An income portfolio focuses on generating regular cash flow through investments such as dividend-paying stocks, bonds, and real estate investment trusts (REITs). Diversification within this portfolio minimizes risk while ensuring steady income streams to support your financial goals. Discover more strategies to optimize your income portfolio in the full article.
Table of Comparison
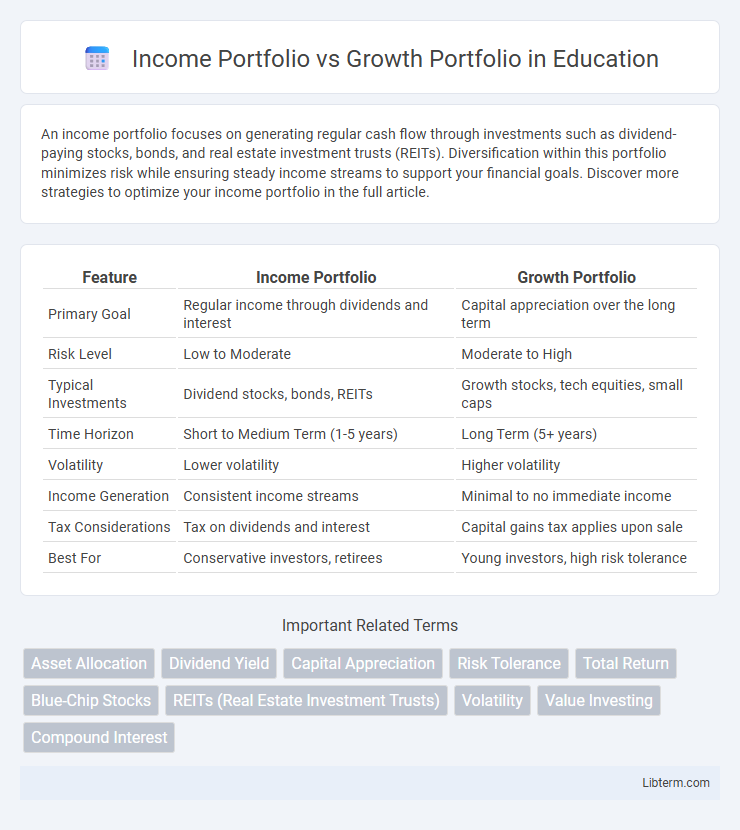
| Feature | Income Portfolio | Growth Portfolio |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Regular income through dividends and interest | Capital appreciation over the long term |
| Risk Level | Low to Moderate | Moderate to High |
| Typical Investments | Dividend stocks, bonds, REITs | Growth stocks, tech equities, small caps |
| Time Horizon | Short to Medium Term (1-5 years) | Long Term (5+ years) |
| Volatility | Lower volatility | Higher volatility |
| Income Generation | Consistent income streams | Minimal to no immediate income |
| Tax Considerations | Tax on dividends and interest | Capital gains tax applies upon sale |
| Best For | Conservative investors, retirees | Young investors, high risk tolerance |
Introduction to Income and Growth Portfolios
Income portfolios primarily focus on generating consistent cash flow through investments in dividend-paying stocks, bonds, and other income-producing assets, appealing to investors seeking regular income streams. Growth portfolios target capital appreciation by investing in stocks of companies with high growth potential, often reinvesting earnings rather than paying dividends. Understanding the risk tolerance and financial goals helps determine the appropriate balance between income and growth portfolios for a diversified investment strategy.
Key Differences Between Income and Growth Portfolios
Income portfolios prioritize generating steady cash flow through dividends or interest from bonds, making them ideal for conservative investors seeking regular income. Growth portfolios focus on capital appreciation by investing in stocks with high potential for price increases, appealing to investors aiming for long-term wealth accumulation. The key differences lie in risk tolerance, investment horizon, and primary objective--income portfolios emphasize stability and income, while growth portfolios target aggressive growth and wealth building.
Investment Objectives: Income vs Growth
Income portfolios prioritize consistent cash flow through dividends or interest, appealing to investors seeking regular income and capital preservation. Growth portfolios emphasize capital appreciation by investing in stocks or assets with high potential for price increase, targeting investors aiming to maximize long-term wealth. Understanding the distinct investment objectives of income versus growth portfolios allows tailored asset allocation aligned with individual financial goals.
Asset Allocation Strategies
Income portfolios prioritize asset allocation toward dividend-paying stocks, bonds, and real estate investment trusts (REITs) to generate steady cash flow and minimize risk. Growth portfolios allocate a higher percentage to equities, including technology and emerging market stocks, aiming for capital appreciation over time despite higher volatility. Balancing these strategies depends on investor goals, risk tolerance, and investment horizons, often blending fixed income and growth assets for diversified returns.
Risk Profiles and Tolerance
Income portfolios prioritize stability and consistent cash flow, typically featuring bonds and dividend-paying stocks, appealing to investors with low to moderate risk tolerance seeking capital preservation. Growth portfolios emphasize capital appreciation, investing heavily in equities and emerging markets, suitable for investors with higher risk tolerance willing to endure volatility for potential long-term gains. Understanding individual risk profiles is crucial, as income portfolios mitigate risk through diversification and steady returns, while growth portfolios accept higher risk in pursuit of substantial wealth accumulation.
Types of Securities in Each Portfolio
Income portfolios primarily consist of dividend-paying stocks, bonds, and other fixed-income securities designed to generate regular cash flow. Growth portfolios emphasize equities with high capital appreciation potential, such as technology stocks, small-cap stocks, and emerging market equities. Income portfolios favor stability and predictable returns, while growth portfolios prioritize reinvestment and long-term capital gains.
Performance Metrics and Expectations
Income portfolios prioritize consistent cash flow through dividends and interest, emphasizing metrics like yield, payout ratio, and income stability. Growth portfolios focus on capital appreciation, with performance assessed via earnings growth rate, price-to-earnings ratio, and total return. Investors in income portfolios expect steady, lower-risk returns, while growth portfolios target higher, long-term gains with increased volatility.
Tax Implications for Investors
Income portfolios typically generate regular dividends or interest, leading to taxable income that investors must report annually, often taxed at ordinary income tax rates. Growth portfolios mainly focus on capital appreciation, with taxes deferred until assets are sold, potentially benefiting from lower long-term capital gains rates. Understanding the tax treatment of dividends versus capital gains is crucial for investors to optimize after-tax returns based on their individual tax situations.
Suitability for Different Investor Profiles
Income portfolios prioritize steady dividends and interest payments, making them ideal for conservative investors seeking regular cash flow and lower risk. Growth portfolios focus on capital appreciation through investing in stocks with high growth potential, suiting aggressive investors willing to accept higher volatility for long-term gains. Balanced investors may blend both portfolio types to optimize income and growth based on their risk tolerance and financial goals.
Choosing the Right Portfolio for Your Financial Goals
An income portfolio prioritizes stable, dividend-paying assets like bonds and dividend stocks, providing consistent cash flow suitable for retirees or those seeking steady income. A growth portfolio focuses on capital appreciation through investments in high-growth stocks and emerging sectors, ideal for investors with longer time horizons aiming to maximize wealth. Selecting the right portfolio depends on your financial objectives, risk tolerance, and investment timeline, ensuring alignment between expected returns and personal goals.
Income Portfolio Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com