Differentiated instruction tailors teaching methods and materials to accommodate diverse learning styles, abilities, and interests within a classroom. By personalizing lessons, educators enhance student engagement and improve academic outcomes. Explore the rest of this article to discover practical strategies for implementing differentiated instruction in your teaching.
Table of Comparison
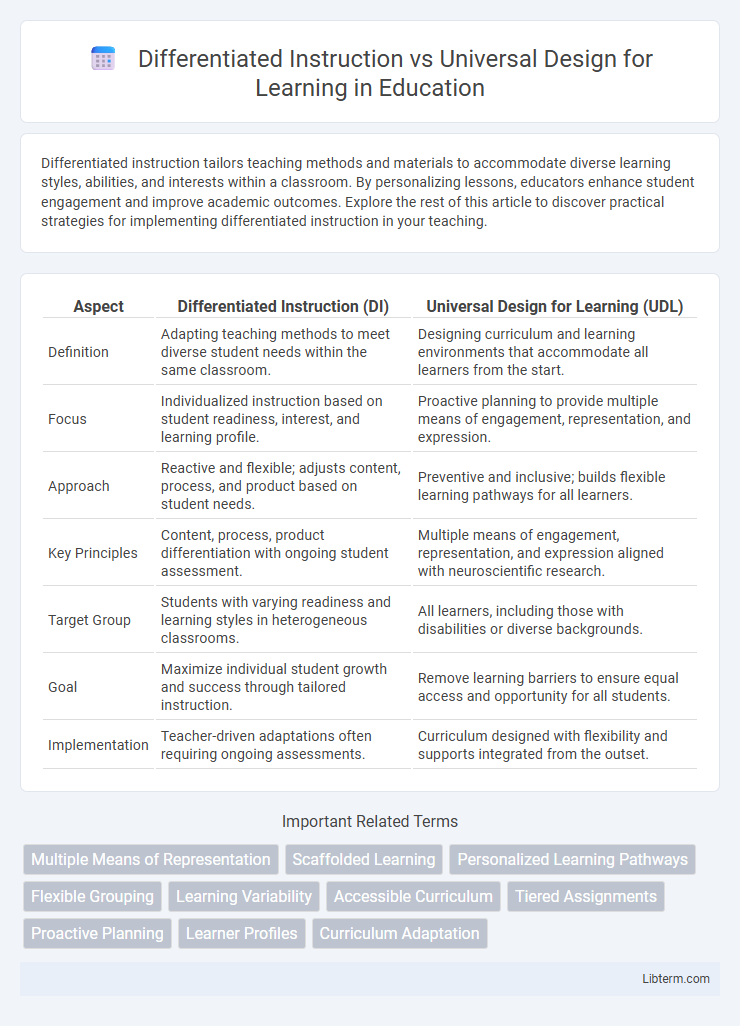
| Aspect | Differentiated Instruction (DI) | Universal Design for Learning (UDL) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adapting teaching methods to meet diverse student needs within the same classroom. | Designing curriculum and learning environments that accommodate all learners from the start. |
| Focus | Individualized instruction based on student readiness, interest, and learning profile. | Proactive planning to provide multiple means of engagement, representation, and expression. |
| Approach | Reactive and flexible; adjusts content, process, and product based on student needs. | Preventive and inclusive; builds flexible learning pathways for all learners. |
| Key Principles | Content, process, product differentiation with ongoing student assessment. | Multiple means of engagement, representation, and expression aligned with neuroscientific research. |
| Target Group | Students with varying readiness and learning styles in heterogeneous classrooms. | All learners, including those with disabilities or diverse backgrounds. |
| Goal | Maximize individual student growth and success through tailored instruction. | Remove learning barriers to ensure equal access and opportunity for all students. |
| Implementation | Teacher-driven adaptations often requiring ongoing assessments. | Curriculum designed with flexibility and supports integrated from the outset. |
Introduction to Differentiated Instruction and Universal Design for Learning
Differentiated Instruction tailors teaching methods, content, and assessments to meet diverse student needs, promoting personalized learning experiences within heterogeneous classrooms. Universal Design for Learning (UDL) establishes flexible learning environments by providing multiple means of engagement, representation, and expression to accommodate all learners from the outset. Both frameworks aim to enhance student accessibility and achievement by addressing variability in learning preferences and abilities through strategic planning and implementation.
Defining Differentiated Instruction: Key Principles
Differentiated Instruction is an educational approach that tailors teaching methods, content, and assessment to meet the diverse needs, readiness levels, and interests of individual students. Key principles include flexible grouping, ongoing assessment, and the use of varied instructional strategies to optimize learning for all students. This approach emphasizes personalized learning experiences that address students' unique strengths and learning profiles within the same classroom environment.
Understanding Universal Design for Learning: Core Concepts
Universal Design for Learning (UDL) centers on creating flexible learning environments that accommodate diverse learner needs through multiple means of engagement, representation, and expression. It emphasizes proactive curriculum design that anticipates barriers and integrates accessible resources to support all students. Unlike Differentiated Instruction, which adapts teaching based on individual student readiness, UDL provides a framework for inclusive education by embedding variability into the learning experience from the outset.
Historical Background and Educational Foundations
Differentiated Instruction (DI) emerged in the 1990s, rooted in Carol Ann Tomlinson's work emphasizing tailored teaching strategies to meet diverse learner needs, while Universal Design for Learning (UDL) originated from the Center for Applied Special Technology (CAST) in the 1990s, focusing on creating flexible learning environments accessible to all students. DI's educational foundation is built on Vygotsky's zone of proximal development and constructivist theories promoting individualized scaffolding, whereas UDL is grounded in neuroscience research, highlighting multiple means of engagement, representation, and expression to address learner variability. Both frameworks aim to maximize student success but differ in their approach: DI adapts instruction based on learner profiles, while UDL proactively designs curricula that anticipate diverse learning needs.
Instructional Strategies in Differentiated Instruction
Instructional strategies in Differentiated Instruction emphasize tailoring content, process, and product based on student readiness, interests, and learning profiles to enhance engagement and mastery. Methods include flexible grouping, tiered assignments, and choice boards that provide diverse pathways for students to access curriculum and demonstrate understanding. This targeted approach contrasts with Universal Design for Learning's focus on creating inclusive learning environments that proactively address variability through multiple means of representation, engagement, and expression.
UDL Framework: Guidelines and Implementation
The Universal Design for Learning (UDL) framework emphasizes creating flexible learning environments that accommodate diverse student needs by implementing its three core principles: multiple means of engagement, representation, and action/expression. UDL guidelines guide educators in designing curriculum and assessments that provide varied methods for information delivery and student interaction, promoting inclusivity and accessibility. Effective UDL implementation involves ongoing assessment and adaptation, using technology and varied instructional strategies to support all learners in achieving individualized and collective educational goals.
Comparing Goals: Equity, Accessibility, and Personalization
Differentiated Instruction aims to tailor teaching methods and content to individual student needs, promoting personalized learning experiences that address diverse abilities and interests. Universal Design for Learning (UDL) focuses on creating flexible learning environments and materials accessible to all students, ensuring equity by removing barriers from the outset. Both frameworks prioritize equity and accessibility, but Differentiated Instruction emphasizes reactive adaptations, while UDL promotes proactive, inclusive design for personalized learning.
Benefits and Challenges of Differentiated Instruction
Differentiated Instruction offers tailored teaching strategies that address diverse student needs, promoting enhanced engagement and improved academic outcomes by customizing content, process, and product based on learners' readiness and interests. Challenges include the increased demand on teachers' time, expertise, and resources to create multiple instructional pathways, potentially leading to inconsistency and difficulty in assessment standardization. Despite these obstacles, Differentiated Instruction provides flexibility that supports individual growth and fosters inclusive learning environments in varied educational settings.
Advantages and Limitations of Universal Design for Learning
Universal Design for Learning (UDL) offers significant advantages such as promoting inclusive education by accommodating diverse learning styles and needs through flexible materials and varied assessment methods. It enhances accessibility by providing multiple means of engagement, representation, and expression, reducing barriers for students with disabilities and those from different cultural backgrounds. However, limitations include the potential complexity and resource intensity of implementing UDL strategies effectively, as well as the need for extensive teacher training and institutional support to ensure consistent application across all educational settings.
Choosing the Right Approach: Integrating DI and UDL in Practice
Choosing the right approach between Differentiated Instruction (DI) and Universal Design for Learning (UDL) involves understanding their complementary strengths: DI tailors instruction to individual learner needs while UDL designs flexible learning environments accessible to all students. Integrating DI and UDL in practice means creating varied pathways for engagement, representation, and expression, ensuring both personalized support and broad accessibility. Effective implementation leverages data-driven insights and inclusive strategies to accommodate diverse learning profiles and optimize student outcomes.
Differentiated Instruction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com