Social language enhances your ability to connect and communicate effectively in diverse social settings, fostering stronger relationships and collaboration. Mastering social language skills boosts empathy, active listening, and clear expression, which are crucial for personal and professional success. Discover practical tips and strategies to improve your social language throughout this article.
Table of Comparison
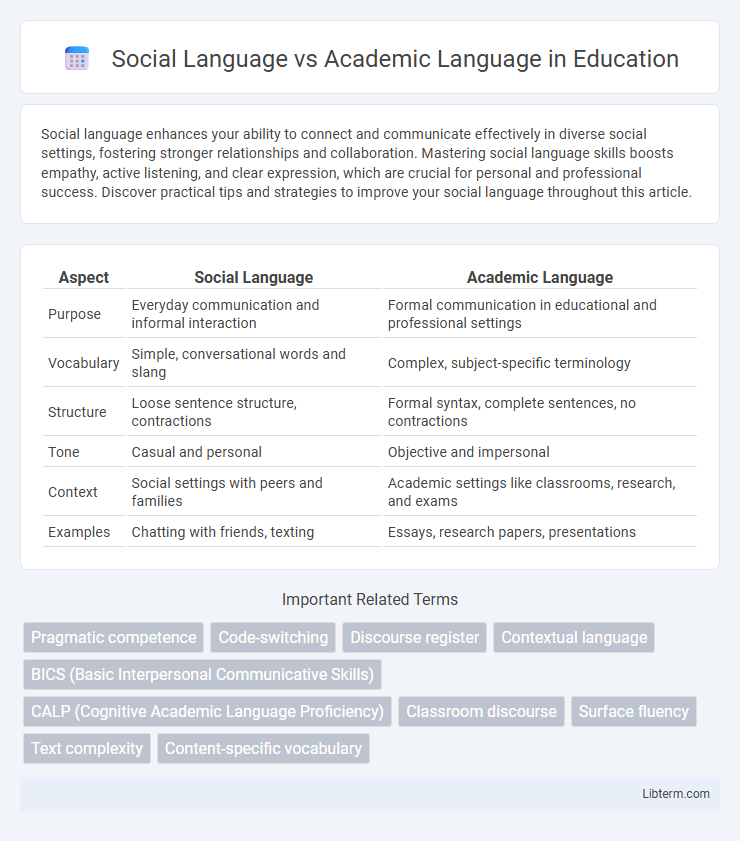
| Aspect | Social Language | Academic Language |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Everyday communication and informal interaction | Formal communication in educational and professional settings |
| Vocabulary | Simple, conversational words and slang | Complex, subject-specific terminology |
| Structure | Loose sentence structure, contractions | Formal syntax, complete sentences, no contractions |
| Tone | Casual and personal | Objective and impersonal |
| Context | Social settings with peers and families | Academic settings like classrooms, research, and exams |
| Examples | Chatting with friends, texting | Essays, research papers, presentations |
Understanding Social Language and Academic Language
Social language involves everyday communication skills used in informal settings, emphasizing conversational tone, slang, and context-driven meaning. Academic language centers on formal vocabulary, complex sentence structures, and discipline-specific terminology essential for comprehension and expression in educational environments. Mastery of both social and academic language enhances communication effectiveness across diverse contexts.
Key Differences Between Social and Academic Language
Social language involves informal communication used in everyday interactions, characterized by casual vocabulary, idiomatic expressions, and contextual cues. Academic language features formal structure, precise terminology, and complex sentence constructions designed for clear, objective transmission of specialized knowledge. While social language emphasizes social relationships and pragmatic use, academic language prioritizes clarity, coherence, and subject-specific conventions essential for academic success.
Importance of Social Language in Everyday Communication
Social language, characterized by informal vocabulary and conversational structures, plays a crucial role in everyday communication by facilitating interpersonal connections and effective social interactions. It enables individuals to express emotions, build relationships, and navigate social contexts, which are essential for mental well-being and community integration. Mastery of social language supports inclusive communication, making it a foundational skill alongside academic language for overall linguistic competence.
The Role of Academic Language in Educational Success
Academic language plays a crucial role in educational success by enabling students to engage deeply with complex texts, express abstract ideas, and follow formal reasoning. Mastery of academic vocabulary, syntax, and discourse structures directly influences comprehension, critical thinking, and the ability to produce coherent written and oral arguments. Schools that explicitly teach academic language skills help bridge the gap between social and academic contexts, improving students' overall performance and equity in learning outcomes.
Vocabulary Distinctions: Social vs. Academic Terms
Social language relies heavily on everyday vocabulary, informal expressions, and colloquialisms used in personal and casual conversations. Academic language requires precise, subject-specific terminology and formal vocabulary to convey complex ideas and critical analysis effectively. Mastery of academic vocabulary enhances comprehension and communication in educational settings, distinguishing it from the more flexible and context-driven social language.
Contexts for Using Social and Academic Language
Social language is primarily used in informal contexts such as conversations with family, friends, or peers, where everyday vocabulary and casual expressions dominate. Academic language is essential in formal settings like classrooms, research papers, and professional presentations, relying on precise terminology, complex sentence structures, and discipline-specific jargon. Mastery of both language forms supports effective communication across diverse social and educational environments.
Challenges Learners Face with Academic Language
Learners often struggle with academic language due to its complex vocabulary, formal syntax, and abstract concepts, which differ significantly from social language used in everyday conversations. Academic language demands precise terminology, critical thinking, and the ability to comprehend and produce disciplinary texts, posing challenges in reading, writing, and oral communication. These hurdles can impact learners' academic performance and require targeted instructional strategies to develop proficiency.
Strategies for Developing Academic Language Proficiency
Effective strategies for developing academic language proficiency include explicit teaching of discipline-specific vocabulary, structured classroom discussions, and scaffolded writing assignments that promote critical thinking. Integrating multimodal resources such as visual aids and graphic organizers enhances comprehension and retention of complex concepts. Regular feedback and practice in formal language contexts support students in transitioning from conversational social language to precise, formal academic communication.
Bridging the Gap Between Social and Academic Language
Bridging the gap between social language and academic language is essential for student success in educational settings, as social language often encompasses informal, conversational skills while academic language involves formal vocabulary and complex sentence structures used in classroom discourse. Effective strategies include explicit teaching of academic vocabulary, scaffolded instruction, and integrating real-life social language contexts into academic tasks to enhance comprehension and expression. Fostering metalinguistic awareness supports learners in navigating different language registers, promoting equitable access to academic content and improving overall literacy outcomes.
Impact of Language Proficiency on Student Achievement
Language proficiency in academic language significantly impacts student achievement by enabling comprehension of complex texts and effective expression of ideas in educational settings. Social language skills, while essential for everyday communication, do not fully equip students to grasp subject-specific vocabulary and discourse structures critical for academic success. Research shows that students with higher academic language proficiency demonstrate improved reading comprehension, critical thinking, and standardized test performance across disciplines.
Social Language Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com