Summative assessment evaluates your learning at the end of an instructional unit by measuring the achievement of specific objectives, typically through exams, projects, or presentations. It provides a comprehensive overview of your understanding and helps educators determine the effectiveness of their teaching strategies. Explore the rest of the article to learn how summative assessment can impact your academic progress and success.
Table of Comparison
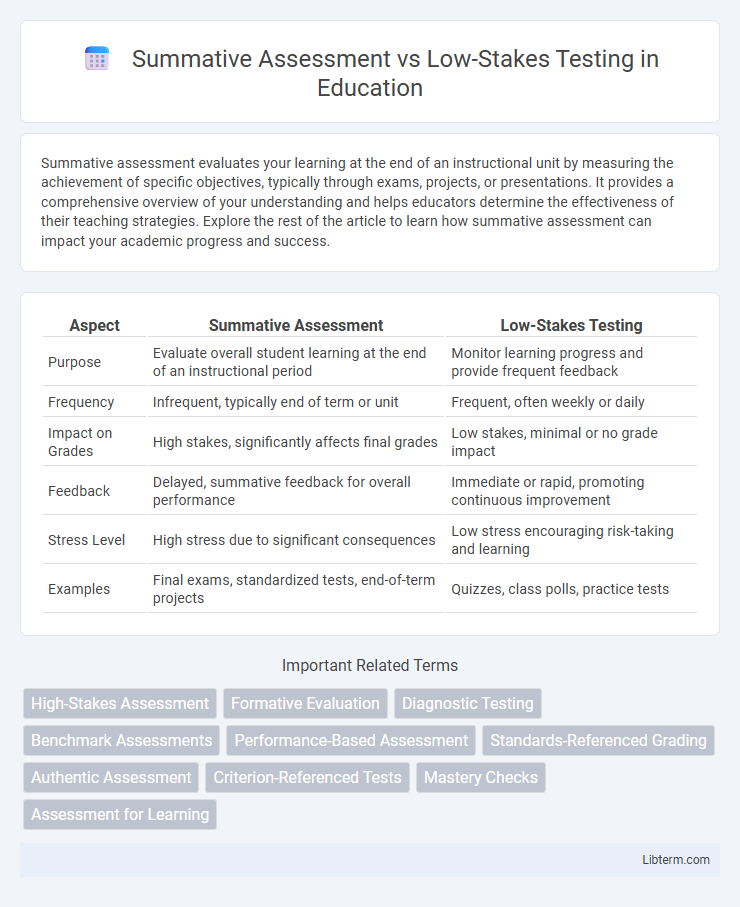
| Aspect | Summative Assessment | Low-Stakes Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Evaluate overall student learning at the end of an instructional period | Monitor learning progress and provide frequent feedback |
| Frequency | Infrequent, typically end of term or unit | Frequent, often weekly or daily |
| Impact on Grades | High stakes, significantly affects final grades | Low stakes, minimal or no grade impact |
| Feedback | Delayed, summative feedback for overall performance | Immediate or rapid, promoting continuous improvement |
| Stress Level | High stress due to significant consequences | Low stress encouraging risk-taking and learning |
| Examples | Final exams, standardized tests, end-of-term projects | Quizzes, class polls, practice tests |
Understanding Summative Assessment
Summative assessment evaluates student learning at the end of an instructional period by measuring mastery of specific learning objectives through standardized tests, final exams, or projects. This form of assessment provides comprehensive data on student performance, enabling educators to make informed decisions about curriculum effectiveness and student readiness. Unlike low-stakes testing, summative assessments carry significant weight and influence final grades or certifications, emphasizing the importance of accurate and thorough evaluation.
Defining Low-Stakes Testing
Low-stakes testing refers to assessments that have minimal or no direct consequences on a student's academic progress or grades, designed primarily to monitor learning and inform instruction. These tests provide ongoing feedback, reduce anxiety, and encourage risk-taking and deeper engagement with the material. Unlike summative assessments, low-stakes tests emphasize formative learning and skill development rather than final evaluation.
Key Differences Between Summative Assessment and Low-Stakes Testing
Summative assessment evaluates student learning at the end of an instructional period, providing a comprehensive measure of achievement through exams, final projects, or standardized tests. Low-stakes testing involves frequent, informal assessments such as quizzes or practice tests designed to monitor progress without heavily impacting grades. Key differences include their purpose, with summative assessments aiming for final evaluation and accountability, whereas low-stakes tests support ongoing learning and feedback.
Purpose and Goals of Each Assessment Type
Summative assessments aim to evaluate student learning by measuring mastery of course objectives at the end of an instructional period, often influencing final grades and academic progression. Low-stakes testing serves to monitor ongoing learning, provide frequent feedback, and reduce anxiety by emphasizing practice and skill development without heavily impacting grades. Each assessment type supports different educational goals: summative assessments validate achievement, while low-stakes tests enhance formative learning and guide instructional adjustments.
Timing and Frequency in the Assessment Process
Summative assessments occur at the end of a learning period to evaluate overall student mastery, typically administered once per term or course. Low-stakes testing involves frequent, informal assessments throughout the instructional process to monitor ongoing progress and provide immediate feedback. The timing and frequency differences highlight summative assessments' role in final evaluation versus low-stakes tests' function in continuous learning support.
Impact on Student Learning and Motivation
Summative assessment, typically administered at the end of a learning period, provides a comprehensive evaluation of student achievement and can influence motivation by emphasizing performance outcomes, often increasing test anxiety. Low-stakes testing, characterized by frequent, formative evaluations with minimal grade impact, promotes a growth mindset by encouraging ongoing learning and reducing pressure, thereby enhancing student engagement and retention. Research indicates that integrating low-stakes assessments supports better long-term academic achievement and sustained motivation compared to reliance solely on summative assessments.
Examples of Summative Assessments
Summative assessments include final exams, standardized tests, end-of-term projects, and cumulative portfolios that evaluate overall student learning at the conclusion of an instructional period. These assessments typically determine course grades or measure competency against established academic standards. Examples such as state achievement tests and final presentations provide critical data for educators and policymakers on student performance and curriculum effectiveness.
Examples of Low-Stakes Testing
Low-stakes testing includes formative quizzes, in-class polls, and practice exams that provide ongoing feedback without heavily impacting final grades. Examples such as weekly vocabulary quizzes, clicker questions during lectures, and ungraded peer review activities help students identify learning gaps and promote continuous improvement. These assessments foster a low-pressure environment, encouraging risk-taking and active engagement in the learning process.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Method
Summative assessment provides a comprehensive evaluation of student learning at the end of an instructional period, enabling educators to measure mastery and inform curriculum decisions, but it can induce high stress and may not offer timely feedback for improvement. Low-stakes testing reduces anxiety by focusing on formative feedback, encouraging continuous learning and skill development, though it may lack the rigor and comprehensive scope necessary for accurately gauging overall achievement. Balancing both methods allows for effective performance measurement while supporting ongoing student engagement and growth.
Choosing the Right Assessment Strategy
Summative assessments provide comprehensive evaluations of student learning at the end of instructional units, making them ideal for measuring overall achievement and accountability. Low-stakes testing offers frequent, low-pressure opportunities to monitor progress and inform instruction without the stress of high-grade consequences. Selecting the right assessment strategy involves balancing accuracy in measuring mastery with fostering a supportive learning environment that encourages continuous improvement.
Summative Assessment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com