Inquiry-based curriculum fosters critical thinking and problem-solving by encouraging students to explore questions and engage actively in learning. This approach promotes deeper understanding through hands-on experiences and collaborative investigation. Discover how implementing an inquiry-based curriculum can transform your educational environment by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
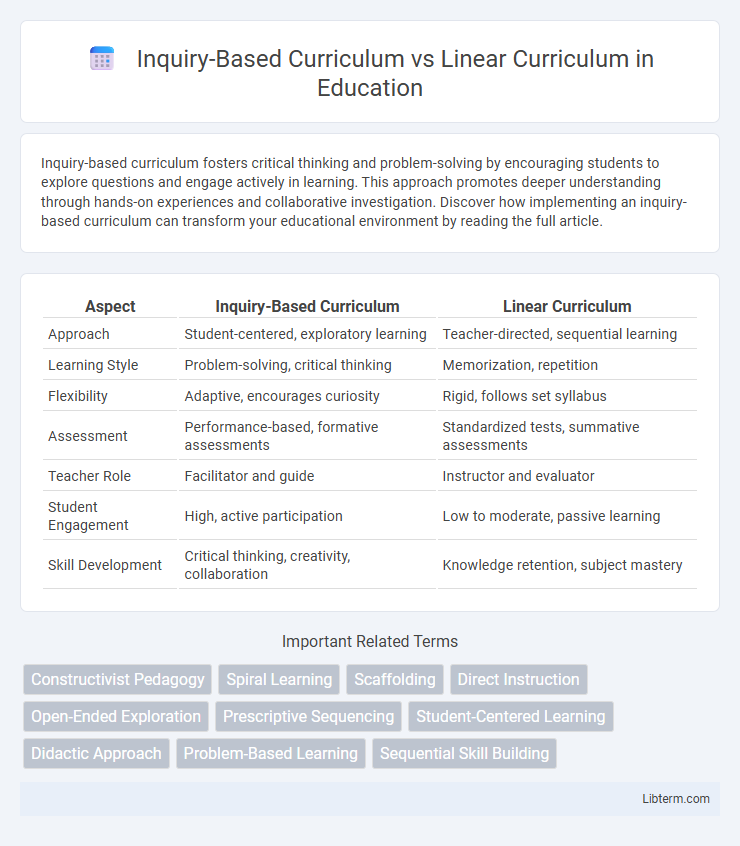
| Aspect | Inquiry-Based Curriculum | Linear Curriculum |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Student-centered, exploratory learning | Teacher-directed, sequential learning |
| Learning Style | Problem-solving, critical thinking | Memorization, repetition |
| Flexibility | Adaptive, encourages curiosity | Rigid, follows set syllabus |
| Assessment | Performance-based, formative assessments | Standardized tests, summative assessments |
| Teacher Role | Facilitator and guide | Instructor and evaluator |
| Student Engagement | High, active participation | Low to moderate, passive learning |
| Skill Development | Critical thinking, creativity, collaboration | Knowledge retention, subject mastery |
Introduction to Curriculum Design Approaches
Inquiry-based curriculum emphasizes student-centered exploration, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving through real-world questions and active learning experiences. Linear curriculum follows a predetermined sequence of topics, prioritizing systematic knowledge acquisition and skill mastery in a structured, teacher-directed format. Curriculum design approaches differ in flexibility and learner autonomy, impacting engagement and adaptability to diverse educational needs.
Defining Inquiry-Based Curriculum
Inquiry-Based Curriculum emphasizes student-centered learning through questioning, exploration, and critical thinking, fostering deeper understanding and active engagement. This approach contrasts with Linear Curriculum, which follows a predetermined, sequential structure focused on content delivery and memorization. Inquiry-Based learning encourages adaptability and problem-solving skills by promoting curiosity and investigative processes within the educational framework.
Understanding Linear Curriculum Structure
The linear curriculum structure is organized sequentially, presenting subjects and skills in a fixed, step-by-step order that builds foundational knowledge before progressing to more complex topics. This approach emphasizes a clear, predictable learning path, ensuring mastery of basic concepts prior to advancing, which supports standardized assessment and curriculum alignment. Understanding the linear curriculum's structured progression helps educators design lessons that scaffold student learning effectively and maintain a consistent pace throughout instructional units.
Core Principles of Inquiry-Based Learning
Inquiry-based curriculum centers on student-driven exploration, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving through open-ended questions and hands-on activities. Core principles emphasize curiosity, active learning, and the development of deeper understanding by encouraging learners to investigate real-world problems. This approach contrasts with linear curriculum's structured, sequential content delivery, prioritizing memorization over conceptual engagement.
Step-by-Step Nature of Linear Curriculum
The step-by-step nature of a linear curriculum provides a clear, structured framework that facilitates consistent knowledge progression and mastery of foundational concepts. Each lesson builds directly on the previous one, ensuring learners develop skills in a logical sequence that minimizes gaps in understanding. This systematic approach contrasts with inquiry-based curricula, which emphasize exploration and self-directed learning over rigid sequencing.
Benefits of Inquiry-Based Curriculum
Inquiry-based curriculum enhances critical thinking and problem-solving skills by encouraging students to explore concepts through questions and experiments. It fosters deeper understanding and retention of knowledge by promoting active engagement and collaborative learning. This approach also cultivates creativity and adaptability, preparing students for complex real-world challenges.
Advantages of Linear Curriculum
Linear curriculum offers structured progression through clearly defined learning objectives, enabling consistent knowledge acquisition and skill development. Its predictable sequence facilitates efficient time management and assessment, ensuring mastery of foundational concepts before advancing. This approach benefits learners who thrive with clear expectations and step-by-step guidance, promoting academic stability and measurable outcomes.
Challenges of Implementing Inquiry-Based Approaches
Implementing an inquiry-based curriculum presents challenges such as the need for extensive teacher training to facilitate open-ended questioning and foster critical thinking skills effectively. Limited classroom time and standardized testing pressures often hinder the deep exploration required by inquiry methods compared to linear curricula. Furthermore, resource constraints and varying student readiness levels can complicate the adaptation of inquiry-based strategies in diverse educational settings.
Limitations of the Linear Curriculum Model
The linear curriculum model often limits student engagement by emphasizing rote memorization and sequential learning without fostering critical thinking or problem-solving skills. This approach restricts flexibility, making it difficult to adapt to diverse learner needs and real-world contexts. Consequently, students may struggle to develop deeper understanding and retain knowledge effectively compared to more explorative methods like inquiry-based curricula.
Comparing Outcomes: Inquiry-Based vs Linear Curriculum
Inquiry-based curriculum fosters critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and deeper understanding by encouraging students to explore and question concepts actively. In contrast, linear curriculum emphasizes structured, sequential learning that can lead to mastery of foundational knowledge but may limit creativity and adaptability. Studies show inquiry-based approaches yield higher engagement and long-term retention, whereas linear methods often support standardized test performance and procedural fluency.
Inquiry-Based Curriculum Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com