The flipped classroom model transforms traditional teaching by delivering instructional content online outside of class, freeing in-person time for interactive, hands-on learning experiences. This approach promotes active student engagement and deeper understanding of the material through collaborative activities and personalized support. Explore the rest of the article to discover how the flipped classroom can enhance Your learning outcomes.
Table of Comparison
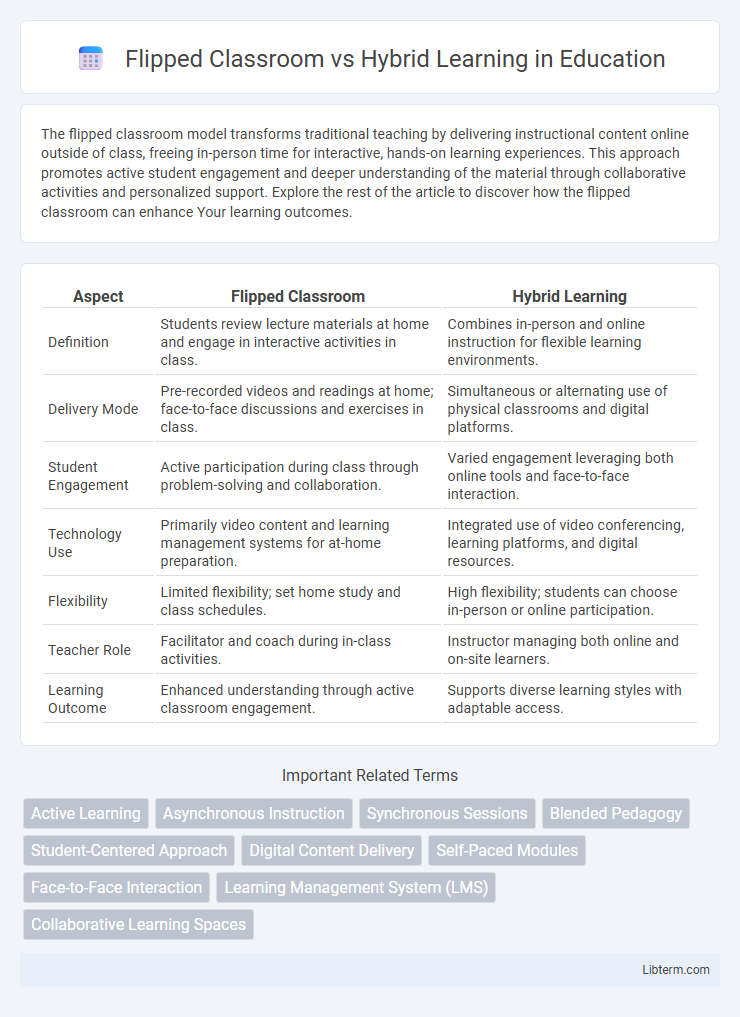
| Aspect | Flipped Classroom | Hybrid Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Students review lecture materials at home and engage in interactive activities in class. | Combines in-person and online instruction for flexible learning environments. |
| Delivery Mode | Pre-recorded videos and readings at home; face-to-face discussions and exercises in class. | Simultaneous or alternating use of physical classrooms and digital platforms. |
| Student Engagement | Active participation during class through problem-solving and collaboration. | Varied engagement leveraging both online tools and face-to-face interaction. |
| Technology Use | Primarily video content and learning management systems for at-home preparation. | Integrated use of video conferencing, learning platforms, and digital resources. |
| Flexibility | Limited flexibility; set home study and class schedules. | High flexibility; students can choose in-person or online participation. |
| Teacher Role | Facilitator and coach during in-class activities. | Instructor managing both online and on-site learners. |
| Learning Outcome | Enhanced understanding through active classroom engagement. | Supports diverse learning styles with adaptable access. |
Introduction to Flipped Classroom and Hybrid Learning
Flipped Classroom redefines traditional education by delivering instructional content online outside of class, allowing in-person sessions to focus on interactive activities and personalized support. Hybrid Learning combines online and face-to-face instruction, offering flexibility and access while maintaining direct teacher-student engagement. Both methods leverage digital technology to enhance learning experiences but differ in structure and the balance between virtual and physical classroom time.
Defining Flipped Classroom: Core Principles
Flipped Classroom centers on reversing traditional teaching by delivering instructional content outside the classroom, often through video lectures, enabling in-class time for interactive activities and personalized guidance. Core principles emphasize active learning, student engagement, and the cultivation of critical thinking skills. This model enhances comprehension by transforming students from passive recipients to active participants in their educational process.
Understanding Hybrid Learning Models
Hybrid learning models combine traditional face-to-face instruction with online educational activities, allowing flexible access to course materials and interactive experiences both in-person and remotely. This approach supports differentiated learning paths, leveraging technology to enhance student engagement and accommodate diverse learning styles. Understanding hybrid learning requires analyzing how synchronous and asynchronous components integrate to optimize pedagogical outcomes and resource utilization.
Key Differences Between Flipped and Hybrid Approaches
Flipped Classroom centers on students reviewing instructional content at home through videos or readings, while class time is dedicated to interactive activities and personalized support. Hybrid Learning blends in-person and online education, allowing students to attend some sessions face-to-face and others remotely, often with synchronous and asynchronous elements. The core difference lies in Flipped Classroom restructuring content delivery to maximize in-class engagement and Hybrid Learning combining delivery modes to offer flexibility in location and scheduling.
Benefits of Flipped Classroom for Student Engagement
Flipped Classroom enhances student engagement by allowing learners to access instructional materials at their own pace, promoting active participation during in-class activities. This approach fosters deeper understanding through interactive discussions and collaborative problem-solving, increasing motivation and retention. Compared to Hybrid Learning, Flipped Classroom specifically empowers students to take control of their learning process, leading to higher levels of critical thinking and personalized feedback.
Advantages of Hybrid Learning for Flexibility
Hybrid learning offers unmatched flexibility by combining online and in-person instruction, allowing students to tailor their schedules to personal needs and learning preferences. This model supports diverse learning environments, enhancing accessibility for students with varying commitments or geographic constraints. The seamless integration of digital tools and face-to-face interaction enriches the educational experience, fostering higher engagement and adaptability.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Model
Flipped Classroom models face challenges such as requiring students to have reliable internet access and self-discipline to complete pre-class assignments, which can create disparities in learning outcomes. Hybrid Learning encounters limitations including difficulties in managing simultaneous in-person and remote students, as well as increased demands on instructors to design flexible lesson plans that engage both groups effectively. Both models require significant technological infrastructure and training to overcome these barriers and optimize student engagement.
Technology’s Role in Flipped and Hybrid Classrooms
Technology in flipped classrooms primarily involves digital tools like video lectures, learning management systems, and interactive apps that enable students to engage with content before class, enhancing self-paced learning and in-class active participation. Hybrid learning integrates technology to facilitate seamless switching between in-person and online instruction, utilizing platforms for live streaming, collaboration, and real-time assessment to support flexible and inclusive education. Both models rely heavily on robust internet connectivity, multimedia resources, and data analytics to monitor student progress and personalize learning experiences effectively.
Choosing the Right Model for Educational Goals
Flipped Classroom emphasizes pre-class content engagement, allowing in-class time for interactive activities and personalized support, ideal for mastery-based learning objectives. Hybrid Learning combines online and face-to-face instruction, offering flexibility and varied delivery modes suited for diverse learner needs and comprehensive curriculum coverage. Selecting the right model depends on factors like student autonomy, technological access, instructional goals, and assessment strategies to maximize educational outcomes.
Future Trends in Innovative Learning Environments
Flipped Classroom models emphasize student-centered learning by delivering instructional content online outside of class and using in-person time for interactive activities, fostering deeper engagement and personalized feedback. Hybrid Learning integrates face-to-face and online education, offering flexibility and scalability that supports diverse learning preferences and access to resources. Emerging trends highlight AI-driven analytics and immersive technologies, such as VR and AR, enhancing adaptive learning environments and real-time collaboration in both flipped and hybrid settings.
Flipped Classroom Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com