Social scaffolding plays a crucial role in supporting individuals as they develop new skills and knowledge through guided interaction with more experienced peers or mentors. This dynamic process enhances learning efficiency and confidence by breaking tasks into manageable steps tailored to Your current ability. Explore the rest of the article to understand how social scaffolds can transform educational and personal growth experiences.
Table of Comparison
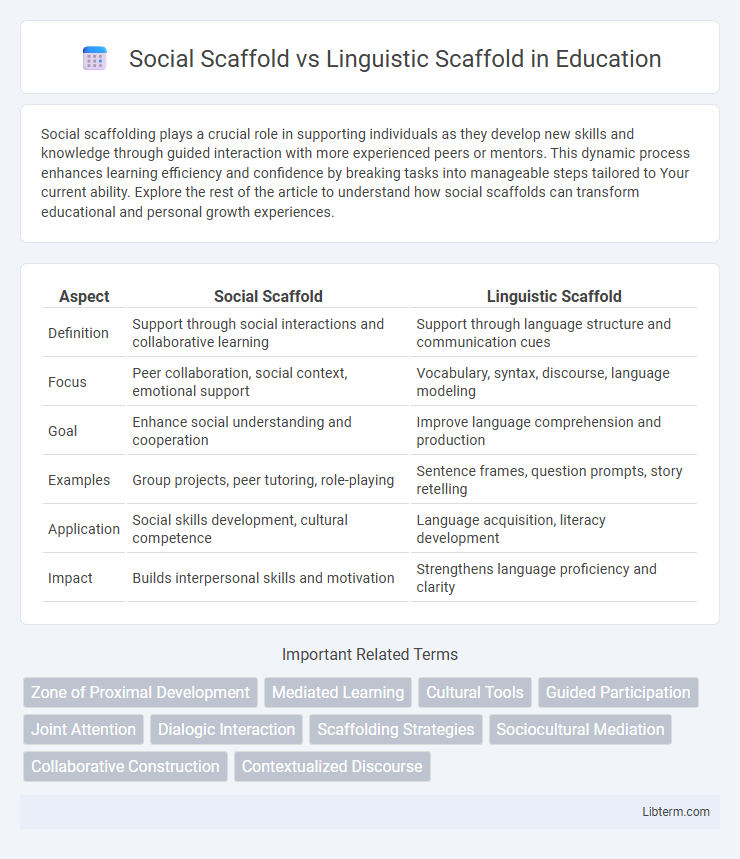
| Aspect | Social Scaffold | Linguistic Scaffold |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Support through social interactions and collaborative learning | Support through language structure and communication cues |
| Focus | Peer collaboration, social context, emotional support | Vocabulary, syntax, discourse, language modeling |
| Goal | Enhance social understanding and cooperation | Improve language comprehension and production |
| Examples | Group projects, peer tutoring, role-playing | Sentence frames, question prompts, story retelling |
| Application | Social skills development, cultural competence | Language acquisition, literacy development |
| Impact | Builds interpersonal skills and motivation | Strengthens language proficiency and clarity |
Understanding Scaffoldings in Learning
Social scaffold in learning emphasizes interpersonal support, where teachers and peers provide guidance tailored to the learner's needs, enhancing motivation and engagement. Linguistic scaffold focuses on language-based assistance, including tailored vocabulary, sentence structures, and discourse markers, which facilitate comprehension and expression in academic contexts. Combining social and linguistic scaffolds creates a comprehensive learning environment that nurtures both cognitive and communicative development.
Defining Social Scaffold
Social scaffold refers to the external support system provided by caregivers, teachers, or peers that facilitates a learner's cognitive and social development through guided interaction and shared activities. It emphasizes collaborative environments where social context and interpersonal relationships assist in building knowledge, problem-solving skills, and cultural understanding. This contrasts with linguistic scaffold, which centers on language-based cues and prompts designed to enhance communication abilities and linguistic competence.
Defining Linguistic Scaffold
Linguistic scaffold refers to the support system provided by language structures and vocabulary that facilitate comprehension and communication in learning environments. It includes tools such as sentence frames, word banks, and questioning techniques that help learners construct meaning and express complex ideas effectively. Unlike social scaffolding, which emphasizes interpersonal support and collaboration, linguistic scaffolding centers on the strategic use of language features to enhance cognitive development and language acquisition.
Key Differences: Social vs Linguistic Scaffold
Social scaffold involves external support from peers, teachers, or community that facilitates learning through interaction and collaboration, emphasizing social context and shared experiences. Linguistic scaffold centers on the use of language tools such as vocabulary, syntax, and discourse structures to support comprehension and communication within learning processes. Key differences lie in social scaffold prioritizing interpersonal engagement and cultural context, while linguistic scaffold focuses on language mechanics and cognitive processing within communication.
The Role of Interaction in Social Scaffolding
Social scaffolding emphasizes the importance of interactive support provided by more knowledgeable individuals, such as teachers or peers, to guide learners through complex tasks, facilitating cognitive development and skill acquisition. Linguistic scaffolding specifically involves the use of language-based strategies, including questioning, modeling, and feedback, to structure learning and promote understanding. Interaction in social scaffolding creates a dynamic environment where learners actively engage, internalize new knowledge, and progressively gain independence.
Language as a Tool: Linguistic Scaffolding Explained
Linguistic scaffolding involves using language structures, such as vocabulary, grammar, and sentence frames, to support a learner's language development and comprehension in real-time interactions. Social scaffolding focuses on the social context and interaction between learner and facilitator, emphasizing collaborative dialogue and shared understanding to promote learning. Using language as a tool in linguistic scaffolding enables precise guidance, allowing learners to internalize language patterns and gradually achieve independence in communication.
Benefits of Social Scaffolding in Education
Social scaffolding enhances student learning by providing emotional support and collaborative opportunities, fostering a positive classroom environment that promotes confidence and motivation. It encourages peer interaction and teacher guidance, which develop social skills and deepen comprehension through shared experiences. This approach supports diverse learners by addressing individual needs within a community context, increasing engagement and academic success.
Enhancing Communication through Linguistic Scaffolding
Linguistic scaffolding enhances communication by providing structured language support that helps individuals progressively build their language skills and express complex ideas more effectively. This approach offers tailored prompts, sentence starters, and vocabulary cues that guide learners toward clearer articulation and comprehension in both spoken and written forms. Unlike social scaffolding, which centers on interpersonal interaction and social context, linguistic scaffolding specifically targets the development of linguistic competence and fluency, making communication more precise and meaningful.
Integrating Both Scaffolds for Optimal Learning
Integrating social scaffold and linguistic scaffold enhances cognitive development by combining interactive social contexts with structured language support, fostering deeper understanding and communication skills. Effective learning environments leverage peer collaboration and teacher guidance while simultaneously promoting vocabulary development and sentence structuring. This dual scaffolding approach maximizes learner engagement and comprehension, crucial for academic success and language acquisition.
Practical Strategies for Effective Scaffolding
Social scaffold involves collaborative interaction and peer support to build knowledge through meaningful communication, while linguistic scaffold emphasizes structured language input to aid comprehension and expression. Practical strategies for effective scaffolding include using open-ended questions to promote dialogue, modeling vocabulary and sentence structures, and providing timely feedback tailored to learners' linguistic abilities. Integrating both social and linguistic scaffolding fosters deeper engagement and enhances language development in diverse learning environments.
Social Scaffold Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com