Project-Based Learning immerses You in real-world challenges that enhance critical thinking, collaboration, and problem-solving skills. This hands-on approach connects academic knowledge with practical application, fostering deeper understanding and retention. Explore the rest of the article to discover how Project-Based Learning can transform Your educational experience.
Table of Comparison
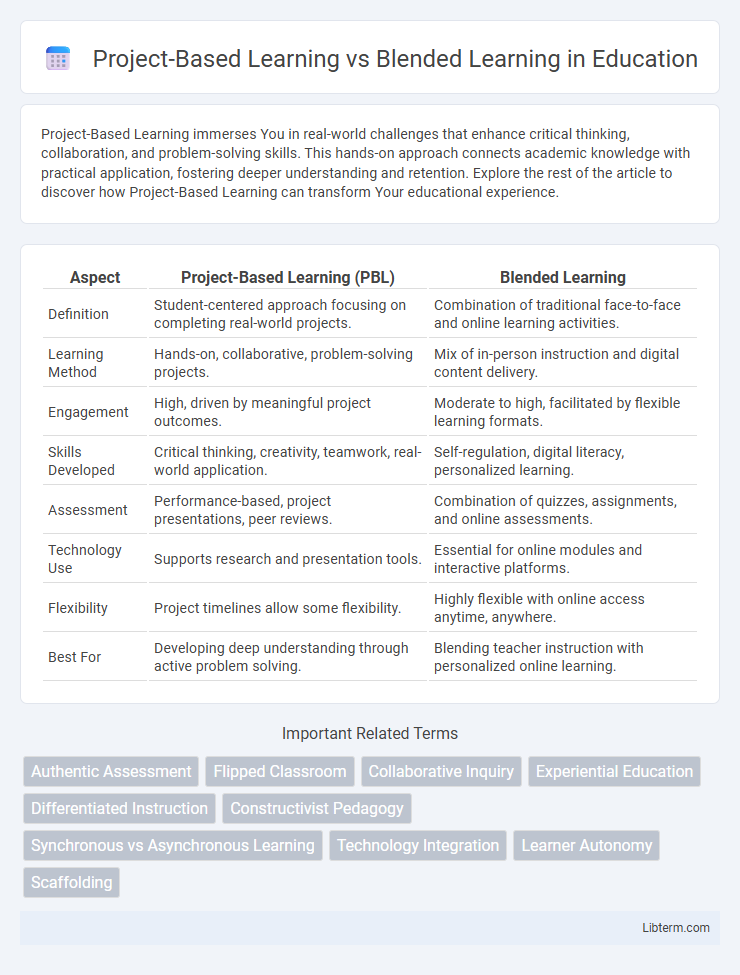
| Aspect | Project-Based Learning (PBL) | Blended Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Student-centered approach focusing on completing real-world projects. | Combination of traditional face-to-face and online learning activities. |
| Learning Method | Hands-on, collaborative, problem-solving projects. | Mix of in-person instruction and digital content delivery. |
| Engagement | High, driven by meaningful project outcomes. | Moderate to high, facilitated by flexible learning formats. |
| Skills Developed | Critical thinking, creativity, teamwork, real-world application. | Self-regulation, digital literacy, personalized learning. |
| Assessment | Performance-based, project presentations, peer reviews. | Combination of quizzes, assignments, and online assessments. |
| Technology Use | Supports research and presentation tools. | Essential for online modules and interactive platforms. |
| Flexibility | Project timelines allow some flexibility. | Highly flexible with online access anytime, anywhere. |
| Best For | Developing deep understanding through active problem solving. | Blending teacher instruction with personalized online learning. |
Introduction to Project-Based Learning and Blended Learning
Project-Based Learning (PBL) engages students through hands-on projects that promote critical thinking, problem-solving, and collaboration, enhancing real-world application of knowledge. Blended Learning combines traditional face-to-face instruction with online digital media, allowing personalized pacing and diversified instructional methods. Both methodologies leverage active learning but differ in delivery, with PBL centered on immersive projects and Blended Learning integrating multiple teaching formats for a flexible educational experience.
Key Principles of Project-Based Learning
Project-Based Learning (PBL) emphasizes student-centered inquiry through real-world projects that develop critical thinking, collaboration, and problem-solving skills. Key principles include sustained inquiry where students engage deeply over time, authentic tasks that have meaningful outcomes, and reflection to foster deeper understanding and self-assessment. PBL also prioritizes student voice and choice, allowing learners to direct their own projects and build ownership over their educational experience.
Core Components of Blended Learning
Blended Learning integrates online digital content with traditional face-to-face instruction, emphasizing core components such as personalized learning paths, flexible scheduling, and data-driven assessment to optimize student engagement and mastery. Project-Based Learning centers on student-driven projects that develop critical thinking and collaboration skills, but when combined within Blended Learning environments, it benefits from technology-enhanced resources and adaptive feedback systems. The core components of Blended Learning--meaningful content delivery through digital platforms, teacher-facilitated guidance, and ongoing performance analytics--create a dynamic framework that supports both individualized and project-based instructional approaches.
Differences in Instructional Design
Project-Based Learning (PBL) centers instructional design around student-driven projects that require critical thinking, collaboration, and real-world problem-solving over extended periods. Blended Learning integrates traditional face-to-face teaching with online digital media, balancing synchronous instruction and self-paced learning activities to accommodate diverse learning styles. The primary difference lies in PBL's emphasis on immersive project completion as the core pedagogical approach, whereas Blended Learning combines various delivery methods to enhance flexibility and accessibility in instruction.
Levels of Student Engagement
Project-Based Learning (PBL) significantly enhances student engagement by promoting active participation through real-world problem-solving and collaboration, leading to deeper understanding and retention of knowledge. Blended Learning integrates traditional face-to-face teaching with online resources, offering flexible, personalized learning experiences that cater to diverse student needs and increase motivation. Both methods foster higher engagement levels compared to conventional teaching but differ in execution: PBL centers on immersive projects while Blended Learning leverages digital tools for continuous, adaptive interaction.
Assessment Methods in Both Approaches
Project-Based Learning employs performance-based assessments, where students demonstrate their understanding through real-world projects, presentations, and portfolios, emphasizing critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Blended Learning combines formative assessments and digital tools, enabling continuous feedback and personalized learning paths by integrating online quizzes, interactive assignments, and teacher evaluations. Both approaches prioritize authentic assessment but differ in delivery, with Project-Based Learning focusing on applied knowledge and Blended Learning leveraging technology for ongoing measurement of student progress.
Technology Integration and Its Role
Project-Based Learning (PBL) leverages technology as a central tool for research, collaboration, and real-world problem-solving, enabling students to create digital presentations, simulations, and prototypes. Blended Learning combines traditional face-to-face instruction with online digital resources, using technology to personalize learning paths and provide immediate feedback through learning management systems and interactive platforms. Both approaches rely heavily on technology integration to enhance engagement, foster critical thinking, and support differentiated instruction in modern classrooms.
Teacher’s Role and Facilitation
In Project-Based Learning, teachers act as facilitators who guide students through complex tasks by providing resources, feedback, and scaffolding to promote independent critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Blended Learning teachers balance in-person instruction with digital tools, tailoring support to individual student needs while managing online platforms for content delivery and assessment. Both approaches require educators to shift from traditional lecturing to active mentorship, fostering student engagement and self-directed learning.
Real-World Applications and Outcomes
Project-Based Learning immerses students in real-world problems, fostering critical thinking, collaboration, and practical skill development through hands-on projects directly tied to authentic challenges. Blended Learning combines online digital resources with traditional classroom methods, allowing personalized pacing and immediate access to real-world case studies that enhance understanding and application. Both approaches improve outcomes by connecting theory to practice, but Project-Based Learning emphasizes active creation while Blended Learning provides flexible, multifaceted access to relevant content.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Classroom
Project-Based Learning emphasizes hands-on, real-world problem solving that boosts critical thinking and collaboration skills among students, making it ideal for classrooms aiming to foster creativity and autonomy. Blended Learning combines traditional face-to-face instruction with digital tools, providing flexibility and personalized pacing, which suits diverse learning styles and improves engagement through technology integration. Selecting the right approach depends on factors like curriculum goals, available resources, student needs, and teacher expertise to maximize educational outcomes effectively.
Project-Based Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com