Performance-based assessment evaluates your ability to apply skills and knowledge in real-world scenarios, focusing on practical tasks rather than traditional exams. This method enhances critical thinking, problem-solving, and hands-on experience through authentic activities tailored to specific learning objectives. Explore the full article to discover how performance-based assessments can transform your approach to evaluation and learning.
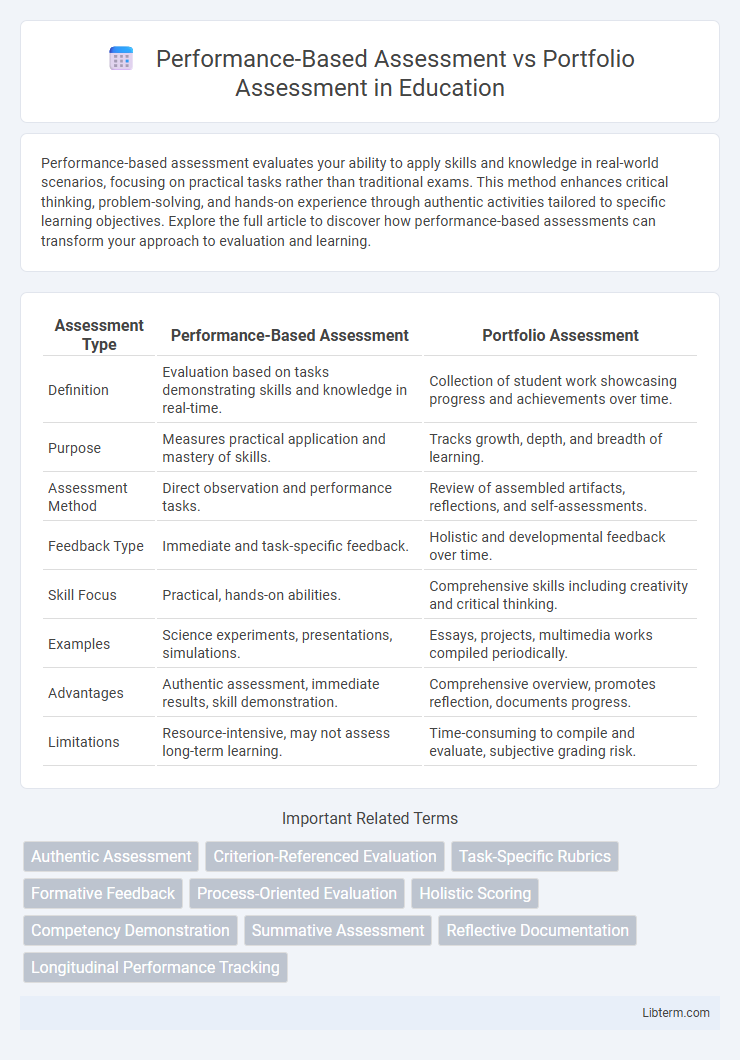
Table of Comparison
| Assessment Type | Performance-Based Assessment | Portfolio Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Evaluation based on tasks demonstrating skills and knowledge in real-time. | Collection of student work showcasing progress and achievements over time. |
| Purpose | Measures practical application and mastery of skills. | Tracks growth, depth, and breadth of learning. |
| Assessment Method | Direct observation and performance tasks. | Review of assembled artifacts, reflections, and self-assessments. |
| Feedback Type | Immediate and task-specific feedback. | Holistic and developmental feedback over time. |
| Skill Focus | Practical, hands-on abilities. | Comprehensive skills including creativity and critical thinking. |
| Examples | Science experiments, presentations, simulations. | Essays, projects, multimedia works compiled periodically. |
| Advantages | Authentic assessment, immediate results, skill demonstration. | Comprehensive overview, promotes reflection, documents progress. |
| Limitations | Resource-intensive, may not assess long-term learning. | Time-consuming to compile and evaluate, subjective grading risk. |
Understanding Performance-Based Assessment
Performance-Based Assessment evaluates students through real-world tasks that demonstrate their application of knowledge and skills, emphasizing practical understanding and problem-solving abilities. It involves activities such as presentations, experiments, or simulations that require active engagement and critical thinking. This form of assessment provides authentic evidence of learning by measuring how well students perform specific academic or professional tasks.
Defining Portfolio Assessment
Portfolio assessment involves the systematic collection and evaluation of a student's work over time to demonstrate learning progress, skills, and achievements. It emphasizes authentic evidence of performance through diverse artifacts such as projects, written reflections, and presentations, offering a holistic view of student development. This method contrasts with performance-based assessments by prioritizing continuous documentation and self-assessment rather than singular task execution.
Core Differences Between the Two Approaches
Performance-based assessment evaluates students through tasks that demonstrate their skills and knowledge in real-world scenarios, emphasizing practical application and immediate demonstration of competence. Portfolio assessment collects a curated compilation of student work over time, highlighting growth, reflection, and a broad range of abilities across various contexts. Key differences include the time frame of evaluation, with performance-based assessments focusing on specific moments, while portfolios provide a longitudinal view of student progress and depth.
Learning Outcomes: Which Method Measures Better?
Performance-based assessment offers direct evaluation of students' practical skills and application of knowledge through tasks that mimic real-world challenges, providing clear evidence of competency and learning outcomes. Portfolio assessment compiles a curated collection of student work over time, reflecting growth, self-reflection, and a broad range of skills, but may lack immediate performance context. When measuring learning outcomes, performance-based assessments typically deliver more precise, task-specific insights, whereas portfolios excel in showcasing longitudinal development and depth of understanding.
Skills Development: Practical vs. Reflective Learning
Performance-based assessment emphasizes practical skills development by requiring students to demonstrate competencies in real-world tasks, enhancing hands-on learning and immediate application. Portfolio assessment fosters reflective learning through continuous documentation and self-evaluation, encouraging critical thinking and personal growth over time. Both methods support skill acquisition but emphasize different aspects of experiential education and cognitive engagement.
Assessment Criteria: Objectivity and Subjectivity
Performance-Based Assessment emphasizes objective criteria by measuring specific skills and tasks through standardized rubrics, ensuring consistent evaluation across different learners. Portfolio Assessment relies more on subjective criteria, as it involves the holistic review of accumulated work samples and reflections, allowing for personalized interpretation of student growth. Both methods benefit from clear, well-defined assessment criteria to balance objectivity and subjectivity in evaluating student performance.
Student Engagement and Motivation
Performance-Based Assessment actively engages students by requiring them to apply knowledge and skills in real-world tasks, which enhances motivation through meaningful, hands-on learning experiences. Portfolio Assessment fosters sustained student motivation by encouraging reflection and self-assessment, allowing learners to track progress and showcase growth over time. Both assessment types promote deep engagement by aligning evaluation with authentic student work and personal investment in learning outcomes.
Implementation Challenges and Solutions
Performance-based assessment faces challenges including time-intensive administration, subjective grading, and resource constraints, requiring standardized rubrics and targeted teacher training to ensure consistency. Portfolio assessment struggles with maintaining student engagement and ensuring authentic representation of learning, which can be addressed through regular checkpoints and clear criteria for content selection. Both methods benefit from technology integration to streamline collection, evaluation, and feedback processes, enhancing overall feasibility and effectiveness.
Teacher Roles in Assessment Practices
Teacher roles in performance-based assessment involve designing authentic tasks that reflect real-world skills, facilitating student engagement, and providing immediate, formative feedback to guide improvement. In portfolio assessment, teachers act as curators and evaluators, helping students select representative work over time and conducting reflective discussions to assess progress and depth of learning. Both approaches require teachers to shift from traditional evaluators to collaborators and coaches, emphasizing continuous assessment and personalized support.
Selecting the Right Assessment for Educational Goals
Performance-based assessment emphasizes evaluating students through real-world tasks that demonstrate applied skills and knowledge, making it ideal for objectives centered on practical competency and critical thinking. Portfolio assessment compiles a curated collection of student work over time, effectively capturing growth, reflection, and mastery across diverse learning outcomes. Selecting the right assessment method depends on aligning the educational goals with the need for either authentic skill demonstration or comprehensive evidence of progress and development.
Performance-Based Assessment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com