Project-Based Learning immerses students in hands-on, real-world challenges that promote critical thinking, collaboration, and creativity. This educational approach enhances your ability to apply knowledge practically while fostering deeper understanding and retention. Explore the rest of the article to discover how Project-Based Learning can transform your educational experience.
Table of Comparison
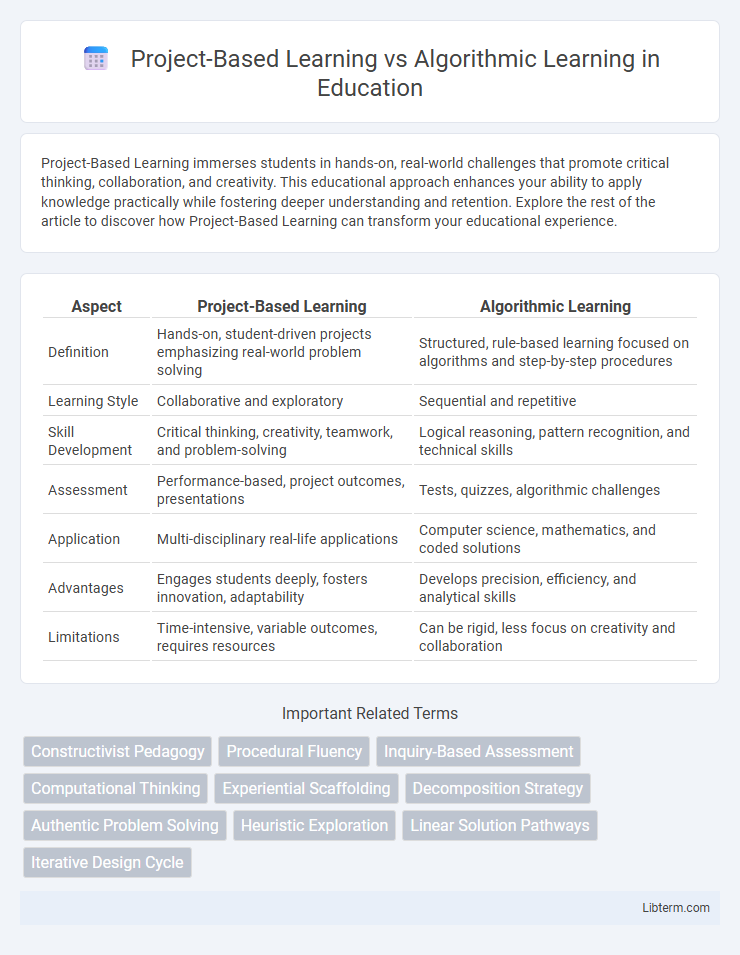
| Aspect | Project-Based Learning | Algorithmic Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Hands-on, student-driven projects emphasizing real-world problem solving | Structured, rule-based learning focused on algorithms and step-by-step procedures |
| Learning Style | Collaborative and exploratory | Sequential and repetitive |
| Skill Development | Critical thinking, creativity, teamwork, and problem-solving | Logical reasoning, pattern recognition, and technical skills |
| Assessment | Performance-based, project outcomes, presentations | Tests, quizzes, algorithmic challenges |
| Application | Multi-disciplinary real-life applications | Computer science, mathematics, and coded solutions |
| Advantages | Engages students deeply, fosters innovation, adaptability | Develops precision, efficiency, and analytical skills |
| Limitations | Time-intensive, variable outcomes, requires resources | Can be rigid, less focus on creativity and collaboration |
Introduction to Project-Based Learning and Algorithmic Learning
Project-Based Learning (PBL) emphasizes active student engagement through real-world problem-solving and collaborative projects, fostering critical thinking and creativity. Algorithmic Learning centers on step-by-step procedures and rule-based approaches, promoting procedural knowledge and mastery of specific skills. Both methodologies offer distinct advantages in educational contexts, with PBL enhancing experiential learning and Algorithmic Learning ensuring structured skill development.
Defining the Core Concepts
Project-Based Learning centers on engaging students in real-world challenges, fostering critical thinking, collaboration, and practical application of knowledge through extended projects. Algorithmic Learning emphasizes step-by-step problem-solving procedures, focusing on mastering specific algorithms and structured tasks to build computational proficiency. Understanding these core concepts highlights the experiential, integrative nature of Project-Based Learning compared to the systematic, procedural focus of Algorithmic Learning.
Historical Background and Educational Context
Project-Based Learning (PBL) emerged in the early 20th century, inspired by John Dewey's constructivist theories emphasizing experiential learning and real-world problem solving. In contrast, Algorithmic Learning roots trace back to behaviorist models and programmed instruction popularized by B.F. Skinner in the mid-20th century, focusing on step-by-step mastery of skills through repetition and reinforcement. Educational contexts show PBL thrives in fostering critical thinking and collaboration in modern STEM education, whereas Algorithmic Learning remains prevalent in foundational skill acquisition, such as mathematics and language drills.
Key Features of Project-Based Learning
Project-Based Learning emphasizes student-driven exploration, real-world problem solving, and collaborative engagement, allowing learners to develop critical thinking and creativity through complex, authentic projects. It integrates interdisciplinary knowledge and fosters communication skills by encouraging teamwork and presentations. This learner-centered approach contrasts with Algorithmic Learning, which focuses on repetitive practice and step-by-step problem-solving for skill acquisition.
Key Features of Algorithmic Learning
Algorithmic learning emphasizes structured, step-by-step problem-solving methods, relying on predefined rules and sequences to reach solutions efficiently. It incorporates repetitive practice and pattern recognition, enabling learners to automate tasks and enhance precision in subjects like mathematics and computer science. This approach focuses on mastering specific algorithms, promoting logical thinking and systematic analysis over exploratory or hands-on project work.
Comparative Benefits and Challenges
Project-Based Learning fosters critical thinking and creativity by engaging students in real-world problem-solving, promoting collaboration and deeper understanding of concepts. Algorithmic Learning offers systematic skill acquisition and efficiency through repetitive practice and well-defined procedures, ideal for mastering foundational knowledge and technical tasks. While Project-Based Learning can face challenges such as time constraints and assessment difficulties, Algorithmic Learning may limit innovation and flexibility, highlighting the importance of balancing both approaches for comprehensive education.
Applicability Across Different Subjects
Project-Based Learning (PBL) excels in subjects like science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) by promoting hands-on experimentation and real-world problem-solving. Algorithmic learning is highly effective in disciplines requiring step-by-step procedural knowledge, such as mathematics, computer science, and language grammar. Both approaches can be blended to enhance adaptability and engagement across diverse educational fields, fostering critical thinking and practical skill application.
Impact on Student Engagement and Motivation
Project-Based Learning (PBL) significantly enhances student engagement and motivation by fostering hands-on experiences, real-world problem-solving, and collaborative teamwork, which stimulate deeper cognitive involvement. In contrast, Algorithmic Learning primarily emphasizes repetitive practice and step-by-step procedures, often resulting in lower intrinsic motivation and limited creative exploration. Research shows that PBL increases student enthusiasm and retention of knowledge by connecting academic content to meaningful projects, while Algorithmic Learning can lead to disengagement due to its prescriptive and less interactive nature.
Assessing Outcomes and Skill Development
Project-Based Learning emphasizes real-world problem-solving and collaboration, fostering critical thinking, creativity, and communication skills through practical application. Algorithmic Learning prioritizes step-by-step procedural mastery, enhancing computational thinking, logical reasoning, and precision in following defined processes. Assessing outcomes in Project-Based Learning involves evaluating project deliverables and teamwork, while Algorithmic Learning assessments focus on accuracy, efficiency, and adherence to algorithms.
Choosing the Right Approach for Diverse Learners
Project-Based Learning (PBL) promotes critical thinking, creativity, and real-world application by engaging learners in hands-on tasks, ideal for students who thrive on exploration and collaboration. Algorithmic Learning emphasizes step-by-step procedures and repetitive practice, benefiting learners who excel with structure and clear, measurable outcomes. Selecting the right approach depends on assessing learners' cognitive styles, motivation levels, and educational goals to tailor instruction that fosters effective knowledge retention and skill development.
Project-Based Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com