Station teaching divides the classroom into multiple learning areas, each focusing on different skills or subjects, promoting active student engagement and personalized instruction. This collaborative method allows teachers to work with smaller groups, tailoring lessons to meet diverse learning needs effectively. Discover how station teaching can transform your classroom dynamics and enhance student outcomes in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
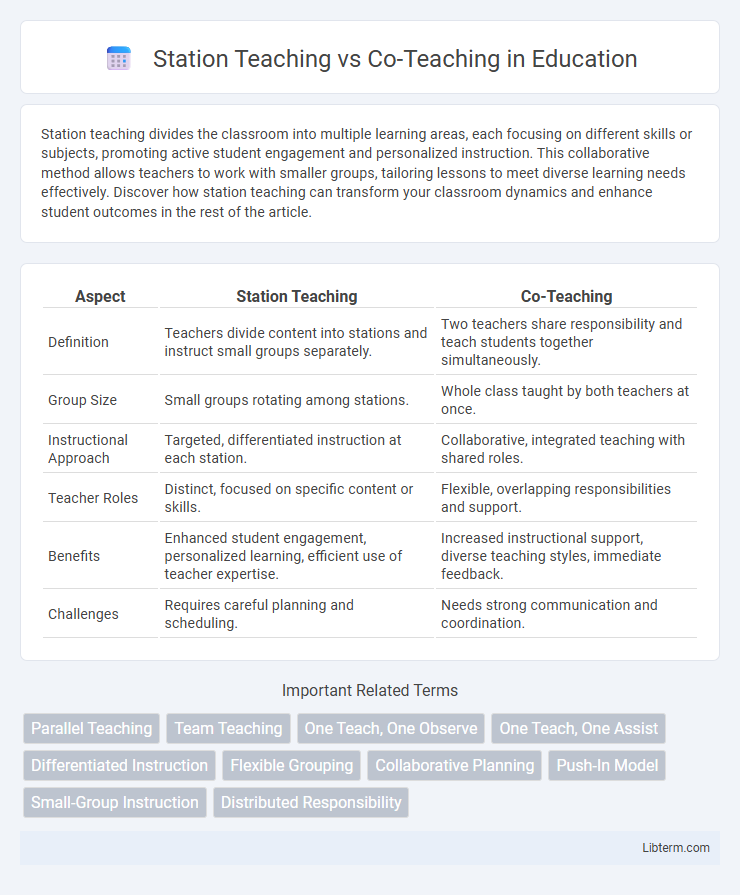
| Aspect | Station Teaching | Co-Teaching |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Teachers divide content into stations and instruct small groups separately. | Two teachers share responsibility and teach students together simultaneously. |
| Group Size | Small groups rotating among stations. | Whole class taught by both teachers at once. |
| Instructional Approach | Targeted, differentiated instruction at each station. | Collaborative, integrated teaching with shared roles. |
| Teacher Roles | Distinct, focused on specific content or skills. | Flexible, overlapping responsibilities and support. |
| Benefits | Enhanced student engagement, personalized learning, efficient use of teacher expertise. | Increased instructional support, diverse teaching styles, immediate feedback. |
| Challenges | Requires careful planning and scheduling. | Needs strong communication and coordination. |
Introduction to Station Teaching and Co-Teaching
Station teaching divides students into small groups that rotate through teacher-led stations, enabling targeted instruction and active learning tailored to diverse needs. Co-teaching involves two or more educators collaboratively planning, instructing, and assessing students within the same classroom, enhancing expertise and support. Both models improve engagement, differentiate instruction, and promote inclusive education through strategic collaboration.
Defining Station Teaching: Key Features
Station teaching divides the classroom into multiple learning centers where small groups of students rotate through stations, each led by a teacher or independent activity. Key features include differentiated instruction tailored to specific skill sets, increased student engagement through active learning, and efficient use of teacher resources by facilitating simultaneous instruction. This method supports diverse learning styles and fosters collaboration without requiring both teachers to deliver the same lesson simultaneously.
Understanding Co-Teaching Models
Co-teaching involves two educators collaborating to deliver instruction within a single classroom, with station teaching being a specific co-teaching model where the class is divided into smaller groups rotating through stations led by each teacher. This model enhances differentiated instruction by allowing teachers to target diverse student needs, promote active engagement, and manage classroom dynamics effectively. Understanding various co-teaching models, such as one teach-one assist, parallel teaching, and team teaching, helps educators select the most suitable strategy to optimize learning outcomes.
Comparing Station Teaching and Co-Teaching
Station Teaching divides students into small groups rotating through various learning stations, allowing teachers to target specific skills with focused instruction. Co-Teaching involves two educators collaboratively delivering lessons simultaneously in the same classroom, facilitating shared responsibilities and diverse instructional strategies. While Station Teaching emphasizes differentiated, paced learning in separate areas, Co-Teaching prioritizes joint planning and real-time support within a unified classroom environment.
Benefits of Station Teaching in the Classroom
Station teaching enhances student engagement by allowing small group instruction tailored to diverse learning needs, promoting active participation and collaboration. This method facilitates differentiated instruction, enabling teachers to target specific skills and provide immediate feedback, improving academic outcomes. The structured rotation in station teaching maximizes classroom management efficiency and optimizes instructional time utilization.
Advantages of Traditional Co-Teaching Approaches
Traditional co-teaching approaches offer significant advantages such as enhanced student engagement through collaborative instruction and diversified teaching strategies. These methods promote individualized support by allowing educators to simultaneously address different learning styles and needs within the same classroom. Co-teaching also fosters professional growth as teachers share expertise and continuously adapt their practices to improve student outcomes.
Challenges Faced in Station Teaching
Station teaching presents challenges such as maintaining consistent student engagement and managing transitions between stations effectively to avoid downtime and confusion. Teachers must ensure clear instructions and adequate support at each station, which can be difficult with varying student needs and group dynamics. Limited opportunities for immediate feedback and individualized attention may hinder progress for some learners, complicating differentiated instruction.
Potential Drawbacks of Co-Teaching
Co-teaching can present challenges such as role ambiguity, which may lead to confusion among students regarding authority and responsibilities in the classroom. Scheduling conflicts between teachers can reduce instructional time and impact lesson continuity. Limited collaboration or mismatched teaching styles may hinder the effectiveness of co-teaching, affecting student engagement and learning outcomes.
Choosing the Right Model for Your Classroom
Station teaching divides students into small groups rotating among teachers, allowing targeted instruction and personalized support, ideal for diverse learning levels. Co-teaching involves two educators simultaneously delivering lessons, promoting collaboration and shared responsibility, effective for inclusive classrooms with varied learner needs. Selecting the right model depends on classroom size, student diversity, teacher expertise, and instructional goals to maximize engagement and learning outcomes.
Best Practices for Effective Collaborative Teaching
Station teaching involves dividing content into segments where small groups rotate through different instructors, allowing for targeted, differentiated instruction that addresses diverse learning needs effectively. Co-teaching pairs educators in the same space delivering simultaneous instruction, leveraging complementary expertise to enhance student engagement and instructional quality. Best practices for effective collaborative teaching include clear role definitions, consistent communication, mutual respect, and ongoing joint planning to align objectives and maximize instructional impact.
Station Teaching Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com