Competency-based advancement focuses on promoting employees based on their demonstrated skills and abilities rather than seniority or tenure. This approach ensures that Your career growth aligns with measurable performance and relevant expertise. Explore the rest of the article to understand how adopting competency-based advancement can transform your professional development.
Table of Comparison
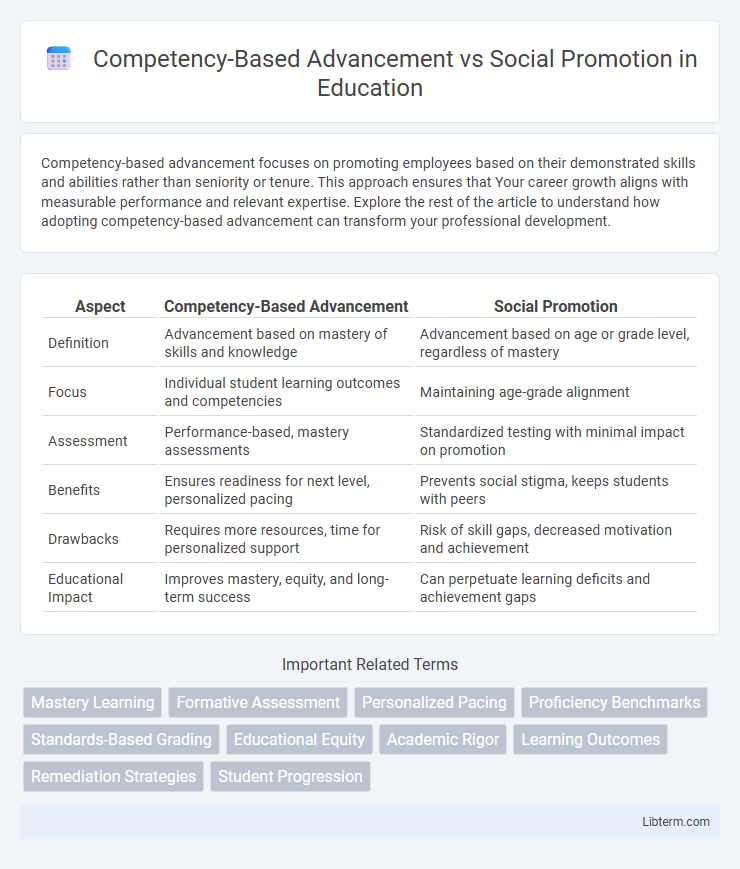
| Aspect | Competency-Based Advancement | Social Promotion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Advancement based on mastery of skills and knowledge | Advancement based on age or grade level, regardless of mastery |
| Focus | Individual student learning outcomes and competencies | Maintaining age-grade alignment |
| Assessment | Performance-based, mastery assessments | Standardized testing with minimal impact on promotion |
| Benefits | Ensures readiness for next level, personalized pacing | Prevents social stigma, keeps students with peers |
| Drawbacks | Requires more resources, time for personalized support | Risk of skill gaps, decreased motivation and achievement |
| Educational Impact | Improves mastery, equity, and long-term success | Can perpetuate learning deficits and achievement gaps |
Understanding Competency-Based Advancement
Competency-Based Advancement emphasizes promoting students based on demonstrated mastery of specific skills or knowledge rather than age or grade level, ensuring personalized learning and readiness for subsequent challenges. This approach relies on clear competency frameworks and continuous assessment to tailor instruction and support, fostering deeper understanding and skill acquisition. Research indicates that competency-based models enhance student engagement, reduce achievement gaps, and better prepare learners for academic and career success compared to traditional social promotion practices.
The Principles of Social Promotion
Social promotion advances students to the next grade level regardless of their mastery of academic skills, aiming to maintain age-based peer groups and avoid stigmatization. This principle often prioritizes social and emotional development over demonstrated competency, potentially leading to gaps in essential knowledge and skills. Critics argue that social promotion may undermine long-term academic success by promoting students without ensuring readiness for subsequent educational challenges.
Key Differences Between Competency-Based Advancement and Social Promotion
Competency-Based Advancement promotes students based on demonstrated mastery of specific skills and knowledge, ensuring readiness for the next grade level. Social Promotion advances students primarily to keep them with their age peers, regardless of academic achievement or skill proficiency. This key difference highlights competency-based models' focus on learning outcomes, while social promotion prioritizes social and developmental considerations.
Measuring Student Progress: Competency vs Age-Based Promotion
Measuring student progress through competency-based advancement emphasizes mastery of specific skills and knowledge before moving to the next level, ensuring personalized learning outcomes. In contrast, social promotion advances students based on age or grade level, often overlooking individual academic readiness. Competency-based models utilize clear performance metrics and assessments to track progress, fostering targeted interventions and meaningful growth.
Benefits of Competency-Based Advancement
Competency-based advancement ensures students progress upon demonstrating mastery of key skills, leading to a personalized learning experience that addresses individual strengths and weaknesses. This method improves academic outcomes by fostering deeper understanding and reducing knowledge gaps commonly found in grade-level promotions. Schools adopting competency-based systems report higher student engagement, better preparedness for future challenges, and enhanced self-confidence due to clear, skill-focused benchmarks.
Challenges and Criticisms of Social Promotion
Social promotion faces significant challenges, including promoting students who lack essential skills, leading to gaps in knowledge that hinder future academic and career success. Critics argue it undermines accountability by advancing students regardless of mastery, which can decrease motivation and lower overall educational standards. This practice often results in teachers and schools failing to address individual learning needs appropriately, perpetuating cycles of underachievement.
Impact on Student Motivation and Engagement
Competency-based advancement enhances student motivation and engagement by allowing learners to progress upon mastering skills, fostering a sense of achievement and personalized growth. Social promotion often undermines motivation as students advance without mastering content, leading to disengagement and decreased academic confidence. Research indicates that competency-based models align better with intrinsic motivation theories, promoting active participation and sustained learning outcomes.
Equity and Fairness in Academic Progression
Competency-based advancement ensures equity and fairness by promoting students only when they demonstrate mastery of specific academic skills, preventing gaps in learning and supporting individualized progress. Social promotion, by advancing students based on age or grade level regardless of mastery, can undermine academic equity by allowing some students to progress without the necessary competencies, potentially widening achievement gaps. Prioritizing competency-based models fosters a more just academic environment by aligning advancement with measurable learning outcomes rather than arbitrary timelines.
Long-Term Outcomes for Students: A Comparative Analysis
Competency-based advancement prioritizes mastering specific skills and knowledge before progressing, resulting in higher long-term academic achievement and better preparedness for future challenges compared to social promotion, which advances students regardless of skill mastery. Research indicates students in competency-based systems exhibit increased retention rates and improved critical thinking abilities over time, while social promotion often correlates with higher dropout rates and lower college readiness. Emphasizing personalized learning paths within competency-based models fosters sustainable educational growth, benefiting students' career and lifelong learning prospects.
Future Trends in Student Advancement Policies
Competency-based advancement emphasizes mastery of skills and knowledge before progressing, aligning with personalized learning and digital assessments shaping future education. Social promotion, often criticized for advancing students regardless of readiness, is increasingly replaced by data-driven policies supporting tailored interventions and competency benchmarks. Emerging trends highlight adaptive learning technologies and holistic assessments as critical tools for ensuring meaningful student progression and success.
Competency-Based Advancement Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com