Inquiry-Based learning fosters critical thinking and deep understanding by encouraging active questioning and exploration. This approach empowers learners to take charge of their education, promoting curiosity and problem-solving skills. Discover how incorporating inquiry-based methods can transform Your educational experience by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
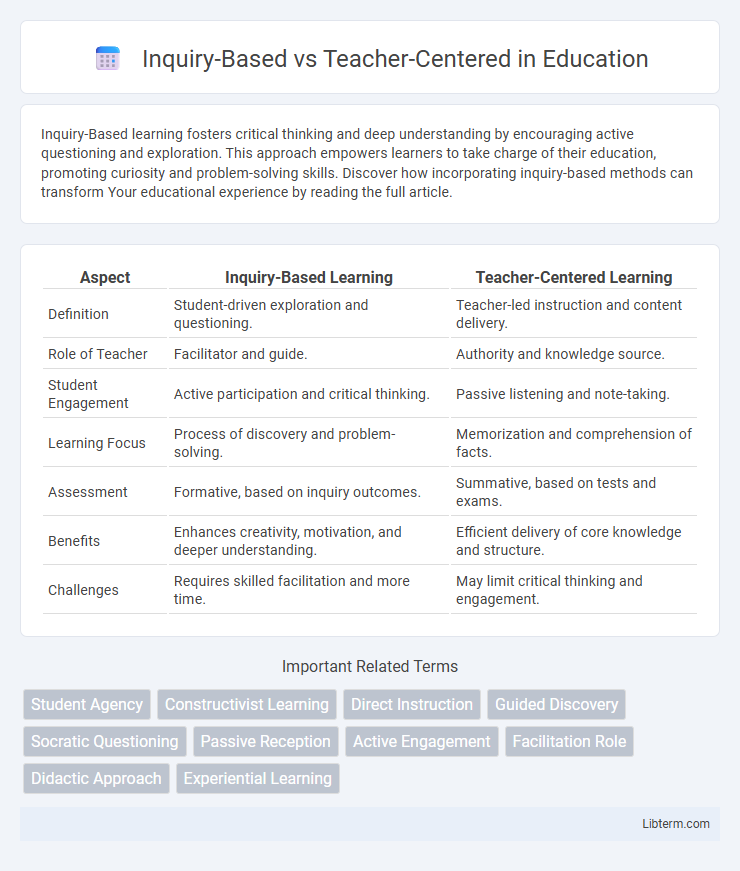
| Aspect | Inquiry-Based Learning | Teacher-Centered Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Student-driven exploration and questioning. | Teacher-led instruction and content delivery. |
| Role of Teacher | Facilitator and guide. | Authority and knowledge source. |
| Student Engagement | Active participation and critical thinking. | Passive listening and note-taking. |
| Learning Focus | Process of discovery and problem-solving. | Memorization and comprehension of facts. |
| Assessment | Formative, based on inquiry outcomes. | Summative, based on tests and exams. |
| Benefits | Enhances creativity, motivation, and deeper understanding. | Efficient delivery of core knowledge and structure. |
| Challenges | Requires skilled facilitation and more time. | May limit critical thinking and engagement. |
Understanding Inquiry-Based Learning
Inquiry-based learning emphasizes student curiosity, exploration, and critical thinking by encouraging learners to ask questions and investigate topics independently. This approach contrasts with teacher-centered methods, where instruction is primarily lecture-based and knowledge transmission flows from teacher to student. Understanding inquiry-based learning highlights its role in developing deeper conceptual comprehension, problem-solving skills, and active engagement in the educational process.
Defining Teacher-Centered Instruction
Teacher-centered instruction prioritizes the teacher's role as the primary source of knowledge, emphasizing direct instruction, structured lessons, and a controlled classroom environment. This approach focuses on efficient content delivery, with students receiving information passively through lectures, demonstrations, and rote memorization. It contrasts with student-centered models by minimizing student autonomy and fostering a teacher-led learning process.
Core Principles of Inquiry-Based Approaches
Inquiry-based approaches emphasize student-driven exploration, critical thinking, and problem-solving by encouraging learners to ask questions, investigate, and construct knowledge through active engagement. Core principles include fostering curiosity, promoting collaboration, and integrating real-world context to deepen understanding. Teacher roles shift from knowledge transmitters to facilitators who guide inquiry processes and support reflective learning.
Key Features of Teacher-Centered Classrooms
Teacher-centered classrooms prioritize direct instruction where the teacher is the primary authority and source of knowledge, guiding students through structured lessons and standardized curricula. Emphasis is on memorization, repetition, and mastery of factual information, with assessments typically focusing on accuracy and recall. Classroom management is centered on maintaining order and discipline to optimize student focus and minimize distractions.
Student Engagement: Inquiry vs Teacher-Led
Inquiry-based learning significantly enhances student engagement by encouraging active exploration, critical thinking, and problem-solving, enabling students to construct knowledge through hands-on experiences. Teacher-centered approaches often limit engagement by prioritizing passive reception of information, reducing opportunities for students to interact with content or ask questions. Research indicates that inquiry-driven classrooms foster deeper cognitive involvement and motivation compared to traditional teacher-led instruction.
Developing Critical Thinking Skills
Inquiry-based learning actively engages students in questioning, exploring, and problem-solving, fostering deep critical thinking skills by encouraging analysis, evaluation, and synthesis of information. Teacher-centered instruction typically follows a more structured approach, focusing on knowledge transmission rather than on developing students' independent analytical abilities. Research shows inquiry-based methods significantly enhance students' capacity for critical thinking by promoting curiosity and self-directed learning.
Classroom Management and Structure
Inquiry-based classrooms prioritize student autonomy and collaborative learning, requiring flexible classroom management strategies that encourage exploration and critical thinking. Teacher-centered classrooms emphasize direct instruction and strict control over classroom dynamics, maintaining a structured environment with clear rules and routines to manage student behavior effectively. Effective classroom management in inquiry-based settings relies on guiding inquiry processes and fostering student responsibility, while teacher-centered approaches depend on authoritative oversight and consistent enforcement of procedures.
Assessing Learning Outcomes
Inquiry-based learning encourages students to actively explore and construct knowledge, leading to improved critical thinking and problem-solving skills, which are often assessed through formative evaluations and project-based assessments. Teacher-centered approaches typically rely on summative assessments like standardized tests to measure student understanding and retention of content. Effectively assessing learning outcomes requires aligning evaluation methods with instructional strategies to capture both cognitive processes and factual knowledge.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Method
Inquiry-based learning often faces challenges such as the need for significant student motivation, extensive teacher guidance, and potential gaps in foundational knowledge. Teacher-centered methods can limit critical thinking development and student engagement, relying heavily on rote memorization and passive learning. Both approaches require balancing structure and flexibility to effectively address diverse student needs and classroom dynamics.
Choosing the Best Approach for Diverse Learners
Inquiry-based learning fosters critical thinking and student engagement by encouraging exploration and problem-solving, ideal for diverse learners who benefit from active participation and personalized discovery. Teacher-centered approaches provide structured guidance and clear expectations, supporting learners who thrive under direct instruction and need consistent reinforcement of foundational knowledge. Balancing both methods according to students' individual needs and learning styles ensures an inclusive educational environment that maximizes academic achievement and motivation.
Inquiry-Based Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com