Dual Language Programs enhance bilingual proficiency by immersing students in both languages throughout the curriculum, promoting cognitive development and cultural awareness. These programs support academic achievement while fostering a deeper understanding of diverse perspectives. Discover how participating in a Dual Language Program can transform Your educational experience by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
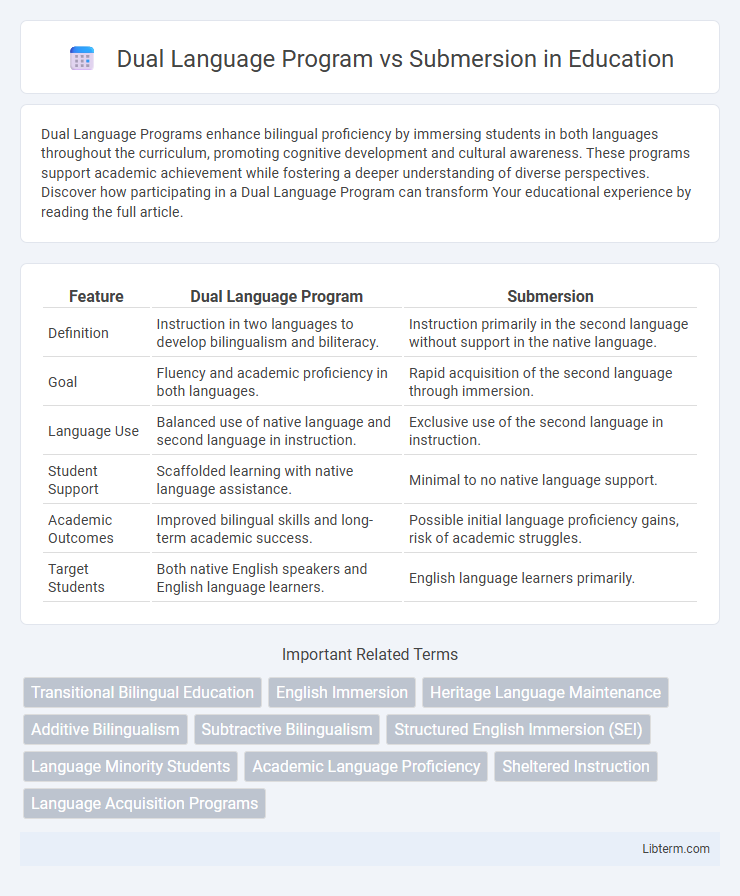
| Feature | Dual Language Program | Submersion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Instruction in two languages to develop bilingualism and biliteracy. | Instruction primarily in the second language without support in the native language. |
| Goal | Fluency and academic proficiency in both languages. | Rapid acquisition of the second language through immersion. |
| Language Use | Balanced use of native language and second language in instruction. | Exclusive use of the second language in instruction. |
| Student Support | Scaffolded learning with native language assistance. | Minimal to no native language support. |
| Academic Outcomes | Improved bilingual skills and long-term academic success. | Possible initial language proficiency gains, risk of academic struggles. |
| Target Students | Both native English speakers and English language learners. | English language learners primarily. |
Introduction to Dual Language Programs and Submersion
Dual Language Programs immerse students in both their native language and a second language, promoting bilingualism, biliteracy, and cross-cultural competence from an early age. Submersion programs, on the other hand, place non-English speakers in mainstream English-only classrooms without targeted language support, often leading to limited academic progress and decreased self-esteem. Research highlights that Dual Language Programs yield higher academic achievement and stronger language proficiency compared to submersion approaches.
Key Concepts: Bilingualism vs Monolingual Immersion
Dual Language Programs promote bilingualism by fostering proficiency in two languages through balanced instruction, enhancing cognitive flexibility and cultural awareness. In contrast, Submersion immerses students solely in the majority language, often leading to monolingual outcomes and limited comprehension in the native language. Research highlights that bilingual education supports long-term academic achievement and identity development, whereas submersion may cause language attrition and hinder academic success for non-native speakers.
Language Development Outcomes
Dual Language Programs promote bilingual proficiency and cognitive flexibility by providing instruction in two languages, resulting in stronger language development outcomes compared to submersion. Submersion, where students are placed in an environment using only the second language without support, often leads to slower language acquisition and lower academic achievement. Research highlights that Dual Language Programs enhance literacy, vocabulary, and cultural competence more effectively than submersion models.
Academic Achievement Comparison
Dual Language Programs consistently demonstrate higher academic achievement compared to Submersion methods by promoting bilingual proficiency and cognitive development. Research indicates students in Dual Language settings outperform peers in Submersion classrooms on standardized tests in reading and math. Enhanced comprehension and critical thinking abilities in Dual Language learners contribute to sustained academic success across subjects.
Cognitive and Social Benefits
Dual Language Programs enhance cognitive flexibility, executive function, and metalinguistic awareness by promoting balanced bilingualism and cultural appreciation. These programs foster social benefits such as increased empathy, cross-cultural communication skills, and stronger peer relationships compared to Submersion models, which often lead to language isolation and social alienation. Research shows that students in Dual Language environments demonstrate improved problem-solving abilities and higher self-esteem due to inclusive, supportive learning contexts.
Impact on Minority and Majority Language Learners
Dual Language Programs promote bilingualism and biliteracy by supporting both minority and majority language learners, enhancing cognitive skills and cultural awareness. Submersion strategies often lead to limited language development for minority students, risking academic delays and loss of heritage language. Majority language learners benefit from Dual Language Programs through increased multicultural competence, while submersion primarily reinforces dominant language acquisition without bilingual advantages.
Teacher Qualifications and Instructional Approaches
Dual Language Programs require teachers with specialized bilingual certification and expertise in culturally responsive pedagogy, enabling instruction in two languages to promote biliteracy and cognitive development. Instructional approaches emphasize balanced use of both languages, integration of content and language objectives, and scaffolding techniques to support English learners while maintaining their native language. In contrast, Submersion programs typically involve instruction primarily in the dominant language, often with teachers lacking bilingual training, which can limit differentiated strategies and reduce support for English language acquisition and cultural relevance.
Program Implementation Challenges
Dual Language Program implementation faces challenges including finding qualified bilingual teachers, aligning curricula across languages, and securing sustained funding for resources and training. Submersion programs often struggle with insufficient language support for English language learners, leading to gaps in academic achievement and increased dropout rates. Both approaches require careful planning and ongoing assessment to address diverse student needs and ensure equitable language development.
Long-Term Advantages and Disadvantages
Dual Language Programs promote bilingual proficiency and cognitive flexibility, leading to enhanced academic performance and cultural awareness over time. In contrast, Submersion methods often result in limited language acquisition and increased risk of academic struggles due to insufficient support for non-native speakers. Long-term disadvantages of Submersion include lower self-esteem and reduced opportunities in a globalized job market, whereas Dual Language Programs foster social integration and expanded career prospects.
Choosing the Right Path: Factors for Families and Schools
Dual Language Programs promote bilingualism and biliteracy by integrating native speakers of two languages, enhancing cognitive development and cultural competence. Submersion, or English-only instruction, immerses students in English but often leads to limited comprehension and slower language acquisition for non-native speakers. Families and schools should consider factors such as student language background, academic goals, and community support when selecting the most effective approach to language learning.
Dual Language Program Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com