Remedial education focuses on helping students who struggle to meet standard academic benchmarks by providing targeted instruction tailored to their specific learning gaps. This approach improves foundational skills in reading, writing, and math, enabling learners to catch up with their peers and build confidence in their abilities. Discover how remedial education can transform your learning journey by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
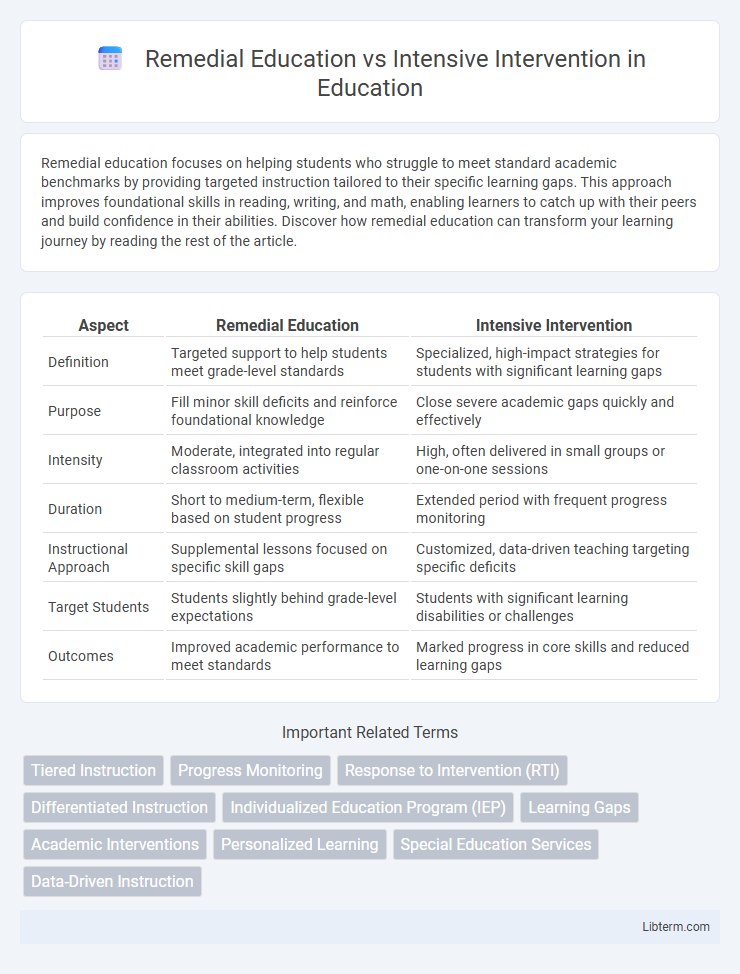
| Aspect | Remedial Education | Intensive Intervention |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Targeted support to help students meet grade-level standards | Specialized, high-impact strategies for students with significant learning gaps |
| Purpose | Fill minor skill deficits and reinforce foundational knowledge | Close severe academic gaps quickly and effectively |
| Intensity | Moderate, integrated into regular classroom activities | High, often delivered in small groups or one-on-one sessions |
| Duration | Short to medium-term, flexible based on student progress | Extended period with frequent progress monitoring |
| Instructional Approach | Supplemental lessons focused on specific skill gaps | Customized, data-driven teaching targeting specific deficits |
| Target Students | Students slightly behind grade-level expectations | Students with significant learning disabilities or challenges |
| Outcomes | Improved academic performance to meet standards | Marked progress in core skills and reduced learning gaps |
Understanding Remedial Education
Remedial education targets students who struggle to meet grade-level standards by providing tailored instruction that reinforces foundational skills in reading, mathematics, or writing. This approach emphasizes diagnosing learning gaps and delivering structured, evidence-based support to improve comprehension and academic performance. Effective remedial programs often incorporate continuous assessment to adjust strategies and ensure gradual skill mastery.
Defining Intensive Intervention
Intensive intervention refers to specialized, high-impact instructional strategies designed to address significant learning difficulties through frequent, targeted support sessions. It typically involves small group or one-on-one instruction tailored to individual student needs, emphasizing skill mastery and progress monitoring. This approach exceeds the scope of general remedial education by providing systematic, data-driven interventions calibrated to accelerate academic improvement.
Core Objectives: Remediation vs. Intervention
Remedial education targets fundamental skill deficits by reinforcing basic knowledge and ensuring mastery of essential concepts, primarily addressing gaps in literacy, numeracy, and comprehension. Intensive intervention focuses on tailored, evidence-based strategies designed to accelerate learning progress in students with persistent or severe learning difficulties, emphasizing personalized support and frequent progress monitoring. Both approaches aim to improve academic outcomes but differ in immediacy and specificity of instructional methods.
Target Student Populations
Remedial education primarily targets students who have fallen behind in basic skills such as reading, writing, or mathematics, often due to gaps in prior learning or developmental delays. Intensive intervention focuses on students with significant learning disabilities or persistent academic struggles, providing individualized, evidence-based strategies to address specific deficits. Both approaches aim to improve student outcomes but serve distinct populations based on the severity and nature of learning challenges.
Instructional Strategies Compared
Remedial education employs targeted instruction strategies focused on reinforcing foundational skills through repetition and scaffolded practice, aiming to fill specific learning gaps. Intensive intervention uses data-driven, individualized approaches that adjust pacing and complexity based on frequent progress monitoring to accelerate student growth. Both prioritize explicit teaching but differ in adaptability and emphasis on continuous assessment for tailored support.
Curriculum Design Differences
Remedial Education curriculum centers on reinforcing foundational skills through repetitive practice and scaffolded learning tailored to the student's current level, emphasizing mastery of basic concepts. Intensive Intervention curriculum adopts a more targeted, data-driven approach with frequent progress monitoring and individualized instructional strategies designed to accelerate learning gaps quickly. The key difference lies in the flexibility and personalization of Intensive Intervention, which integrates real-time assessments to adjust content, whereas Remedial Education follows a more standardized, slower-paced curriculum structure.
Monitoring and Progress Assessment
Monitoring in remedial education involves regular, formative assessments to track student understanding and adjust instruction accordingly, ensuring foundational skill gaps are addressed. Intensive intervention requires more frequent and detailed progress assessments, often using standardized tools and data-driven benchmarks to quantify gains and refine targeted strategies. Effective progress assessment in both approaches relies on continuous data collection and analysis to inform personalized instructional adjustments and maximize student outcomes.
Teacher Training and Expertise
Effective remedial education relies on teacher training that emphasizes diagnostic assessment skills and tailored instructional strategies to address diverse learning gaps. Intensive intervention demands advanced expertise in applying evidence-based methodologies and progress monitoring techniques to support students with significant academic challenges. Both approaches require continuous professional development to ensure educators remain proficient in adapting instruction to individual student needs.
Scalability and Resource Allocation
Remedial education often requires sustained, individualized attention, making scalability challenging due to the significant time and personnel resources needed. Intensive intervention targets specific skill deficits with focused, short-term strategies, enabling more efficient resource allocation and easier implementation across larger student populations. Schools balancing scalability prioritize intensive intervention to maximize impact while managing limited instructional resources effectively.
Choosing the Right Approach for Students
Selecting between remedial education and intensive intervention requires analyzing students' individual learning deficits and skill gaps through comprehensive assessments. Remedial education targets foundational skill reinforcement over an extended period, while intensive intervention involves concentrated, evidence-based strategies for students with significant learning disabilities or delays. Prioritizing data-driven instruction and ongoing progress monitoring ensures the chosen approach effectively addresses students' specific academic challenges and promotes measurable growth.
Remedial Education Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com