Experiential learning immerses you in hands-on activities that enhance understanding and retention by connecting theory with real-world practice. This approach fosters critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and deeper engagement through direct experience. Explore the rest of the article to discover how experiential learning can transform your educational journey.
Table of Comparison
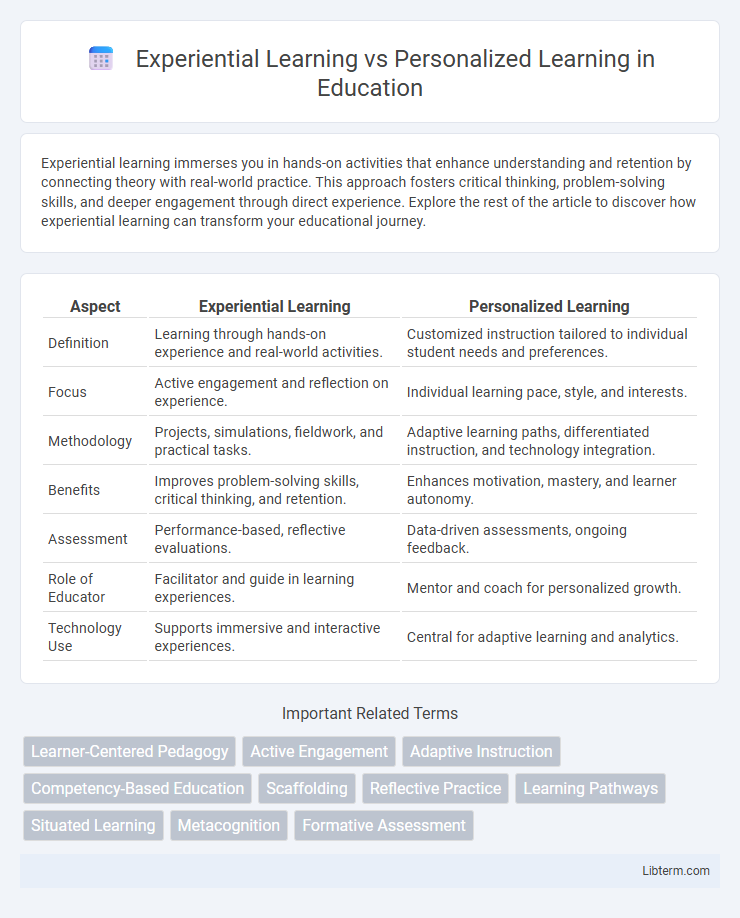
| Aspect | Experiential Learning | Personalized Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Learning through hands-on experience and real-world activities. | Customized instruction tailored to individual student needs and preferences. |
| Focus | Active engagement and reflection on experience. | Individual learning pace, style, and interests. |
| Methodology | Projects, simulations, fieldwork, and practical tasks. | Adaptive learning paths, differentiated instruction, and technology integration. |
| Benefits | Improves problem-solving skills, critical thinking, and retention. | Enhances motivation, mastery, and learner autonomy. |
| Assessment | Performance-based, reflective evaluations. | Data-driven assessments, ongoing feedback. |
| Role of Educator | Facilitator and guide in learning experiences. | Mentor and coach for personalized growth. |
| Technology Use | Supports immersive and interactive experiences. | Central for adaptive learning and analytics. |
Understanding Experiential Learning
Experiential learning emphasizes acquiring knowledge through direct experience, engaging learners in real-world tasks that promote critical thinking and problem-solving skills. This method leverages active participation and reflection, enabling deeper understanding by connecting theory to practice. Unlike personalized learning, which tailors content to individual preferences and pace, experiential learning focuses on hands-on activities that foster collaboration and practical skill development.
Defining Personalized Learning
Personalized learning tailors educational experiences to individual student needs, preferences, and learning styles by leveraging data-driven insights and adaptive technologies. It emphasizes learner agency, allowing students to set goals, pace their progress, and engage with content that matches their unique strengths and interests. In contrast to experiential learning's focus on hands-on activities and real-world experiences, personalized learning centers on customizable pathways to optimize academic outcomes and motivation.
Key Principles of Experiential Learning
Experiential learning centers on active engagement, where learners gain knowledge through direct experience, reflection, and application, emphasizing concrete involvement over passive reception. Key principles include learning by doing, critical reflection on experiences, and the integration of hands-on activities that connect theory with practice. This approach fosters deeper understanding and skill acquisition by encouraging learners to actively participate in real-world scenarios and continuously adapt their learning strategies.
Core Elements of Personalized Learning
Core elements of personalized learning include learner profiles, customized learning paths, and competency-based progression, allowing instruction to adapt to individual needs and preferences. Experiential learning emphasizes hands-on, real-world experiences, but personalized learning integrates these experiences through tailored pacing and targeted feedback. This individualized approach enhances engagement and mastery by aligning educational content with each student's strengths and goals.
Differences in Instructional Strategies
Experiential learning uses hands-on activities, real-world experiences, and reflection to deepen understanding and develop practical skills, emphasizing active participation in authentic contexts. Personalized learning tailors instruction to individual learners' needs, preferences, and pace by leveraging adaptive technologies and data-driven insights for customized content and assessment. While experiential learning focuses on engagement through experience, personalized learning centers on customization and learner autonomy to optimize educational outcomes.
Impact on Student Engagement
Experiential learning significantly boosts student engagement by immersing learners in hands-on, real-world activities that enhance understanding and retention. Personalized learning further elevates engagement by tailoring instruction to individual student needs, preferences, and pace, promoting autonomy and motivation. Combining both approaches creates a dynamic learning environment where active participation and customized experiences drive deeper academic commitment.
Assessment Methods: Experiential vs Personalized
Experiential learning assessment methods emphasize performance-based evaluations such as projects, simulations, and real-world problem-solving tasks that measure applied skills and critical thinking. Personalized learning assessments rely on adaptive tests, learning analytics, and continuous feedback mechanisms tailored to individual progress and mastery levels. Both approaches prioritize formative assessment but differ in context, with experiential focusing on practical application and personalized on individualized learning paths.
Real-World Applications and Examples
Experiential learning immerses students in hands-on activities like internships and simulations, fostering practical skills through real-world problem solving in fields such as engineering and healthcare. Personalized learning tailors educational experiences to individual interests and goals, integrating projects that reflect students' career aspirations, such as custom research assignments or personalized tech development tasks. Both approaches emphasize active engagement, but experiential learning centers on direct interaction with tangible environments, whereas personalized learning adapts content and pace for maximal relevance and motivation.
Benefits and Limitations Compared
Experiential learning enhances skill acquisition through hands-on activities, fostering critical thinking and real-world problem-solving, but may lack customization for diverse learning paces. Personalized learning tailors content to individual needs, improving engagement and retention, yet it can require significant technological resources and may reduce collaborative experiences. Both methods benefit learners by addressing different educational goals, but integrating them strategically maximizes strengths while mitigating limitations.
Choosing the Right Approach for Learners
Experiential learning emphasizes hands-on experiences and real-world application, engaging learners through active participation and reflection to deepen understanding. Personalized learning tailors educational content, pace, and style to individual learner needs, promoting autonomy and maximizing engagement. Choosing the right approach depends on learner goals, context, and preferred learning styles, ensuring a balance between practical skills development and customized educational pathways.
Experiential Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com