance summaries to drive continuous growth and competency mastery.
Continuous Feedback Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com