Immersion education places students in environments where the target language is the primary medium of instruction, accelerating language acquisition through natural communication. This method enhances cognitive skills and cultural understanding by engaging learners in immersive, context-rich experiences. Discover how immersion education can transform your language learning journey in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
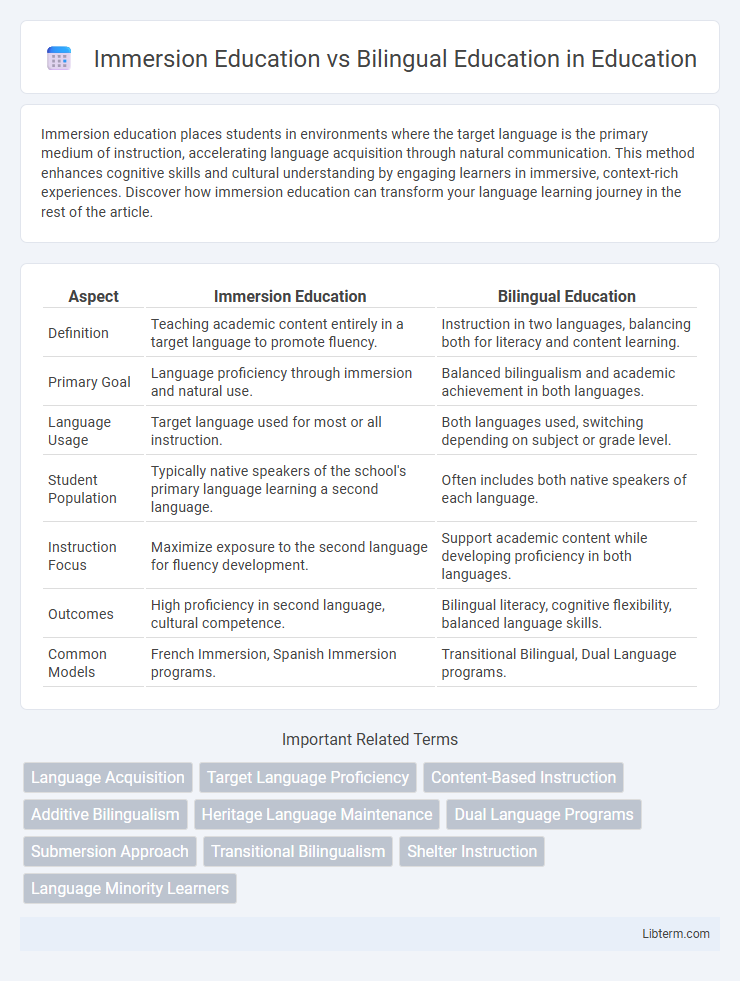
| Aspect | Immersion Education | Bilingual Education |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Teaching academic content entirely in a target language to promote fluency. | Instruction in two languages, balancing both for literacy and content learning. |
| Primary Goal | Language proficiency through immersion and natural use. | Balanced bilingualism and academic achievement in both languages. |
| Language Usage | Target language used for most or all instruction. | Both languages used, switching depending on subject or grade level. |
| Student Population | Typically native speakers of the school's primary language learning a second language. | Often includes both native speakers of each language. |
| Instruction Focus | Maximize exposure to the second language for fluency development. | Support academic content while developing proficiency in both languages. |
| Outcomes | High proficiency in second language, cultural competence. | Bilingual literacy, cognitive flexibility, balanced language skills. |
| Common Models | French Immersion, Spanish Immersion programs. | Transitional Bilingual, Dual Language programs. |
Understanding Immersion Education
Immersion education is a language teaching approach where students are taught core subjects in a target language, promoting natural language acquisition through context and content. This method enhances fluency by surrounding learners with the language daily, fostering both linguistic and cognitive development. Unlike traditional bilingual education, immersion emphasizes immersive exposure over separate language instruction periods.
Defining Bilingual Education
Bilingual education refers to instructional programs that use two languages for teaching academic content, helping students develop proficiency in both their native language and a second language. This approach supports cognitive development, cultural awareness, and academic achievement by integrating language learning with subject matter instruction. Effective bilingual education balances language acquisition with curriculum goals, differentiating it from immersion education, which emphasizes intensive exposure to a single target language.
Key Differences Between Immersion and Bilingual Approaches
Immersion education emphasizes teaching students primarily in a target language to develop fluency, often starting from early grades with minimal use of the native language. In contrast, bilingual education integrates instruction in both the native and target languages to promote balanced proficiency and cultural understanding. Key differences include the degree of native language use, instructional goals--immersion focuses on rapid second language acquisition while bilingual education supports cognitive development in both languages--and the methods of assessment tailored to each approach.
Language Acquisition Goals
Immersion education prioritizes rapid language acquisition by teaching subjects primarily in the target language, fostering natural context-based learning and fluency development. Bilingual education emphasizes balanced proficiency, integrating instruction in both the native and target languages to promote academic achievement alongside language skills. Both approaches aim to enhance multilingual competence but differ in intensity and focus on language use within the curriculum.
Curriculum Design and Structure
Immersion education features a curriculum designed to teach academic content primarily through a target language, promoting language proficiency by integrating language learning with subject instruction. Bilingual education employs a dual-language curriculum that balances instruction in both the native and target languages to develop literacy and content knowledge in both languages concurrently. The structured approach in immersion programs often emphasizes full language immersion early on, while bilingual education strategically divides instructional time to support bilingual competence and cultural understanding.
Cognitive Benefits and Challenges
Immersion education enhances cognitive flexibility and executive function by requiring students to process and switch between languages in real-time, fostering improved problem-solving and multitasking skills. Bilingual education supports metalinguistic awareness and cultural competence, which strengthens memory and verbal abilities, yet may present challenges in balancing language proficiency and academic content mastery. Both models contribute to cognitive development but necessitate tailored instructional strategies to address potential language interference and fluency disparities.
Cultural Integration and Identity Formation
Immersion education fosters cultural integration by surrounding students with the target language and culture, facilitating authentic identity formation through immersive experiences. Bilingual education supports identity development by valuing both the native and second languages, promoting a balanced cultural awareness and self-concept. Both approaches contribute to linguistic proficiency and cultural competence, but immersion education offers deeper cultural immersion while bilingual education emphasizes maintaining heritage language and identity.
Teacher Qualifications and Training
Teacher qualifications in immersion education typically require fluency in the target language and specialized training in language acquisition methods, ensuring effective content delivery solely in the second language. In contrast, bilingual education educators often possess certifications in both languages and training in cross-linguistic instructional strategies to support simultaneous development of students' native and second languages. Professional development for immersion teachers emphasizes cultural competence and immersive pedagogies, whereas bilingual educators focus on balancing linguistic and academic skills across two languages.
Parental Involvement and Community Support
Parental involvement in immersion education often requires active engagement in reinforcing target language use at home, enhancing students' linguistic competence and cultural understanding, while in bilingual education, parents tend to support dual language development balanced between both languages. Community support for immersion programs typically includes partnerships with cultural organizations and native speaker networks, fostering authentic language experiences, whereas bilingual education benefits from broader institutional backing that promotes academic achievement and cultural inclusivity across diverse populations. Research indicates that strong parental commitment and community collaboration are crucial for maximizing language proficiency outcomes and sustaining program effectiveness in both educational models.
Choosing the Right Model for Your Child
Selecting the right language learning approach depends on your child's specific needs, language goals, and learning environment. Immersion education places your child predominantly in a target language setting, fostering fluency through constant exposure, while bilingual education balances instruction equally between two languages to develop proficiency in both. Consider factors such as your child's age, cultural background, and long-term language objectives to determine whether immersive practice or balanced bilingualism best supports their cognitive and academic growth.
Immersion Education Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com