Project-Based Learning immerses students in real-world challenges, promoting critical thinking, collaboration, and practical problem-solving skills. This hands-on approach fosters deeper understanding and retention compared to traditional methods. Discover how implementing Project-Based Learning can transform your educational experience by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
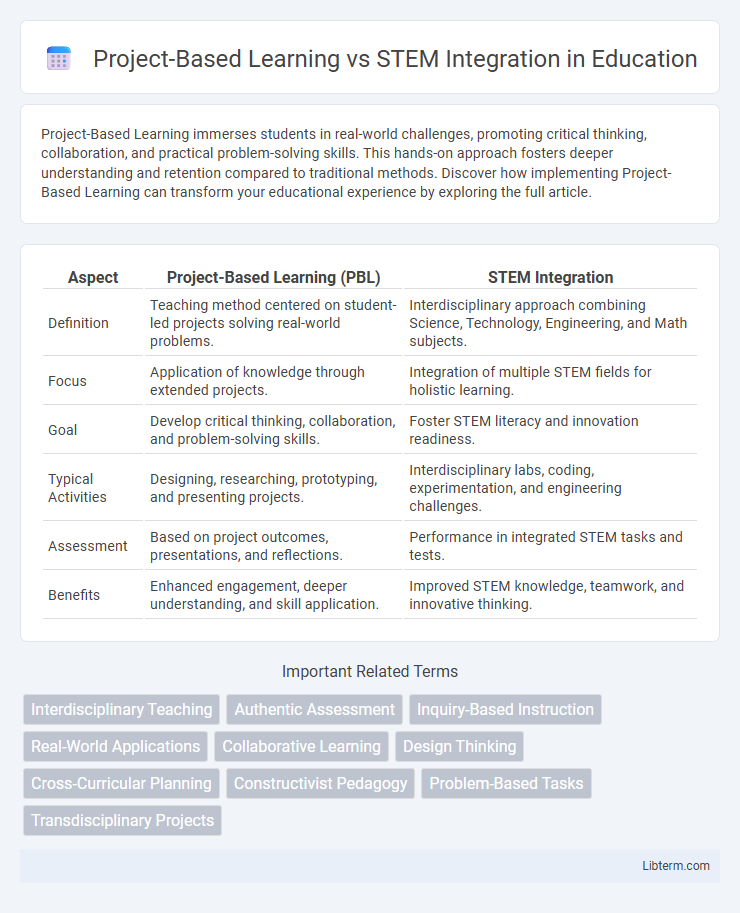
| Aspect | Project-Based Learning (PBL) | STEM Integration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Teaching method centered on student-led projects solving real-world problems. | Interdisciplinary approach combining Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math subjects. |
| Focus | Application of knowledge through extended projects. | Integration of multiple STEM fields for holistic learning. |
| Goal | Develop critical thinking, collaboration, and problem-solving skills. | Foster STEM literacy and innovation readiness. |
| Typical Activities | Designing, researching, prototyping, and presenting projects. | Interdisciplinary labs, coding, experimentation, and engineering challenges. |
| Assessment | Based on project outcomes, presentations, and reflections. | Performance in integrated STEM tasks and tests. |
| Benefits | Enhanced engagement, deeper understanding, and skill application. | Improved STEM knowledge, teamwork, and innovative thinking. |
Understanding Project-Based Learning
Project-Based Learning (PBL) emphasizes student-centered inquiry where learners engage in complex, real-world projects to develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills. This approach fosters deep understanding by integrating interdisciplinary knowledge and promoting collaboration, creativity, and reflection throughout the learning process. PBL contrasts with STEM integration by focusing on comprehensive project outcomes rather than solely combining science, technology, engineering, and math content.
Defining STEM Integration
STEM integration involves combining science, technology, engineering, and mathematics into cohesive learning experiences that reflect real-world applications. Unlike Project-Based Learning, which centers on completing specific projects, STEM integration emphasizes interdisciplinary connections and the seamless blending of STEM disciplines to enhance critical thinking and problem-solving skills. This approach fosters collaboration and innovation by engaging students in authentic tasks that mirror industry challenges.
Core Principles: PBL vs STEM Integration
Project-Based Learning (PBL) centers on student-driven inquiry and real-world problem-solving through extended projects that foster critical thinking and collaboration. STEM Integration emphasizes the seamless blending of science, technology, engineering, and mathematics disciplines to develop interdisciplinary skills and innovative solutions. Both approaches prioritize active learning, but PBL focuses on project completion within any subject, while STEM Integration targets expertise across interconnected STEM fields.
Learning Outcomes Compared
Project-Based Learning (PBL) enhances critical thinking, collaboration, and real-world problem-solving by engaging students in complex tasks over extended periods. STEM integration emphasizes interdisciplinary connections among science, technology, engineering, and mathematics, boosting content knowledge and technical skills. Comparative studies reveal PBL fosters deeper retention and application of knowledge, while STEM integration accelerates mastery of specific disciplinary competencies.
Real-World Application in Classrooms
Project-Based Learning (PBL) emphasizes hands-on, student-centered projects that mirror real-world challenges, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills. STEM integration combines science, technology, engineering, and mathematics, enabling students to apply interdisciplinary knowledge to authentic situations. Implementing both approaches in classrooms enhances engagement by connecting curriculum content with practical, real-life applications, preparing students for future careers.
Teacher Roles and Collaboration
In Project-Based Learning (PBL), teachers act as facilitators guiding students through inquiry and real-world problem-solving, emphasizing autonomy and critical thinking. STEM integration requires educators to adopt collaborative roles, merging expertise across science, technology, engineering, and math to create interdisciplinary learning experiences. Both approaches demand strong teacher collaboration to design, implement, and assess complex projects that foster deep understanding and skill development.
Assessment Strategies and Challenges
Project-Based Learning (PBL) assessment strategies emphasize performance tasks, real-world problem solving, and portfolio evaluations to measure critical thinking and collaboration skills. STEM integration assessment often incorporates standardized tests and diagnostic tools targeting content knowledge in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics disciplines. Challenges in PBL include ensuring objective grading and alignment with standards, while STEM integration faces difficulties in balancing interdisciplinary approaches and maintaining depth in individual subjects during evaluation.
Student Engagement and Motivation
Project-Based Learning (PBL) enhances student engagement by encouraging hands-on, real-world problem solving that fosters intrinsic motivation and deeper understanding. STEM Integration promotes collaboration across science, technology, engineering, and mathematics, increasing relevancy and driving curiosity through interdisciplinary challenges. Both approaches improve motivation by connecting content to practical applications, but PBL emphasizes student-driven inquiry while STEM Integration focuses on skill synthesis across disciplines.
Curriculum Design Considerations
Project-Based Learning (PBL) emphasizes real-world problem-solving through student-driven projects, enhancing engagement and critical thinking, whereas STEM integration focuses on a cohesive curriculum blending science, technology, engineering, and math disciplines. Effective curriculum design for PBL requires clear learning objectives aligned with authentic projects, scaffolding skills across cognitive levels, and assessment strategies that capture process and product outcomes. STEM integration demands interdisciplinary planning, ensuring content coherence and depth, promoting collaboration among faculty, and embedding technology and engineering practices within science and math instruction.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your School
Selecting the appropriate educational method depends on your school's goals, resources, and student needs. Project-Based Learning (PBL) emphasizes real-world problem-solving and interdisciplinary projects, fostering creativity and collaboration, while STEM Integration combines science, technology, engineering, and math curricula to enhance technical skills and critical thinking. Evaluating factors such as teacher expertise, curriculum alignment, and desired student outcomes ensures an effective choice between PBL and STEM Integration for maximizing educational impact.
Project-Based Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com