Resource room models provide specialized support within schools, offering targeted instruction tailored to students with learning disabilities or difficulties. These rooms enhance individualized education by integrating specialized teaching methods and tools that complement mainstream classroom learning. Explore the full article to understand how resource room models can transform Your educational experience and support diverse learning needs.
Table of Comparison
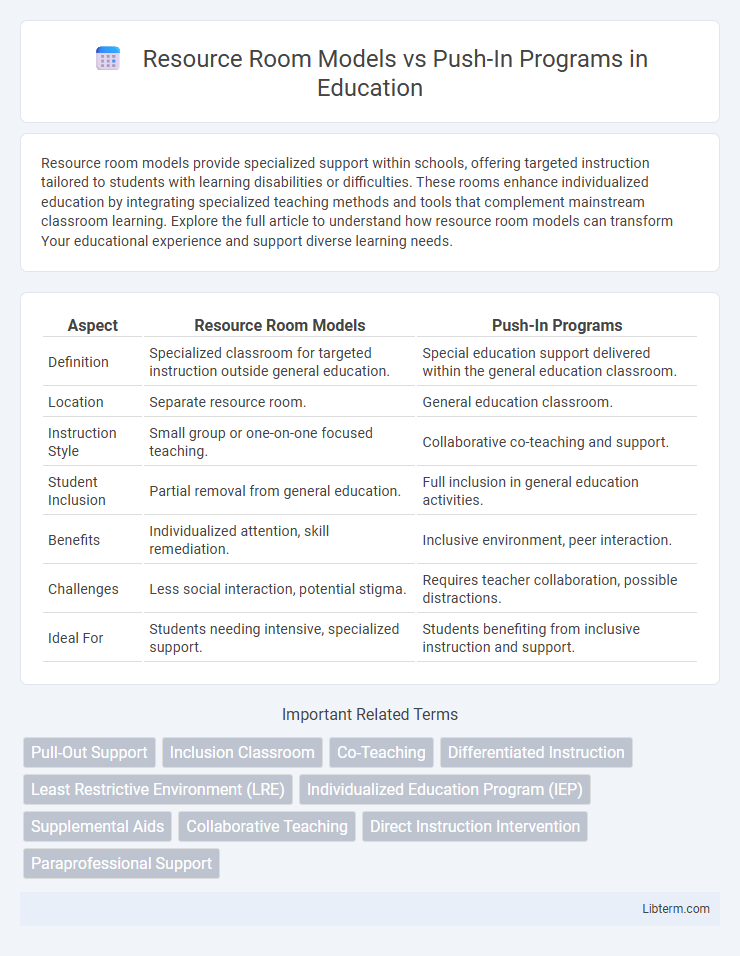
| Aspect | Resource Room Models | Push-In Programs |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Specialized classroom for targeted instruction outside general education. | Special education support delivered within the general education classroom. |
| Location | Separate resource room. | General education classroom. |
| Instruction Style | Small group or one-on-one focused teaching. | Collaborative co-teaching and support. |
| Student Inclusion | Partial removal from general education. | Full inclusion in general education activities. |
| Benefits | Individualized attention, skill remediation. | Inclusive environment, peer interaction. |
| Challenges | Less social interaction, potential stigma. | Requires teacher collaboration, possible distractions. |
| Ideal For | Students needing intensive, specialized support. | Students benefiting from inclusive instruction and support. |
Understanding Resource Room Models
Resource Room Models provide specialized instruction by pulling students out of the general education classroom for targeted support in specific subjects or skills. These models emphasize small-group or one-on-one teaching, allowing educators to tailor lessons to individual learning needs and address particular academic challenges. This approach helps improve focus and skill mastery while maintaining overall inclusion in the standard curriculum.
Key Features of Push-In Programs
Push-in programs feature in-class support where special education teachers collaborate directly with general education teachers to provide tailored instruction without removing students from the mainstream classroom. These models emphasize real-time intervention, fostering inclusive learning environments and promoting social interaction between students with and without disabilities. Push-in programs often utilize co-teaching methods, individualized accommodations, and flexible support to enhance accessibility and academic outcomes for diverse learners.
Historical Development of Both Approaches
Resource Room models originated in the 1960s as specialized settings designed to provide intensive, individualized instruction for students with learning disabilities outside the general classroom. Push-in programs emerged in the 1990s, reflecting a shift toward inclusive education by delivering support services directly within the general education environment to promote collaboration and access. Both approaches evolved in response to changing educational policies and increased recognition of the need for tailored instructional methods to serve diverse learners effectively.
Target Student Populations
Resource room models primarily serve students with moderate learning disabilities needing specialized instruction in a separate setting, allowing targeted skill remediation. Push-in programs target a broader range of students, including those with mild to moderate disabilities, by integrating support within the general education classroom to promote inclusivity. Both models adapt interventions based on Individualized Education Program (IEP) goals, but resource rooms concentrate on intensive, individualized remediation, while push-in supports collaborative learning for diverse student populations.
Benefits of Resource Room Models
Resource Room Models provide targeted, individualized instruction in a specialized setting, allowing students with learning disabilities to receive focused support tailored to their unique needs. This approach enhances academic achievement by offering a structured environment with expert educators and specialized resources. Resource Rooms also promote self-paced learning and reduce distractions, fostering improved comprehension and skill mastery compared to inclusive push-in programs.
Advantages of Push-In Programs
Push-in programs promote inclusive education by allowing special education teachers to support students within the general classroom environment, enhancing social interaction and reducing stigma. These programs enable immediate, context-specific assistance tailored to individual learning needs without removing students from peer interactions. Integrating support services in regular classrooms increases collaboration between general and special educators, leading to more cohesive instructional strategies and improved student outcomes.
Comparative Challenges and Limitations
Resource Room Models often face challenges with limited individualized support due to scheduled pull-out times, which can disrupt students' mainstream classroom engagement and peer interaction. Push-In Programs may struggle with maintaining adequate attention to diverse learning needs within a general education setting, potentially diluting specialized instruction. Both models encounter limitations related to resource allocation, staff collaboration, and balancing curriculum alignment with inclusive educational goals.
Impact on Academic Achievement
Resource Room Models provide targeted, individualized instruction in a separate setting, which often leads to improved mastery of specific academic skills for students with learning disabilities. Push-In Programs integrate special education support within the general education classroom, promoting collaboration and immediate academic assistance that can enhance engagement and comprehension. Studies show that combining both models strategically maximizes academic achievement by addressing diverse needs through personalized and inclusive approaches.
Collaboration Among Educators
Resource Room Models and Push-In Programs differ in their approach to collaboration among educators, with Push-In Programs fostering more inclusive teamwork by integrating special education teachers within general classrooms. This model encourages real-time co-teaching and immediate support, enhancing communication and joint lesson planning between special educators and general teachers. In contrast, Resource Room Models often result in more isolated instruction, limiting continuous collaboration and reducing opportunities for shared strategies tailored to individual student needs.
Choosing the Right Model for Student Needs
Selecting the appropriate support model depends on assessing individual student needs, with resource room models offering intensive, individualized instruction for students requiring targeted remediation. Push-in programs provide support within the general education classroom, promoting inclusivity and real-time skill application for students who benefit from integrated assistance. Evaluating factors such as the severity of learning challenges, social-emotional needs, and curriculum demands guides educators in choosing between these models for optimal student outcomes.
Resource Room Models Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com